Short QT syndrome: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{Genetic disorders}} | {{Genetic disorders}} | ||
[[Category:Syndromes]] {{stub}} | [[Category:Syndromes]] {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:SinusRhythmLabels.svg|Sinus Rhythm Labels | |||
File:QT interval.jpg|QT Interval | |||
File:Sqts (CardioNetworks ECGpedia).svg|Short QT Syndrome | |||
File:Labelled DDD ICD.jpg|Labelled DDD ICD | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:08, 20 February 2025
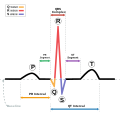
Short QT syndrome (SQTS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the heart's electrical system. It is characterized by a shortened QT interval, which can be detected on an electrocardiogram (ECG). This condition can lead to life-threatening arrhythmias and sudden death.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of Short QT syndrome is a high risk of sudden, life-threatening arrhythmias. These can lead to syncope, or fainting, and sudden death. Some individuals with SQTS may not exhibit any symptoms until an arrhythmia occurs.
Causes
Short QT syndrome is a genetic disorder, caused by mutations in certain genes that regulate the heart's electrical activity. These include the KCNH2, KCNQ1, and KCNJ2 genes. The condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning an affected individual has a 50% chance of passing the disorder onto their children.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Short QT syndrome is based on the measurement of the QT interval on an ECG. A QT interval of less than 360 milliseconds is generally considered indicative of SQTS. Genetic testing can also be used to confirm a diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment for Short QT syndrome primarily involves managing the risk of arrhythmias. This can include the use of beta blockers, implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs), and in some cases, surgical procedures.
Prognosis
With appropriate management, individuals with Short QT syndrome can lead normal lives. However, the risk of sudden death remains, making regular monitoring and treatment essential.
See also
Cardiovascular disease A-Z
Most common cardiac diseases
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Cardiogenetic disorders
- Cardiomegaly
- Cardiomyopathy
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Chronic rheumatic heart diseases
- Congenital heart defects
- Heart neoplasia
- Ischemic heart diseases
- Pericardial disorders
- Syndromes affecting the heart
- Valvular heart disease
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
A
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
- Acute decompensated heart failure
- Arteriosclerotic heart disease
- Athletic heart syndrome
- Atrial flutter
- Atrioventricular fistula
- Cardiovascular disease in Australia
- Autoimmune heart disease
B
C
- Ebb Cade
- Cardiac allograft vasculopathy
- Cardiac amyloidosis
- Cardiac asthma
- Cardiac tamponade
- Cardiogenic shock
- Cardiogeriatrics
- Cardiorenal syndrome
- Cardiotoxicity
- Carditis
- Coronary artery aneurysm
- Coronary artery anomaly
- Coronary artery disease
- Spontaneous coronary artery dissection
- Coronary artery ectasia
- Coronary occlusion
- Coronary steal
- Coronary thrombosis
- Coronary vasospasm
- Cœur en sabot
- Coxsackievirus-induced cardiomyopathy
D
E
H
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
- Heart to Heart (1949 film)
- High-output heart failure
- Hyperdynamic precordium
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
I
- Idiopathic giant-cell myocarditis
- Interventricular dyssynchrony
- Intraventricular dyssynchrony
- Isolated atrial amyloidosis
K
L
M
- Mydicar
- Myocardial bridge
- Myocardial disarray
- Myocardial rupture
- Myocardial scarring
- Myocardial stunning
- Myocarditis
N
O
P
- Papillary fibroelastoma
- Pathophysiology of heart failure
- Postpericardiotomy syndrome
- Pulmonary vein stenosis
R
S
- Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease
- SCAR-Fc
- Shone's syndrome
- Strain pattern
- Subacute bacterial endocarditis
- Sudden cardiac death of athletes
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
T
V
W
| Genetic disorders relating to deficiencies of transcription factor or coregulators | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|