Intravascular ultrasound
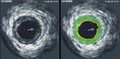
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) is a medical imaging methodology using a specially designed catheter with a miniaturized ultrasound probe attached to the distal end of the catheter. The proximal end of the catheter is attached to computerized ultrasound equipment. It allows the application of ultrasound technology, such as piezoelectric transducer or CMUT, to see from inside blood vessels out through the surrounding blood column, visualizing the endothelium (inner wall) of blood vessels in living individuals.
Procedure[edit]
The arteries of the heart (the coronary arteries) are the most frequent imaging target for IVUS. IVUS is used in the coronary arteries to determine the amount of atherosclerotic plaque build up in the vessel wall. IVUS is of particular interest to interventional cardiologists for determining the amount of atheroma in a segment of artery, the area of the vessel lumen, and the area of the vessel wall and outer vessel area (within the adventitia).
Clinical Applications[edit]
IVUS is used during angioplasty and stenting procedures. It helps in assessing the lesion that is to be stented, guiding stent placement and expansion, and assessing the result of the intervention. IVUS can also be used to assess non-atherosclerotic coronary artery disease conditions, such as coronary artery aneurysm or coronary dissection.
Advantages[edit]
IVUS has the advantage of being able to visualize the vessel in a cross-sectional view. It can measure the vessel lumen diameter, vessel area, plaque area and volume, and the plaque morphology. IVUS is the only method that can measure the plaque burden, vessel remodelling, and the plaque composition.
Limitations[edit]
IVUS has a limited penetration depth, which restricts its use in large vessels. It also has a limited resolution, which restricts its ability to accurately measure thin-cap fibroatheromas and small calcium deposits.
See Also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian