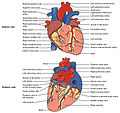
The Heart
Anatomy > Gray's Anatomy of the Human Body > V. Angiology > 4b. The Heart
Henry Gray (1821–1865). Anatomy of the Human Body. 1918.
The Heart[edit]
(Cor)
The heart is a hollow muscular organ of a somewhat conical form; it lies between the lungs in the middle mediastinum and is enclosed in the pericardium (Fig. 490). It is placed obliquely in the chest behind the body of the sternum and adjoining parts of the rib cartilages, and projects farther into the left than into the right half of the thoracic cavity, so that about one-third of it is situated on the right and two-thirds on the left of the median plane.
Size[edit]
The heart, in the adult, measures about 12 cm. in length, 8 to 9 cm. in breadth at the broadest part, and 6 cm. in thickness. Its weight, in the male, varies from 280 to 340 grams; in the female, from 230 to 280 grams. The heart continues to increase in weight and size up to an advanced period of life; this increase is more marked in men than in women.
Component Parts[edit]
As has already been stated (page 497), the heart is subdivided by septa into right and left halves, and a constriction subdivides each half of the organ into two cavities, the upper cavity being called the atrium the lower the ventricle
The heart therefore consists of four chambers, viz., right and left atria, and right and left ventricles. The division of the heart into four cavities is indicated on its surface by grooves. The atria are separated from the ventricles by the coronary sulcus (auriculoventricular groove); this contains the trunks of the nutrient vessels of the heart, and is deficient in front, where it is crossed by the root of the pulmonary artery.
The interatrial groove separating the two atria, is scarcely marked on the posterior surface, while anteriorly it is hidden by the pulmonary artery and aorta.
The ventricles are separated by two grooves, one of which, the anterior longitudinal sulcus is situated on the sternocostal surface of the heart, close to its left margin, the other posterior longitudinal sulcus on the diaphragmatic surface near the right margin; these grooves extend from the base of the ventricular portion to a notch, the incisura apicis cordis on the acute margin of the heart just to the right of the apex.

Base[edit]
The base (basis cordis) (Fig. 491), directed upward, backward, and to the right, is separated from the fifth, sixth, seventh, and eighth thoracic vertebrae by the esophagus, aorta, and thoracic duct. It is formed mainly by the left atrium, and, to a small extent, by the back part of the right atrium.
Somewhat quadrilateral in form, it is in relation above with the bifurcation of the pulmonary artery, and is bounded below by the posterior part of the coronary sulcus, containing the coronary sinus. On the right it is limited by the sulcus terminalis of the right atrium, and on the left by the ligament of the left vena cava and the oblique vein of the left atrium.
The four pulmonary veins, two on either side, open into the left atrium, while the superior vena cava opens into the upper, and the anterior vena cava into the lower, part of the right atrium.
The Apex (apex cordis)[edit]
The apex is directed downward, forward, and to the left, and is overlapped by the left lung and pleura: it lies behind the fifth left intercostal space, 8 to 9 cm. from the mid-sternal line, or about 4 cm. below and 2 mm. to the medial side of the left mammary papilla.
sternocostal surface[edit]
The sternocostal surface (Fig. 492) is directed forward, upward, and to the left. Its lower part is convex, formed chiefly by the right ventricle, and traversed near its left margin by the anterior longitudinal sulcus. Its upper part is separated from the lower by the coronary sulcus, and is formed by the atria; it presents a deep concavity (Fig. 494), occupied by the ascending aorta and the pulmonary artery.
Diaphragmatic surface[edit]
The diaphragmatic surface (Fig. 491), directed downward and slightly backward, is formed by the ventricles, and rests upon the central tendon and a small part of the left muscular portion of the diaphragm. It is separated from the base by the posterior part of the coronary sulcus, and is traversed obliquely by the posterior longitudinal sulcus.
right margin[edit]
The right margin of the heart is long, and is formed by the right atrium above and the right ventricle below. The atrial portion is rounded and almost vertical; it is situated behind the third, fourth, and fifth right costal cartilages about 1.25 cm. from the margin of the sternum. The ventricular portion, thin and sharp, is named the acute margin it is nearly horizontal, and extends from the sternal end of the sixth right costal cartilage to the apex of the heart.

