Thyroid dyshormonogenesis: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
{{Thyroid disease}} | {{Thyroid disease}} | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
== Thyroid dyshormonogenesis == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Autosomal_recessive_-_en.svg | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 22:09, 16 February 2025
Thyroid dyshormonogenesis is a type of congenital hypothyroidism caused by defects in the synthesis of thyroid hormones. It is a rare, inherited disorder, which can lead to growth and development problems if not treated early.
Causes
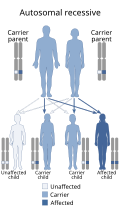
Thyroid dyshormonogenesis is caused by mutations in several genes that are involved in the production of thyroid hormones. These include the thyroglobulin (TG), thyroid peroxidase (TPO), iodotyrosine deiodinase (IYD), sodium-iodide symporter (NIS), and dual oxidase 2 (DUOX2) genes. The mutations can be inherited from one or both parents.
Symptoms
The symptoms of thyroid dyshormonogenesis are similar to those of other forms of congenital hypothyroidism. They include poor growth, delayed development, constipation, dry skin, and a large tongue. If left untreated, the condition can lead to intellectual disability and physical abnormalities.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of thyroid dyshormonogenesis is usually made shortly after birth through newborn screening tests. These tests measure the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood. If the levels are low, further tests are done to determine the cause of the hypothyroidism.
Treatment
The treatment for thyroid dyshormonogenesis is lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy. This involves taking a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) every day. With early diagnosis and treatment, children with thyroid dyshormonogenesis can lead normal, healthy lives.
See also
| Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases related article is a stub.
|
| Genetic disorders relating to deficiencies of transcription factor or coregulators | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Thyroid disease | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|