Artery
An artery is a type of blood vessel that is specifically designed to carry blood away from the heart. Unlike veins, which return blood to the heart, arteries transport blood to various parts of the body to ensure the delivery of oxygen and essential nutrients to cells and tissues.
Types of Arteries[edit]
- Pulmonary Arteries: These arteries are responsible for carrying blood that is relatively low in oxygen content from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs. Here, the blood is oxygenated before being sent back to the heart.
- Systemic Arteries: These arteries convey oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the rest of the body tissues.
Structure and Function[edit]
Blood is thrust from the ventricles into expansive elastic arteries. These arteries then undergo repeated branching, evolving into progressively smaller arteries until they culminate in minuscule arteries known as arterioles. Arterioles are instrumental in steering blood flow into the tissue capillaries. The systemic arterial system contains approximately 10% of the body's total blood volume at any given point.
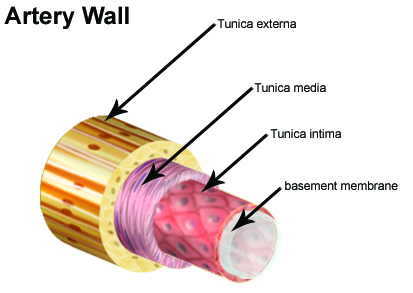
Artery Wall Structure[edit]
The wall of an artery can be divided into three distinct layers:
- Tunica Intima (or Tunica Interna): This innermost layer is made up of simple squamous epithelium that is ensconced by a connective tissue basement membrane embedded with elastic fibers.
- Tunica Media: Predominantly comprised of smooth muscle, this middle layer is usually the most substantial. Apart from providing support to the vessel, it plays a pivotal role in adjusting the vessel diameter, which in turn influences blood flow and blood pressure.
- Tunica Externa (or Tunica Adventitia): This outer layer, which secures the vessel to the neighboring tissue, is constructed from connective tissue integrated with a mix of elastic and collagenous fibers. Near the tunica media, the connective tissue is denser, becoming more lax towards the vessel's periphery.
Capillaries[edit]
Capillaries stand as the tiniest and most abundant blood vessels, forging the link between arteries and veins. Their main role is to facilitate the exchange of substances between blood and tissue cells.
Depending on the metabolic demands of body tissues, the distribution of capillaries varies. Tissues that are metabolically active, such as the liver, kidneys, and skeletal muscles, have intricate capillary networks due to their increased need for oxygen and nutrients. In contrast, tissues like connective tissues possess fewer capillaries. It's worth noting that the epidermis of the skin, as well as the lens and cornea of the eye, are devoid of capillaries. Approximately 5% of the overall blood volume resides in the systemic capillaries at any given time, with an additional 10% situated in the lungs.
Regulation of blood flow from arterioles into capillaries is managed by smooth muscle cells located in the arterioles, right at their branching point to form capillaries.
See also[edit]
Also see veins.
|
|
|
| Human systems and organs | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Arteries and veins | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
-
Artery
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