The left or obtuse margin is shorter, full, and rounded: it is formed mainly by the left ventricle, but to a slight extent, above, by the left atrium. It extends from a point in the second left intercostal space, about 2.5 mm. from the sternal margin, obliquely downward, with a convexity to the left, to the apex of the heart.
Right Atrium (atrium dextrum; right auricle)[edit]
The right atrium is larger than the left, but its walls are somewhat thinner, measuring about 2 mm.; its cavity is capable of containing about 57 c.c. It consists of two parts: a principal cavity, or sinus venarum situated posteriorly, and an anterior, smaller portion, the auricula
Sinus Venarum (sinus venosus) =[edit]
The sinus venarum is the large quadrangular cavity placed between the two venae cavae. Its walls, which are extremely thin, are connected below with the right ventricle, and medially with the left atrium, but are free in the rest of their extent.
'Auricula (auricula dextra; right auricular appendix)[edit]
The auricula is a small conical muscular pouch, the margins of which present a dentated edge. It projects from the upper and front part of the sinus forward and toward the left side, overlapping the root of the aorta.

The separation of the auricula from the sinus venarum is indicated externally by a groove, the terminal sulcus which extends from the front of the superior vena cava to the front of the inferior vena cava, and represents the line of union of the sinus venosus of the embryo with the primitive atrium. On the inner wall of the atrium the separation is marked by a vertical, smooth, muscular ridge, the terminal crest Behind the crest the internal surface of the atrium is smooth, while in front of it the muscular fibers of the wall are raised into parallel ridges resembling the teeth of a comb, and hence named the musculi pectinati
Its interior (Fig. 493) presents the following parts for examination:
Openings »
- Superior vena cava.
- Inferior vena cava.
Coronary sinus.
Valves »
Valve of the inferior vena cava.
Foramina venarum minimarum. Valve of the coronary sinus. Atrioventricular.
- Fossa ovalis.
- Limbus fossae ovalis.
- Intervenous tubercle.
- Musculi pectinati.
- Crista terminalis
The superior vena cava returns the blood from the upper half of the body, and opens into the upper and back part of the atrium, the direction of its orifice being downward and forward. Its opening has no valve.
The inferior vena cava larger than the superior, returns the blood from the lower half of the body, and opens into the lowest part of the atrium, near the atrial septum, its orifice being directed upward and backward, and guarded by a rudimentary valve, the valve of the inferior vena cava (Eustachian valve). The blood entering the atrium through the superior vena cava is directed downward and forward, i.e toward the atrioventricular orifice, while that entering through the inferior vena cava is directed upward and backward, toward the atrial septum. This is the normal direction of the two currents in fetal life.
The coronary sinus opens into the atrium, between the orifice of the inferior vena cava and the atrioventricular opening. It returns blood from the substance of the heart and is protected by a semicircular valve, the valve of the coronary sinus (valve of Thebesius).

The foramina venarum minimarum (foramina Thebesii) are the orifices of minute veins (venœ cordis minimœ), which return blood directly from the muscular substance of the heart.
The [[atrioventricularʼ opening (tricuspid orifice) is the large oval aperture of communication between the atrium and the ventricle; it will be described with the right ventricle.
The valve of the inferior vena cava (valvula venœ cavœ inferioris [Eustachii]; Eustachian valve) is situated in front of the orifice of the inferior vena cava. It is semilunar in form, its convex margin being attached to the anterior margin of the orifice; its concave margin, which is free, ends in two cornua, of which the left is continuous with the anterior edge of the limbus fossae ovalis while the right is lost on the wall of the atrium. The valve is formed by a duplicature of the lining membrane of the atrium, containing a few muscular fibers. In the fetus this valve is of large size, and serves to direct the blood from the inferior vena cava, through the foramen ovale, into the left atrium. In the adult it occasionally persists, and may assist in preventing the reflux of blood into the inferior vena cava; more commonly it is small, and may present a cribriform or filamentous appearance; sometimes it is altogether wanting.
