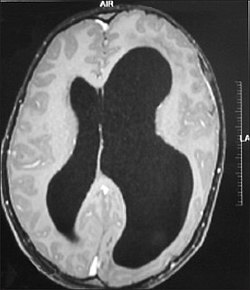
Hemimegalencephaly

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Hemimegalencephaly | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Seizures, developmental delay, hemiparesis, macrocephaly |
| Complications | Intellectual disability, epilepsy, cerebral palsy |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutation |
| Risks | Family history of genetic disorders |
| Diagnosis | MRI, CT scan |
| Differential diagnosis | Focal cortical dysplasia, tuberous sclerosis complex, Sturge-Weber syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Anticonvulsants, hemispherectomy, physical therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
A rare neurological condition characterized by the enlargement of one hemisphere of the brain
Hemimegalencephaly is a rare neurological disorder characterized by the abnormal enlargement of one hemisphere of the brain. This condition is a type of cortical dysplasia, which involves abnormal development of the cerebral cortex. Hemimegalencephaly can lead to a variety of neurological symptoms, including seizures, developmental delays, and hemiparesis.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Hemimegalencephaly results from a disruption in the normal development of the brain during embryogenesis. The exact cause of this disruption is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve genetic mutations that affect cell proliferation and differentiation. The overgrowth of one hemisphere leads to an imbalance in brain structure and function. The affected hemisphere may exhibit increased neuronal size, abnormal gyral patterns, and disorganized cortical layers. These structural abnormalities can disrupt normal neural networks, leading to the clinical manifestations of the disorder.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
The symptoms of hemimegalencephaly can vary widely depending on the extent and location of the brain abnormalities. Common clinical features include:
- Seizures: Often the first symptom to appear, seizures in hemimegalencephaly can be difficult to control with medication. They may present as infantile spasms, focal seizures, or generalized seizures.
- Developmental Delay: Children with hemimegalencephaly often experience delays in reaching developmental milestones, such as sitting, walking, and talking.
- Hemiparesis: Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body may occur, corresponding to the affected hemisphere.
- Intellectual Disability: Cognitive impairment is common, with varying degrees of severity.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of hemimegalencephaly is typically made through a combination of clinical evaluation and neuroimaging studies. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred imaging modality, as it provides detailed information about the structure of the brain. MRI findings in hemimegalencephaly include asymmetrical enlargement of one hemisphere, abnormal cortical thickening, and disorganized white matter.
Management[edit]
Management of hemimegalencephaly is primarily symptomatic and supportive. Treatment options include:
- Antiepileptic Drugs (AEDs): Used to control seizures, although they may be less effective in this condition.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases where seizures are refractory to medication, surgical options such as hemispherectomy or hemispherotomy may be considered to remove or disconnect the affected hemisphere.
- Rehabilitation Therapies: Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help improve motor skills, communication, and overall development.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with hemimegalencephaly varies depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment. Early intervention and comprehensive management can improve outcomes, but many individuals will continue to experience significant neurological challenges throughout their lives.
See also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian