Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | TTP |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
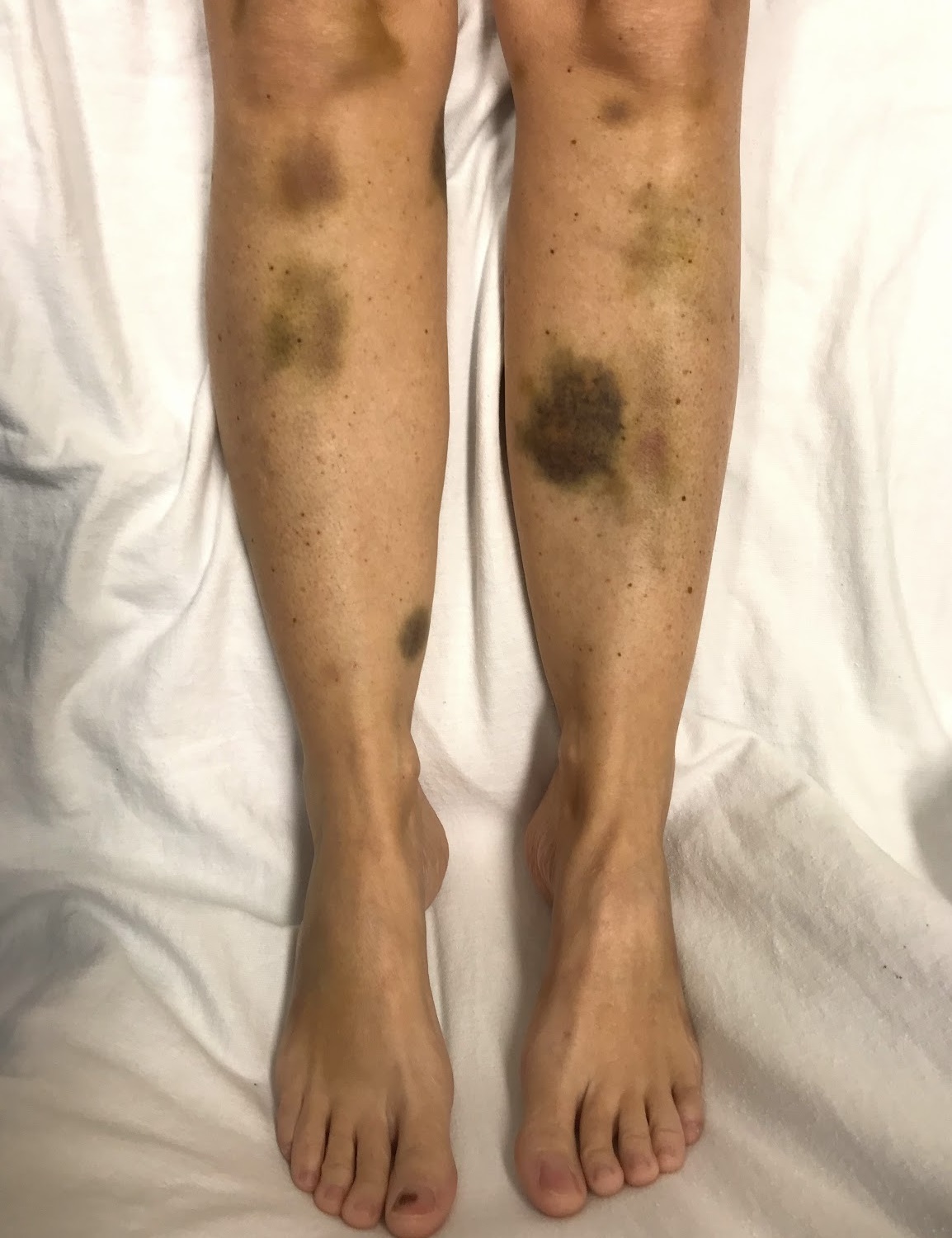
| Symptoms | Purpura, petechiae, anemia, neurological symptoms, renal failure |
| Complications | Stroke, myocardial infarction, renal failure |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | ADAMTS13 deficiency, autoimmune disease, genetic mutation |
| Risks | HIV, pregnancy, cancer, chemotherapy |
| Diagnosis | Blood test, ADAMTS13 activity, clinical presentation |
| Differential diagnosis | Hemolytic uremic syndrome, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, disseminated intravascular coagulation |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Plasma exchange, corticosteroids, rituximab |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, can be life-threatening |
| Frequency | 3-4 cases per million per year |
| Deaths | 10-20% with treatment |
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a rare and potentially life-threatening blood disorder characterized by the formation of small blood clots (thrombi) throughout the body. These blood clots can cause damage to organs and tissues and lead to a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia), which results in easy bruising and bleeding.

