Lissencephaly: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
No edit summary Tag: visualeditor-wikitext |
CSV import |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Lissencephaly | |||
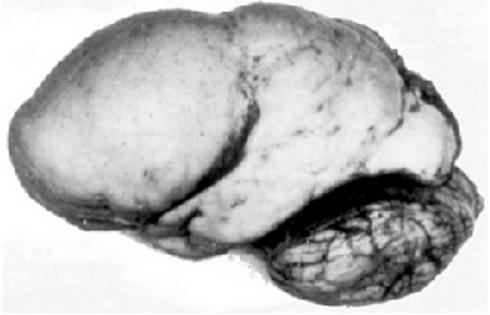
| image = [[File:Lissencephaly.jpg|alt=CT scan of a brain with lissencephaly]] | |||
| caption = CT scan of a brain with lissencephaly | |||
| field = [[Neurology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Developmental delay]], [[seizures]], [[muscle stiffness]] | |||
| complications = [[Intellectual disability]], [[feeding difficulties]], [[respiratory problems]] | |||
| onset = [[Congenital disorder|Congenital]] | |||
| duration = [[Lifelong]] | |||
| causes = [[Genetic mutation]] | |||
| risks = Family history of the condition | |||
| diagnosis = [[MRI]], [[CT scan]], [[genetic testing]] | |||
| differential = [[Polymicrogyria]], [[Schizencephaly]], [[Cortical dysplasia]] | |||
| treatment = [[Supportive care]], [[anticonvulsants]], [[physical therapy]] | |||
| prognosis = Varies, often severe | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
== '''Definition''' == | == '''Definition''' == | ||
Lissencephaly, which literally means "smooth brain," is a rare, gene-linked brain malformation characterized by the absence of normal convolutions (folds) in the [[cerebral cortex]] and an abnormally small head ([[microcephaly]]). | Lissencephaly, which literally means "smooth brain," is a rare, gene-linked brain malformation characterized by the absence of normal convolutions (folds) in the [[cerebral cortex]] and an abnormally small head ([[microcephaly]]). | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
| Line 12: | Line 29: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
== '''Epidemiology''' == | == '''Epidemiology''' == | ||
The incidence of all forms of type I lissencephaly is around 1 in 100,000 births. | The incidence of all forms of type I lissencephaly is around 1 in 100,000 births. | ||
== '''Types and etiology''' == | == '''Types and etiology''' == | ||
* Multiple forms of lissencephaly have been described and their current classification is based on the associated malformations and underlying aetiology. | * Multiple forms of lissencephaly have been described and their current classification is based on the associated malformations and underlying aetiology. | ||
* Two large groups can be distinguished: '''classical lissencephaly''' (and its variants) and '''cobblestone lissencephaly'''. | * Two large groups can be distinguished: '''classical lissencephaly''' (and its variants) and '''cobblestone lissencephaly'''. | ||
* The''' classical lissencephalies''' and the variant forms can be further divided into several subgroups. Four forms can be distinguished on the basis of their genetic aetiology: anomalies in the '''LIS1 gene''' (isolated lissencephaly and [[Miller-Dieker syndrome]]), anomalies in the '''TUBA3 and DCX genes''', and lissencephalies caused by mutations in the '''ARX gene''' (X-linked lissencephaly with agenesis of the corpus callosum (XLAG) syndrome). | * The''' classical lissencephalies''' and the variant forms can be further divided into several subgroups. Four forms can be distinguished on the basis of their genetic aetiology: anomalies in the '''LIS1 gene''' (isolated lissencephaly and [[Miller-Dieker syndrome]]), anomalies in the '''TUBA3 and DCX genes''', and lissencephalies caused by mutations in the '''ARX gene''' (X-linked lissencephaly with agenesis of the corpus callosum (XLAG) syndrome). | ||
* In addition to these four entities, isolated lissencephalies without a known genetic defect, lissencephalies with severe microcephaly ([[microlissencephaly]]) and lissencephalies associated with polymalformative syndromes are also included in the group of classical lissencephalies. | * In addition to these four entities, isolated lissencephalies without a known genetic defect, lissencephalies with severe microcephaly ([[microlissencephaly]]) and lissencephalies associated with polymalformative syndromes are also included in the group of classical lissencephalies. | ||
* '''Cobblestone lissencephaly''' (formally referred to as type II) is present in three entities: the Walker-Warburg, Fukuyama and MEB (Muscle-Eye-Brain) syndromes . | * '''Cobblestone lissencephaly''' (formally referred to as type II) is present in three entities: the Walker-Warburg, Fukuyama and MEB (Muscle-Eye-Brain) syndromes . | ||
== '''Cause''' == | == '''Cause''' == | ||
Lissencephaly is caused by defective neuronal migration during embryonic development, the process in which nerve cells move from their place of origin to their permanent location within the [[cerebral cortex]] gray matter. | Lissencephaly is caused by defective neuronal migration during embryonic development, the process in which nerve cells move from their place of origin to their permanent location within the [[cerebral cortex]] gray matter. | ||
== '''Signs and symptoms''' == | == '''Signs and symptoms''' == | ||
* Symptoms of the disorder may include unusual facial appearance, difficulty swallowing, [[failure to thrive]], muscle [[spasm]]s, [[seizures]], and severe [[psychomotor]] retardation. Hands, fingers, or toes may be deformed. | * Symptoms of the disorder may include unusual facial appearance, difficulty swallowing, [[failure to thrive]], muscle [[spasm]]s, [[seizures]], and severe [[psychomotor]] retardation. Hands, fingers, or toes may be deformed. | ||