The valve of the coronary sinus (valvula sinus coronarii [Thebesii]; Thebesian valve) is a semicircular fold of the lining membrane of the atrium, at the orifice of the coronary sinus. It prevents the regurgitation of blood into the sinus during the contraction of the atrium. This valve may be double or it may be cribriform.
The fossa ovalis is an oval depression on the septal wall of the atrium, and corresponds to the situation of the foramen ovale in the fetus. It is situated at the lower part of the septum, above and to the left of the orifice of the inferior vena cava. The limbus fossae ovalis (annulus ovalis) is the prominent oval margin of the fossa ovalis. It is most distinct above and at the sides of the fossa; below, it is deficient. A small slit-like valvular opening is occasionally found, at the upper margin of the fossa, leading upward beneath the limbus, into the left atrium; it is the remains of the fetal aperture between the two atria. The intervenous tubercle (tuberculum intervenosum; tubercle of Lower) is a small projection on the posterior wall of the atrium, above the fossa ovalis. It is distinct in the hearts of quadrupeds, but in man is scarcely visible. It was supposed by Lower to direct the blood from the superior vena cava toward the atrioventricular opening.
Right Ventricle[edit]
(ventriculus dexter)[edit]
The right ventricle is triangular in form, and extends from the right atrium to near the apex of the heart. Its anterosuperior surface is rounded and convex, and forms the larger part of the sternocostal surface of the heart. Its under surface is flattened, rests upon the diaphragm, and forms a small part of the diaphragmatic surface of the heart. Its posterior wall is formed by the ventricular septum, which bulges into the right ventricle, so that a transverse section of the cavity presents a semilunar outline. Its upper and left angle forms a conical pouch, the conus arteriosus from which the pulmonary artery arises. A tendinous band, which may be named the tendon of the conus arteriosus extends upward from the right atrioventricular fibrous ring and connects the posterior surface of the conus arteriosus to the aorta. The wall of the right ventricle is thinner than that of the left, the proportion between them being as 1 to 3; it is thickest at the base, and gradually becomes thinner toward the apex. The cavity equals in size that of the left ventricle, and is capable of containing about 85 c.c.
Its interior (Fig. 493) presents the following parts for examination:
Openings » Right atrioventricular. Valves » Tricuspid.
Pulmonary artery. Pulmonary.
- Trabeculae carnecae
- Chordae tendineae
The right atrioventricular orifice is the large oval aperture of communication between the right atrium and ventricle. Situated at the base of the ventricle, it measures about 4 cm. in diameter and is surrounded by a fibrous ring, covered by the lining membrane of the heart; it is considerably larger than the corresponding aperture on the left side, being sufficient to admit the ends of four fingers. It is guarded by the tricuspid valve.
The opening of the pulmonary artery is circular in form, and situated at the summit of the conus arteriosus, close to the ventricular septum. It is placed above and to the left of the atrioventricular opening, and is guarded by the pulmonary semilunar valves.
The tricuspid valve (valvula tricuspidalis) (Figs. 493, 495) consists of three somewhat triangular cusps or segments. The largest cusp is interposed between the atrioventricular orifice and the conus arteriosus and is termed the anterior or infundibular cusp A second, the posterior or marginal cusp is in relation to the right margin of the ventricle, and a third, the medial or septal cusp to the ventricular septum.
They are formed by duplicatures of the lining membrane of the heart, strengthened by intervening layers of fibrous tissue: their central parts are thick and strong, their marginal portions thin and translucent, and in the angles between the latter small intermediate segments are sometimes seen.
