Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
File:UPPP._4_figures..png|Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty | File:UPPP._4_figures..png|Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty == | |||
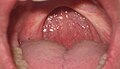
'''Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty''' (UPPP) is a surgical procedure used to remove tissue and/or remodel tissue in the throat. It is primarily used to treat [[obstructive sleep apnea]] (OSA) and [[snoring]]. The procedure involves the removal of the [[uvula]], part of the [[soft palate]], and sometimes the [[tonsils]] and other tissue in the throat. | |||
== Indications == | |||
UPPP is indicated for patients with obstructive sleep apnea who have not responded to other treatments such as [[continuous positive airway pressure]] (CPAP) therapy. It may also be considered for patients with severe snoring that affects their quality of life or that of their partners. | |||
== Procedure == | |||
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon removes or repositions tissues in the throat to widen the airway. This may include: | |||
* Removal of the uvula | |||
* Trimming of the soft palate | |||
* Removal of the tonsils (if present) | |||
* Removal of excess tissue from the pharynx | |||
The goal is to increase the size of the airway and reduce the potential for airway collapse during sleep. | |||
== Risks and Complications == | |||
As with any surgical procedure, UPPP carries risks and potential complications, including: | |||
* Bleeding | |||
* Infection | |||
* Changes in voice | |||
* Difficulty swallowing | |||
* Nasal regurgitation | |||
* Persistent sleep apnea or snoring | |||
Patients should discuss these risks with their surgeon prior to the procedure. | |||
== Recovery == | |||
Recovery from UPPP can take several weeks. Patients may experience a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and changes in voice during the recovery period. Pain management and a soft diet are typically recommended. | |||
== Effectiveness == | |||
The effectiveness of UPPP varies among patients. Some experience significant improvement in symptoms, while others may have persistent sleep apnea or snoring. Success rates are higher in patients with specific anatomical features that contribute to airway obstruction. | |||
== Alternatives == | |||
Alternatives to UPPP include: | |||
* CPAP therapy | |||
* Oral appliances | |||
* Other surgical procedures such as [[genioglossus advancement]] or [[maxillomandibular advancement]] | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Obstructive sleep apnea]] | |||
* [[Snoring]] | |||
* [[Continuous positive airway pressure]] | |||
* [[Tonsillectomy]] | |||
{{Surgery}} | |||
{{Sleep disorders}} | |||
[[Category:Surgical procedures and techniques]] | |||
[[Category:Sleep disorders]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:37, 19 February 2025
-
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
-
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty[edit]
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) is a surgical procedure used to remove tissue and/or remodel tissue in the throat. It is primarily used to treat obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and snoring. The procedure involves the removal of the uvula, part of the soft palate, and sometimes the tonsils and other tissue in the throat.
Indications[edit]
UPPP is indicated for patients with obstructive sleep apnea who have not responded to other treatments such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. It may also be considered for patients with severe snoring that affects their quality of life or that of their partners.
Procedure[edit]
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon removes or repositions tissues in the throat to widen the airway. This may include:
- Removal of the uvula
- Trimming of the soft palate
- Removal of the tonsils (if present)
- Removal of excess tissue from the pharynx
The goal is to increase the size of the airway and reduce the potential for airway collapse during sleep.
Risks and Complications[edit]
As with any surgical procedure, UPPP carries risks and potential complications, including:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Changes in voice
- Difficulty swallowing
- Nasal regurgitation
- Persistent sleep apnea or snoring
Patients should discuss these risks with their surgeon prior to the procedure.
Recovery[edit]
Recovery from UPPP can take several weeks. Patients may experience a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and changes in voice during the recovery period. Pain management and a soft diet are typically recommended.
Effectiveness[edit]
The effectiveness of UPPP varies among patients. Some experience significant improvement in symptoms, while others may have persistent sleep apnea or snoring. Success rates are higher in patients with specific anatomical features that contribute to airway obstruction.
Alternatives[edit]
Alternatives to UPPP include:
- CPAP therapy
- Oral appliances
- Other surgical procedures such as genioglossus advancement or maxillomandibular advancement
Related Pages[edit]
| Surgery | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|