* In '''classical lissencephaly''', extra-cortical anomalies are also present (total or subtotal [[agenesis of the corpus callosum]] and/or cerebellar [[hypoplasia]]). | * In '''classical lissencephaly''', extra-cortical anomalies are also present (total or subtotal [[agenesis of the corpus callosum]] and/or cerebellar [[hypoplasia]]). | ||
* '''Cobblestone lissencephaly''' is characterised by global disorganisation of cerebral organogenesis with an uneven cortical surface (with a pebbled or [[cobblestone]] appearance). | * '''Cobblestone lissencephaly''' is characterised by global disorganisation of cerebral organogenesis with an uneven cortical surface (with a pebbled or [[cobblestone]] appearance). | ||
* Microscopic examination reveals total disorganisation of the cortex and the absence of any distinguishable layers. | * Microscopic examination reveals total disorganisation of the cortex and the absence of any distinguishable layers. | ||
== '''Diagnosis''' == | == '''Diagnosis''' == | ||
* The diagnosis of lissencephaly is usually made at birth or soon after by [[ultrasound]], [[computed tomography]] (CT), or [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI). | * The diagnosis of lissencephaly is usually made at birth or soon after by [[ultrasound]], [[computed tomography]] (CT), or [[magnetic resonance imaging]] (MRI). | ||
* However, these results should be interpreted cautiously since even experienced [[Radiologist|radiologists]] can misdiagnose [[polymicrogyria]], a different developmental malformation of the brain, as lissencephaly. | * However, these results should be interpreted cautiously since even experienced [[Radiologist|radiologists]] can misdiagnose [[polymicrogyria]], a different developmental malformation of the brain, as lissencephaly. | ||
== '''Treatment''' == | == '''Treatment''' == | ||
* There is no cure for lissencephaly, but children can show progress in their development over time. | * There is no cure for lissencephaly, but children can show progress in their development over time. | ||
* Supportive care may be needed to help with comfort, feeding, and nursing needs. | * Supportive care may be needed to help with comfort, feeding, and nursing needs. | ||
* [[Seizures]] may be particularly problematic but [[anticonvulsant]] medications can help. | * [[Seizures]] may be particularly problematic but [[anticonvulsant]] medications can help. | ||
* Progressive [[hydrocephalus]] (an excessive accumulation of [[cerebrospinal fluid]] in the brain) is very rare, seen only in the subtype of [[Walker-Warburg syndrome]], but may require [[Shunt|shunting]]. | * Progressive [[hydrocephalus]] (an excessive accumulation of [[cerebrospinal fluid]] in the brain) is very rare, seen only in the subtype of [[Walker-Warburg syndrome]], but may require [[Shunt|shunting]]. | ||
* If feeding becomes difficult, a [[gastrostomy tube]] may be considered. | * If feeding becomes difficult, a [[gastrostomy tube]] may be considered. | ||
== '''Prognosis''' == | == '''Prognosis''' == | ||
* The prognosis for children with lissencephaly depends on the degree of brain malformation. | * The prognosis for children with lissencephaly depends on the degree of brain malformation. | ||
* Many will die before the age of 10 years. | * Many will die before the age of 10 years. | ||
* The cause of death is usually aspiration of food or fluids, respiratory disease, or severe seizures. | * The cause of death is usually aspiration of food or fluids, respiratory disease, or severe seizures. | ||
* Some will survive, but show no significant development -- usually not beyond a 3- to 5-month-old level. | * Some will survive, but show no significant development -- usually not beyond a 3- to 5-month-old level. | ||
* Others may have near-normal development and intelligence. | * Others may have near-normal development and intelligence. | ||
* Because of this range, it is important to seek the opinion of specialists in lissencephaly and support from family groups with connection to these specialists. | * Because of this range, it is important to seek the opinion of specialists in lissencephaly and support from family groups with connection to these specialists. | ||
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of nervous system}} | {{Congenital malformations and deformations of nervous system}} | ||
{{Transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies}} | {{Transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies}} | ||
[[Category:Congenital disorders of nervous system]] | [[Category:Congenital disorders of nervous system]] | ||
[[Category:Neuronal migration disorders]] | [[Category:Neuronal migration disorders]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:24, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Lissencephaly | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Developmental delay, seizures, muscle stiffness |
| Complications | Intellectual disability, feeding difficulties, respiratory problems |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risks | Family history of the condition |
| Diagnosis | MRI, CT scan, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Polymicrogyria, Schizencephaly, Cortical dysplasia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Supportive care, anticonvulsants, physical therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies, often severe |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Definition[edit]
Lissencephaly, which literally means "smooth brain," is a rare, gene-linked brain malformation characterized by the absence of normal convolutions (folds) in the cerebral cortex and an abnormally small head (microcephaly).