Their bases are attached to a fibrous ring surrounding the atrioventricular orifice and are also joined to each other so as to form a continuous annular membrane, while their apices project into the ventricular cavity. Their atrial surfaces, directed toward the blood current from the atrium, are smooth; their ventricular surfaces, directed toward the wall of the ventricle, are rough and irregular, and, together with the apices and margins of the cusps, give attachment to a number of delicate tendinous cords, the chordae tendineae


The trabeculae carneae (columnœ carneœ) are rounded or irregular muscular columns which project from the whole of the inner surface of the ventricle, with the exception of the conus arteriosus. They are of three kinds: some are attached along their entire length on one side and merely form prominent ridges, others are fixed at their extremities but free in the middle, while a third set (musculi papillares) are continuous by their bases with the wall of the ventricle, while their apices give origin to the chordae tendineae which pass to be attached to the segments of the tricuspid valve. There are two papillary muscles, anterior and posterior: of these, the anterior is the larger, and its chordae tendineae are connected with the anterior and posterior cusps of the valve: the posterior papillary muscle sometimes consists of two or three parts; its chordae tendineae are connected with the posterior and medial cusps. In addition to these, some chordae tendineae spring directly from the ventricular septum, or from small papillary eminences on it, and pass to the anterior and medial cusps. A muscular band, well-marked in sheep and some other animals, frequently extends from the base of the anterior papillary muscle to the ventricular septum. From its attachments it may assist in preventing overdistension of the ventricle, and so has been named the moderator band
The pulmonary semilunar valves (Fig. 494) are three in number, two in front and one behind, formed by duplicatures of the lining membrane, strengthened by fibrous tissue. They are attached, by their convex margins, to the wall of the artery, at its junction with the ventricle, their free borders being directed upward into the lumen of the vessel. The free and attached margins of each are strengthened by tendinous fibers, and the former presents, at its middle, a thickened nodule (corpus Arantii). From this nodule tendinous fibers radiate through the segment to its attached margin, but are absent from two narrow crescentic portions, the lunulae placed one on either side of the nodule immediately adjoining the free margin. Between the semilunar valves and the wall of the pulmonary artery are three pouches or sinuses (sinuses of Valsalva).
Left Atrium[edit]
(atrium sinistum; left auricle) The left atrium is rather smaller than the right, but its walls are thicker, measuring about 3 mm.; it consists, like the right, of two parts, a principal cavity and an auricula
The principal cavity is cuboidal in form, and concealed, in front, by the pulmonary artery and aorta; in front and to the right it is separated from the right atrium by the atrial septum; opening into it on either side are the two pulmonary veins.
Auricula
(auricula sinistra; left auricular appendix)
The auricula is somewhat constricted at its junction with the principal cavity; it is longer, narrower, and more curved than that of the right side, and its margins are more deeply indented. It is directed forward and toward the right and overlaps the root of the pulmonary artery.

The interior of the left atrium (Fig. 496) presents the following parts for examination:
Openings of the four pulmonary veins.
Left atrioventricular opening.
Musculi pectinati.
The [[pulmonaryʼ veins four in number, open into the upper part of the posterior surface of the left atrium—two on either side of its middle line: they are not provided with valves. The two left veins frequently end by a common opening.
The left atrioventricular opening is the aperture between the left atrium and ventricle, and is rather smaller than the corresponding opening on the right side.
The musculi pectinati fewer and smaller than in the right auricula, are confined to the inner surface of the auricula. On the atrial septum may be seen a lunated impression, bounded below by a crescentic ridge, the concavity of which is turned upward. The depression is just above the fossa ovalis of the right atrium.
Left Ventricle[edit]
(ventriculus sinister)
The left ventricle is longer and more conical in shape than the right, and on transverse section its concavity presents an oval or nearly circular outline. It forms a small part of the sternocostal surface and a considerable part of the diaphragmatic surface of the heart; it also forms the apex of the heart. Its walls are about three times as thick as those of the right ventricle.
Its interior (Fig. 496) presents the following parts for examination:
Openings » Left atrioventricular. Valves » Bicuspid or Mitral.
