Hemarthrosis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tag: visualeditor-wikitext |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
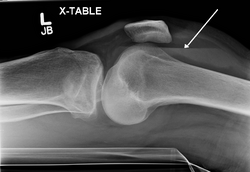
[[File:Medical X-Ray imaging JDG05 nevit.jpg|alt=X-ray of knee hemarthrosis|thumb|X-ray of knee hemarthrosis]] | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hemarthrosis | |||
| image = [[File:Lipohemarthrosis.png|250px]] | |||
| caption = Lipohemarthrosis of the knee joint | |||
| field = [[Rheumatology]], [[Orthopedics]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Joint pain]], [[swelling]], [[stiffness]] | |||
| complications = [[Joint damage]], [[arthritis]] | |||
| onset = Sudden, often after [[trauma]] | |||
| duration = Variable, depending on cause and treatment | |||
| causes = [[Trauma]], [[bleeding disorders]] (e.g., [[hemophilia]]), [[anticoagulant therapy]] | |||
| risks = [[Bleeding disorders]], [[joint injury]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[imaging studies]] (e.g., [[X-ray]], [[MRI]]), [[joint aspiration]] | |||
| differential = [[Septic arthritis]], [[gout]], [[pseudogout]] | |||
| treatment = [[Rest]], [[ice]], [[compression]], [[elevation]] (RICE), [[aspiration]], [[surgery]] | |||
| medication = [[Analgesics]], [[anti-inflammatory drugs]] | |||
| prognosis = Good with treatment, but depends on underlying cause | |||
| frequency = Common in individuals with [[bleeding disorders]] or after [[joint trauma]] | |||
}} | |||
[[File:Medical X-Ray imaging JDG05 nevit.jpg|alt=X-ray of knee hemarthrosis|left|thumb|X-ray of knee hemarthrosis]] | |||
== Etiology == | == Etiology == | ||
Hemarthrosis literally means [[blood]] in the [[joint]] | Hemarthrosis literally means [[blood]] in the [[joint]] | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/BWrrhH76X3w | movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/BWrrhH76X3w | ||
&rel=1 | &rel=1 | ||
| Line 13: | Line 31: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== Definition == | == Definition == | ||
It is defined by [[bleeding]] into and swelling of a [[joint]] | It is defined by [[bleeding]] into and swelling of a [[joint]] | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
Most cases are either due to [[trauma]], [[injection]], [[surgery]] or [[bleeding disorders]] | Most cases are either due to [[trauma]], [[injection]], [[surgery]] or [[bleeding disorders]] | ||
== Signs and symptoms == | == Signs and symptoms == | ||
* Swelling | * Swelling | ||
| Line 26: | Line 41: | ||
* Risk of infection | * Risk of infection | ||
* Warmth | * Warmth | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
* A [[physical examination]] and history | * A [[physical examination]] and history | ||
* Synovial Fluid analysis - Reddish-colored hue of the sample is an indication of the blood being present. | * Synovial Fluid analysis - Reddish-colored hue of the sample is an indication of the blood being present. | ||
* X-rays, CT/MRI imaging, and or joint aspiration | * X-rays, CT/MRI imaging, and or joint aspiration | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment depends on the cause and may include pain control, anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics, synovectomy and or surgery. | Treatment depends on the cause and may include pain control, anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics, synovectomy and or surgery. | ||
[[File:Medical X-Ray imaging JDH05 nevit.jpg|alt=Hemarthrosis|thumb|Hemarthrosis]] | [[File:Medical X-Ray imaging JDH05 nevit.jpg|alt=Hemarthrosis|left|thumb|Hemarthrosis]] | ||
== Hemophilia and hemarthrosis == | == Hemophilia and hemarthrosis == | ||
In hemophilia it may occur spontaneously, and recurrent hemarthroses are a major cause of [[disability]] in hemophilacs leading to [[hemophilic arthropathy]], requiring [[synovectomy]], [[joint replacement]]. Reducing hemarthroses events using intravenous administration of blood clotting factor concentrate on a regular basis starting in early childhood, reduces joint deterioration and increases the person's quality of life compared to "on demand" treatment is recommended. | In hemophilia it may occur spontaneously, and recurrent hemarthroses are a major cause of [[disability]] in hemophilacs leading to [[hemophilic arthropathy]], requiring [[synovectomy]], [[joint replacement]]. Reducing hemarthroses events using intravenous administration of blood clotting factor concentrate on a regular basis starting in early childhood, reduces joint deterioration and increases the person's quality of life compared to "on demand" treatment is recommended. | ||
==Complications== | ==Complications== | ||
Up to a quarter of all severe ligament or capsular knee injuries leading to a haemarthrosis are associated with [[cartilage damage]] that can lead to progressive [[Osteoarthritis|degenerative arthritis]].<ref>Goldberg A, Stansby G "Surgical Talk" 2nd edition</ref> | Up to a quarter of all severe ligament or capsular knee injuries leading to a haemarthrosis are associated with [[cartilage damage]] that can lead to progressive [[Osteoarthritis|degenerative arthritis]].<ref>Goldberg A, Stansby G "Surgical Talk" 2nd edition</ref> | ||
{{Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue}} | {{Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue}} | ||
{{Bleeding and clotting disorders}} | {{Bleeding and clotting disorders}} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:43, 7 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hemarthrosis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Joint pain, swelling, stiffness |
| Complications | Joint damage, arthritis |
| Onset | Sudden, often after trauma |
| Duration | Variable, depending on cause and treatment |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma, bleeding disorders (e.g., hemophilia), anticoagulant therapy |
| Risks | Bleeding disorders, joint injury |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging studies (e.g., X-ray, MRI), joint aspiration |
| Differential diagnosis | Septic arthritis, gout, pseudogout |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), aspiration, surgery |
| Medication | Analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment, but depends on underlying cause |
| Frequency | Common in individuals with bleeding disorders or after joint trauma |
| Deaths | N/A |

Etiology[edit]
Hemarthrosis literally means blood in the joint
Definition[edit]
It is defined by bleeding into and swelling of a joint
Causes[edit]
Most cases are either due to trauma, injection, surgery or bleeding disorders
Signs and symptoms[edit]
- Swelling
- Pain
- Limitation in joint movement
- Risk of infection
- Warmth
Diagnosis[edit]
- A physical examination and history
- Synovial Fluid analysis - Reddish-colored hue of the sample is an indication of the blood being present.
- X-rays, CT/MRI imaging, and or joint aspiration
Treatment[edit]
Treatment depends on the cause and may include pain control, anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics, synovectomy and or surgery.

Hemophilia and hemarthrosis[edit]
In hemophilia it may occur spontaneously, and recurrent hemarthroses are a major cause of disability in hemophilacs leading to hemophilic arthropathy, requiring synovectomy, joint replacement. Reducing hemarthroses events using intravenous administration of blood clotting factor concentrate on a regular basis starting in early childhood, reduces joint deterioration and increases the person's quality of life compared to "on demand" treatment is recommended.
Complications[edit]
Up to a quarter of all severe ligament or capsular knee injuries leading to a haemarthrosis are associated with cartilage damage that can lead to progressive degenerative arthritis.<ref>Goldberg A, Stansby G "Surgical Talk" 2nd edition</ref>
| Diseases of joints | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Disorders of bleeding and clotting | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|