Causes and Pathophysiology[edit]
- TTP is primarily caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of a specific enzyme called ADAMTS13 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13). ADAMTS13 is responsible for breaking down von Willebrand factor (vWF), a protein that helps with blood clotting. When ADAMTS13 is deficient or not functioning properly, there is an accumulation of large vWF multimers in the blood, leading to abnormal clot formation.
- In most cases, TTP is acquired, meaning it develops during a person's lifetime and is not inherited. Acquired TTP can be associated with the presence of autoantibodies that target and inhibit ADAMTS13 activity. These autoantibodies can be triggered by various factors, including infections, certain medications, autoimmune diseases, pregnancy, and cancer.
Signs and Symptoms[edit]
- The classic pentad of TTP includes the following five features, although not all may be present in every case:
- Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia: This refers to the destruction of red blood cells as they pass through small blood vessels obstructed by blood clots. It can result in fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and jaundice.
- Thrombocytopenia: TTP leads to a low platelet count, which can cause easy bruising, petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin), and excessive bleeding.
- Fever: Some individuals with TTP may experience fever, although it is not always present.
- Neurologic Symptoms: TTP can affect the central nervous system and lead to symptoms such as confusion, headache, seizures, visual changes, and even coma.
- Renal Dysfunction: Kidney involvement can occur in TTP, resulting in decreased urine output, kidney failure, and signs of kidney damage.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
- The diagnosis of TTP is based on a combination of clinical features, blood tests, and specialized laboratory evaluations. Laboratory findings may include evidence of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and an elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level. ADAMTS13 activity testing and the presence of ADAMTS13 autoantibodies can help confirm the diagnosis.
- Immediate treatment is crucial in TTP to prevent complications and reduce mortality. The standard treatment approach involves plasma exchange (also known as plasmapheresis), which involves removing a patient's plasma and replacing it with fresh frozen plasma or a plasma substitute. Plasma exchange helps remove the autoantibodies and replenish ADAMTS13 activity. High-dose corticosteroids and immunosuppressive medications may also be administered to inhibit the formation of autoantibodies.
- In severe cases or when plasma exchange is not readily available, other treatments such as rituximab (a monoclonal antibody) or caplacizumab (a medication that blocks vWF) may be considered. Supportive care, including blood transfusions, close monitoring, and management of complications, is an important part of TTP treatment.
Prognosis[edit]
With prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment, the prognosis for TTP has improved significantly. However, TTP is still a serious condition that requires close medical management. Early intervention and ongoing monitoring are crucial to prevent relapses and manage potential long-term complications.
Summary[edit]
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a rare blood disorder characterized by the formation of blood clots throughout the body, leading to low platelet count and organ damage. It is primarily caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of the ADAMTS13 enzyme, which affects the breakdown of vWF. Prompt diagnosis and treatment, including plasma exchange and immunosuppressive medications, are essential in managing TTP and improving outcomes.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references>
- Joly, Béatrice S., and Agnès Veyradier. "Understanding pathogenesis and therapy of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura." Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis 18, no. 12 (2020): 3121-3131.
- Scully, Marie, et al. "Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and related thrombotic microangiopathies: diagnostic and therapeutic advances." Cancer Treatment and Research 177 (2019): 189-207.
- Peyvandi, Flora, et al. "Caplacizumab for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura." New England Journal of Medicine 374, no. 6 (2016): 511-522.
</references>
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