Aortic. Aortic.
- Trabeculae carneae.
- Chordae tendineae
The left atrioventricular opening (mitral orifice) is placed below and to the left of the aortic orifice. It is a little smaller than the corresponding aperture of the opposite side, admitting only two fingers. It is surrounded by a dense fibrous ring, covered by the lining membrane of the heart, and is guarded by the bicuspid or mitral valve.

The aortic opening is a circular aperture, in front and to the right of the atrioventricular, from which it is separated by the anterior cusp of the bicuspid valve. Its orifice is guarded by the aortic semilunar valves The portion of the ventricle immediately below the aortic orifice is termed the aortic vestibule and possesses fibrous instead of muscular walls.
The bicuspid or mitral valve (valvula bicuspidalis [metralis]) (Figs. 495, 496) is attached to the circumference of the left atrioventricular orifice in the same way that the tricuspid valve is on the opposite side. It consists of two triangular cusps, formed by duplicatures of the lining membrane, strengthened by fibrous tissue, and containing a few muscular fibers. The cusps are of unequal size, and are larger, thicker, and stronger than those of the tricuspid valve. The larger cusp is placed in front and to the right between the atrioventricular and aortic orifices, and is known as the anterior or aortic cusp the smaller or [[posteriorʼ cusp is placed behind and to the left of the opening. Two smaller cusps are usually found at the angles of junction of the larger. The cusps of the bicuspid valve are furnished with chordae tendineae, which are attached in a manner similar to those on the right side; they are, however, thicker, stronger, and less numerous.
The aortic semilunar valves (Figs. 494, 497) are three in number, and surround the orifice of the aorta; two are anterior (right and left) and one posterior. They are similar in structure, and in their mode of attachment, to the pulmonary semilunar valves, but are larger, thicker, and stronger; the lunulae are more distinct, and the noduli or corpora Arantii thicker and more prominent. Opposite the valves the aorta presents slight dilatations, the aortic sinuses (sinuses of Valsalva), which are larger than those at the origin of the pulmonary artery.
The trabeculæ carneæ|trabeculae carneae are of three kinds, like those upon the right side, but they are more numerous, and present a dense interlacement, especially at the apex, and upon the posterior wall of the ventricle. The musculi papillares are two in number, one being connected to the anterior, the other to the posterior wall; they are of large size, and end in rounded extremities from which the chordae tendineae arise. The chordae tendineae from each papillary muscle are connected to both cusps of the bicuspid valve.

Ventricular Septum (septum ventriculorum; interventricular septum) (Fig. 498)[edit]
The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backward and to the right, and is curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle: its margins correspond with the anterior and posterior longitudinal sulci. The greater portion of it is thick and muscular and constitutes the muscular ventricular septum but its upper and posterior part, which separates the aortic vestibule from the lower part of the right atrium and upper part of the right ventricle, is thin and fibrous, and is termed the membranous ventricular septum An abnormal communication may exist between the ventricles at this part owing to defective development of the membranous septum.
Strucutre[edit]
The heart consists of muscular fibers, and of fibrous rings which serve for their attachment. It is covered by the visceral layer of the serous pericardium (epicardium), and lined by the endocardium Between these two membranes is the muscular wall or myocardium
The endocardium is a thin, smooth membrane which lines and gives the glistening appearance to the inner surface of the heart; it assists in forming the valves by its reduplications, and is continuous with the lining membrane of the large bloodvessels. It consists of connective tissue and elastic fibers, and is attached to the muscular structure by loose elastic tissue which contains bloodvessels and nerves; its free surface is covered by endothelial cells.
The fibrous rings surround the atrioventricular and arterial orifices, and are stronger upon the left than on the right side of the heart. The atrioventricular rings serve for the attachment of the muscular fibers of the atria and ventricles, and for the attachment of the bicuspid and tricuspid valves. The left atrioventricular ring is closely connected, by its right margin, with the aortic arterial ring; between these and the right atrioventricular ring is a triangular mass of fibrous tissue, the trigonum fibrosum which represents the os cordis seen in the heart of some of the larger animals, as the ox and elephant. Lastly, there is the tendinous band, already referred to, the posterior surface of the conus arteriosus.
