Electrical impedance tomography: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{Radiology}} | {{Radiology}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:CT_of_human_thorax_showing_current_paths_for_EIT_corrected.jpg|CT of human thorax showing current paths for EIT | |||
File:Set_of_16_prototype_electrodes_for_applied_potential_tomography_(APT),_1987._(9663810916).jpg|Set of 16 prototype electrodes for applied potential tomography (APT), 1987 | |||
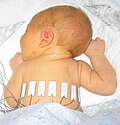
File:Neonate_with_electrical_impedance_tomography_electrodes.jpeg|Neonate with electrical impedance tomography electrodes | |||
File:EIT_ventilation_study_of_infants_Heinrich_2006.png|EIT ventilation study of infants Heinrich 2006 | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 11:29, 18 February 2025
Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) is a non-invasive imaging technique used to create images of the conductivity or impedance of a part of the body. It is based on the principle that different tissues in the body have different electrical properties. EIT is particularly useful in monitoring lung function and diagnosing pulmonary conditions but has applications in other areas such as breast cancer detection and brain imaging.
Overview[edit]
Electrical Impedance Tomography involves applying small electrical currents through electrodes placed on the skin's surface. The resulting voltages are measured and used to reconstruct an image of the electrical impedance within the body. This technique allows for real-time imaging, making it valuable for monitoring physiological and pathological changes in tissues.
Applications[edit]
Lung Imaging[edit]
In pulmonary medicine, EIT is used to monitor ventilation distribution in real-time. It is particularly useful in critical care settings for optimizing mechanical ventilation settings in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or following surgery.
Breast Cancer Detection[edit]
EIT is explored as a complementary technique to traditional methods like mammography for detecting breast cancer. It offers the advantage of being non-invasive and does not involve ionizing radiation.
Brain Imaging[edit]
Research is ongoing into the use of EIT for imaging brain function, particularly for detecting strokes and monitoring cerebral edema.
Advantages[edit]
- Non-invasive: No needles, injections, or incisions are required.
- Safe: It uses very low levels of electrical current, which are not felt by the patient and are not harmful.
- Real-time imaging: EIT can provide images rapidly, allowing for monitoring changes over time.
Limitations[edit]
- Resolution: The spatial resolution of EIT is lower than that of other imaging modalities like CT or MRI.
- Complexity: The interpretation of EIT images can be challenging and requires specialized training.
Technical Aspects[edit]
The quality of EIT images depends on several factors, including the number and placement of electrodes, the electrical properties of tissues, and the algorithms used for image reconstruction. Advances in computational methods and hardware are continually improving the resolution and utility of EIT.
Future Directions[edit]
Ongoing research aims to enhance the resolution and applicability of EIT. Potential future applications include its use in monitoring gastrointestinal and cardiac function. The development of wearable EIT systems could also enable continuous monitoring of patients in various settings.
| Medical imaging | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Category
|
| Radiology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This radiology-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
|
-
CT of human thorax showing current paths for EIT
-
Set of 16 prototype electrodes for applied potential tomography (APT), 1987
-
Neonate with electrical impedance tomography electrodes
-
EIT ventilation study of infants Heinrich 2006