Epidemiology[edit]
The incidence of all forms of type I lissencephaly is around 1 in 100,000 births.
Types and etiology[edit]
- Multiple forms of lissencephaly have been described and their current classification is based on the associated malformations and underlying aetiology.
- Two large groups can be distinguished: classical lissencephaly (and its variants) and cobblestone lissencephaly.
- The classical lissencephalies and the variant forms can be further divided into several subgroups. Four forms can be distinguished on the basis of their genetic aetiology: anomalies in the LIS1 gene (isolated lissencephaly and Miller-Dieker syndrome), anomalies in the TUBA3 and DCX genes, and lissencephalies caused by mutations in the ARX gene (X-linked lissencephaly with agenesis of the corpus callosum (XLAG) syndrome).
- In addition to these four entities, isolated lissencephalies without a known genetic defect, lissencephalies with severe microcephaly (microlissencephaly) and lissencephalies associated with polymalformative syndromes are also included in the group of classical lissencephalies.
- Cobblestone lissencephaly (formally referred to as type II) is present in three entities: the Walker-Warburg, Fukuyama and MEB (Muscle-Eye-Brain) syndromes .
Cause[edit]
Lissencephaly is caused by defective neuronal migration during embryonic development, the process in which nerve cells move from their place of origin to their permanent location within the cerebral cortex gray matter.
Signs and symptoms[edit]
- Symptoms of the disorder may include unusual facial appearance, difficulty swallowing, failure to thrive, muscle spasms, seizures, and severe psychomotor retardation. Hands, fingers, or toes may be deformed.
- In classical lissencephaly, extra-cortical anomalies are also present (total or subtotal agenesis of the corpus callosum and/or cerebellar hypoplasia).
- Cobblestone lissencephaly is characterised by global disorganisation of cerebral organogenesis with an uneven cortical surface (with a pebbled or cobblestone appearance).
- Microscopic examination reveals total disorganisation of the cortex and the absence of any distinguishable layers.
Diagnosis[edit]
- The diagnosis of lissencephaly is usually made at birth or soon after by ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- However, these results should be interpreted cautiously since even experienced radiologists can misdiagnose polymicrogyria, a different developmental malformation of the brain, as lissencephaly.
Treatment[edit]
- There is no cure for lissencephaly, but children can show progress in their development over time.
- Supportive care may be needed to help with comfort, feeding, and nursing needs.
- Seizures may be particularly problematic but anticonvulsant medications can help.
- Progressive hydrocephalus (an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain) is very rare, seen only in the subtype of Walker-Warburg syndrome, but may require shunting.
- If feeding becomes difficult, a gastrostomy tube may be considered.
Prognosis[edit]
- The prognosis for children with lissencephaly depends on the degree of brain malformation.
- Many will die before the age of 10 years.
- The cause of death is usually aspiration of food or fluids, respiratory disease, or severe seizures.
- Some will survive, but show no significant development -- usually not beyond a 3- to 5-month-old level.
- Others may have near-normal development and intelligence.
- Because of this range, it is important to seek the opinion of specialists in lissencephaly and support from family groups with connection to these specialists.
| Congenital malformations and deformations of nervous system | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Genetic disorders relating to deficiencies of transcription factor or coregulators | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NIH genetic and rare disease info[edit]
Lissencephaly is a rare disease.
| Rare and genetic diseases | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rare diseases - Lissencephaly
|