The fibrous rings surrounding the arterial orifices serve for the attachment of the great vessels and semilunar valves. Each ring receives, by its ventricular margin, the attachment of some of the muscular fibers of the ventricles; its opposite margin presents three deep semicircular notches, to which the middle coat of the artery is firmly fixed. The attachment of the artery to its fibrous ring is strengthened by the external coat and serous membrane externally, and by the endocardium internally. From the margins of the semicircular notches the fibrous structure of the ring is continued into the segments of the valves. The middle coat of the artery in this situation is thin, and the vessel is dilated to form the sinuses of the aorta and pulmonary artery.
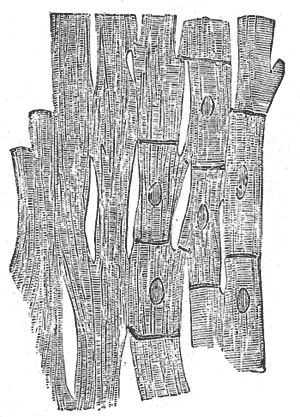

Cardiac Muscular Tissue[edit]
The fibers of the heart differ very remarkably from those of other striped muscles. They are smaller by one-third, and their transverse striae are by no means so well-marked. They show faint longitudinal striation. The fibers are made up of distinct quadrangular cells, joined end to end so as to form a syncytium (Fig. 499). Each cell contains a clear oval nucleus, situated near its center. The extremities of the cells have a tendency to branch or divide, the subdivisions uniting with offsets from other cells, and thus producing an anastomosis of the fibers. The connective tissue between the bundles of fibers is much less than in ordinary striped muscle, and no sarcolemma has been proved to exist.
Purkinje Fibers (Fig. 500)[edit]
Between the endocardium and the ordinary cardiac muscle are found, imbedded in a small amount of connective tissue, peculiar fibers known as Purkinje fibers. They are found in certain mammals and in birds, and can be best seen in the sheep’s heart, where they form a considerable portion of the moderator band and also appear as gelatinous-looking strands on the inner walls of the atria and ventricles. They also occur in the human heart associated with the terminal distributions of the bundle of His. The fibers are very much larger in size than the cardiac cells and differ from them in several ways. In longitudinal section they are quadrilateral in shape, being about twice as long as they are broad. The central portion of each fiber contains one or more nuclei and is made up of granular protoplasm, with no indication of striations, while the peripheral portion is clear and has distinct transverse striations. The fibers are intimately connected with each other, possess no definite sarcolemma, and do not branch.
The muscular structure of the heart consists of bands of fibers, which present an exceedingly intricate interlacement.
They comprise
('a') the fibers of the atria,
('b') the fibers of the ventricles, and
(c) the atrioventricular bundle of His.
The fibers of the atria are arranged in two layers—a superficial, common to both cavities, and a deep, proper to each. The superficial fibers are most distinct on the front of the atria, across the bases of which they run in a transverse direction, forming a thin and incomplete layer. Some of these fibers run into the atrial septum. The deep fibers consist of looped and annular fibers. The looped fibers pass upward over each atrium, being attached by their two extremities to the corresponding atrioventricular ring, in front and behind. The annular fibers surround the auriculae, and form annular bands around the terminations of the veins and around the fossa ovalis.
The fibers of the ventricles are arranged in a complex manner, and various accounts have been given of their course and connections; the following description is based on the work of McCallum. 94 They consist of superficial and deep layers, all of which, with the exception of two, are inserted into the papillary muscles of the ventricles.
The superficial layers consist of the following:
(a') Fibers which spring from the tendon of the conus arteriosus and sweep downward and toward the left across the anterior longitudinal sulcus and around the apex of the heart, where they pass upward and inward to terminate in the papillary muscles of the left ventricle; those arising from the upper half of the tendon of the conus arteriosus pass to the anterior papillary muscle, those from the lower half to the posterior papillary muscle and the papillary muscles of the septum.
