Prenatal testing: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
[[Category:Midwifery]] | [[Category:Midwifery]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Prenatal_Down_syndrome_screening_algorithm.png|Prenatal Down syndrome screening algorithm | |||
File:Amniocentesis.png|Amniocentesis | |||
File:Obsteric_ultrasonograph.jpg|Obstetric ultrasonograph | |||
File:CC-BY_icon.svg|Prenatal testing | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:39, 18 February 2025
Prenatal diagnosis refers to the identification of diseases or conditions in a fetus or embryo before its birth. The primary objective is to detect birth defects such as neural tube defects, chromosome abnormalities, genetic diseases, and other conditions. Prenatal diagnostic methods can be either non-invasive or invasive.
Reasons for Prenatal Diagnosis[edit]
- Early Intervention: Enables parents to plan for any health needs of the baby before birth.
- Emotional Preparation: Allows parents to seek counselling, reducing shock and other reactions post-birth.
- Medical Preparedness: Enables healthcare staff to be ready with suitable treatments during and post delivery.
- Abortion Decision: Gives parents the option to abort if they so choose.
- Genetic Considerations: In families with inheritable genetic conditions, prenatal diagnosis can detect chromosome abnormalities or specific genetic problems.
Risk Factors for Prenatal Testing[edit]
- Age of the pregnant woman (e.g., over 35).
- History of premature babies or babies with defects.
- Maternal health conditions like high blood pressure, lupus, or diabetes.
- Ethnic backgrounds of partners prone to genetic disorders.
Methods of Prenatal Diagnosis[edit]
Non-Invasive Methods[edit]
- External Examination: Feeling the mother's abdomen.
- Ultrasound Detection: Scans to confirm pregnancy dates, twin detection, check for abnormalities, or identify risks of disorders like Down's syndrome.
- AFP Screening: Checks levels of alpha fetoprotein, β-hCG, and estriol in maternal serum.
- Detection of Fetal Blood Cells in Maternal Blood: Allows potential sampling of baby's DNA.
Invasive Methods[edit]
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): Early sampling and testing of the chorionic villus but carries higher risk.
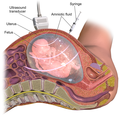
- Amniocentesis: Sampling of amniotic fluid to test floating baby cells.
- Embroscopy and Fetoscopy: Observation or sampling of blood/tissue using a probe and camera.
Ethical and Practical Issues[edit]
- Deciding between continuation of pregnancy or abortion after testing.
- Assessing the risks versus benefits of invasive prenatal diagnosis.
- Concerns about potential societal preferences for certain traits in offspring.
- The impact of false positives and negatives on parents' mental well-being.
- Decisions related to treatment or surgery options for detected abnormalities.
- Assessing societal pressures on women's choices regarding prenatal testing.
- Evaluating the role of genetic counseling in aiding parents' decisions.
See Also[edit]
- Neural tube defects
- Chromosome abnormalities
- Genetic counseling
- Amniocentesis
- Ultrasound
- Amniotic stem cell bank
- Amniotic stem cells
- Chorionic villi
- Genetic counseling
- Newborn screening
- DNA testing
External links[edit]
- Our Bodies Ourselves chapter on Prenatal Testing and Disability Rights
- Prenatal Tests and Why Are They Important? - March Of Dimes
| Pregnancy and childbirth | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Tests and procedures relating to pregnancy and childbirth | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|