(b') Fibers which arise from the right atrioventricular ring and run diagonally across the diaphragmatic surface of the right ventricle and around its right border on to its costosternal surface, where they dip beneath the fibers just described, and, crossing the anterior longitudinal sulcus, wind around the apex of the heart and end in the posterior papillary muscle of the left ventricle.
(c) Fibers which spring from the left atrioventricular ring, and, crossing the posterior longitudinal sulcus, pass successively into the right ventricle and end in its papillary muscles. The deep layers are three in number; they arise in the papillary muscles of one ventricle and, curving in an S-shaped manner, turn in at the longitudinal sulcus and end in the papillary muscles of the other ventricle.
The layer which is most superficial in the right ventricle lies next the lumen of the left, and vice versa Those of the first layer almost encircle the right ventricle and, crossing in the septum to the left, unite with the superficial fibers from the right atrioventricular ring to form the posterior papillary muscle.
Those of the second layer have a less extensive course in the wall of the right ventricle, and a correspondingly greater course in the left, where they join with the superficial fibers from the anterior half of the tendon of the conus arteriosus to form the papillary muscles of the septum.
Those of the third layer pass almost entirely around the left ventricle and unite with the superficial fibers from the lower half of the tendon of the conus arteriosus to form the anterior papillary muscle. Besides the layers just described there are two bands which do not end in papillary muscles. One springs from the right atrioventricular ring and crosses in the atrioventricular septum; it then encircles the deep layers of the left ventricle and ends in the left atrioventricular ring. The second band is apparently confined to the left ventricle; it is attached to the left atrioventricular ring, and encircles the portion of the ventricle adjacent to the aortic orifice.
The atrioventricular bundle of His (Fig. 501), is the only direct muscular connection known to exist between the atria and the ventricles. Its cells differ from ordinary cardiac muscle cells in being more spindle-shaped. They are, moreover, more loosely arranged and have a richer vascular supply than the rest of the heart muscle. It arises in connection with two small collections of spindle-shaped cells, the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes.
The sinoatrial node is situated on the anterior border of the opening of the superior vena cava; from its strands of fusiform fibers run under the endocardium of the wall of the atrium to the atrioventricular node.
The atrioventricular node lies near the orifice of the coronary sinus in the annular and septal fibers of the right atrium; from it the atrioventricular bundle passes forward in the lower part of the membranous septum, and divides into right and left fasciculi. These run down in the right and left ventricles, one on either side of the ventricular septum, covered by endocardium. In the lower parts of the ventricles they break up into numerous strands which end in the papillary muscles and in the ventricular muscle generally. The greater portion of the atrioventricular bundle consists of narrow, somewhat fusiform fibers, but its terminal strands are composed of Purkinje fibers. Dr. A. Morison 95 has shown that in the sheep and pig the atrioventricular bundle “is a great avenue for the transmission of nerves from the auricular to the ventricular heart; large and numerous nerve trunks entering the bundle and coursing with it.”
From these, branches pass off and form plexuses around groups of Purkinje cells, and from these plexuses fine fibrils go to innervate individual cells. Clinical and experimental evidence go to prove that this bundle conveys the impulse to systolic contraction from the atrial septum to the ventricles

Vessels and Nerves[edit]
The arteries supplying the heart are the right and left coronary from the aorta; the veins end in the right atrium.
The lymphatics end in the thoracic and right lymphatic ducts.
The nerves are derived from the cardiac plexus, which are formed partly from the vagi, and partly from the sympathetic trunks. They are freely distributed both on the surface and in the substance of the heart, the separate nerve filaments being furnished with small ganglia.
The Cardiac Cycle and the Actions of the Valves[edit]
By the contractions of the heart the blood is pumped through the arteries to all parts of the body. These contractions occur regularly and at the rate of about seventy per minute. Each wave of contraction or period of activity is followed by a period of rest the two periods constituting what is known as a cardiac cycle
Each cardiac cycle consists of three phases, which succeed each other as follows:
(1) a short simultaneous contraction of both atria, termed the atrial systole followed, lowed, after a slight pause, by
(2) a simultaneous, but more prolonged, contraction of both ventricles, named the ventricular systole and
(3) a period of rest during which the whole heart is relaxed. The atrial contraction commences around the venous openings, and sweeping over the atria forces their contents through the atrioventricular openings into the ventricles, regurgitation into the veins being prevented by the contraction of their muscular coats. When the ventricles contract, the tricuspid and bicuspid valves are closed, and prevent the passage of the blood back into the atria; the musculi papillares at the same time are shortened, and, pulling on the chordae tendineae, prevent the inversion of the valves into the atria. As soon as the pressure in the ventricles exceeds that in the pulmonary artery and aorta, the valves guarding the orifices of these vessels are opened and the blood is driven from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery and from the left into the aorta.
The moment the systole of the ventricles ceases, the pressure of the blood in the pulmonary artery and aorta closes the pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves to prevent regurgitation of blood into the ventricles, the valves remaining shut until reopened by the next ventricular systole. During the period of rest the tension of the tricuspid and bicuspid valves is relaxed, and blood is flowing from the veins into the atria, being aspirated by negative intrathoracic pressure, and slightly also from the atria into the ventricles. The average duration of a cardiac cycle is about 8/10 of a second, made up as follows:
- Atrial systole, 1/10.
- Atrial diastole, 7/10.
- Ventricular systole, 3/10.
- Ventricular diastole, 5/10.
- Total systole, 4/10.
- Complete diastole, 4/10.
The rhythmical action of the heart is muscular in origin—that is to say, the heart muscle itself possesses the inherent property of contraction apart from any nervous stimulation. The more embryonic the muscle the better is it able to initiate and propagate the contraction wave; this explains why the normal systole of the heart starts at the entrance of the veins, for there the muscle is most embryonic in nature.
At the atrioventricular junction there is a slight pause in the wave of muscular contraction. To obviate this so far as possible a peculiar band of marked embryonic type passes across the junction and so carries on the contraction wave to the ventricles. This band, composed of special fibers, is the atrioventricular bundle of His (p. 537). The nerves, although not concerned in originating the contractions of the heart muscle, play an important role in regulating their force and frequency in order to subserve the physiological needs of the organism.
Note 94 Johns Hopkins Hospital Reports, vo
Note 95 Journal of Anatomy and Physiology, vol. xlvi.
Function[edit]
The heart pumps blood with a rhythm determined by a group of pacemaking cells in the sinoatrial node. These generate a current that causes contraction of the heart, traveling through the atrioventricular node and along the conduction system of the heart. The heart receives blood low in oxygen from the systemic circulation, which enters the right atrium from the superior and inferior venae cavae and passes to the right ventricle. From here it is pumped into the pulmonary circulation, through the lungs where it receives oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium, passes through the left ventricle and is pumped out through the aorta to the systemic circulation−where the oxygen is used and metabolized to carbon dioxide.Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:No globals' not found. The heart beats at a resting rate close to 72 beats per minute.Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:No globals' not found. Exercise temporarily increases the rate, but lowers resting heart rate in the long term, and is good for heart health.Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'Module:No globals' not found.
Additional images[edit]
-
The human heart viewed from the front
-
The human heart viewed from behind
-
The human heart viewed from the front and from behind
-
Frontal section of the human heart
-
An anatomical specimen of the heart
-
Heart illustration with circulatory system
| Anatomy of the heart | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Physiology of the cardiovascular system | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gray's Anatomy[edit]
- Gray's Anatomy Contents
- Gray's Anatomy Subject Index
- About Classic Gray's Anatomy
- Glossary of anatomy terms
Anatomy atlases (external)[edit]
[1] - Anatomy Atlases
|
|
|
| Human systems and organs | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian