Gastrointestinal disease

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Gastrointestinal disease | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, bloating, heartburn |
| Complications | Dehydration, malnutrition, intestinal obstruction, perforation |
| Onset | Varies depending on specific condition |
| Duration | Acute or chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Infection, inflammation, autoimmune disease, genetic disorders, dietary factors |
| Risks | Smoking, alcohol consumption, poor diet, stress, family history |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, endoscopy, imaging studies, laboratory tests |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Medication, surgery, dietary changes, lifestyle modifications |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on specific condition |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
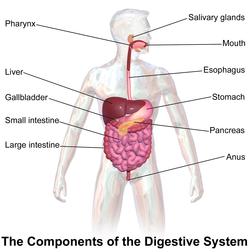
Gastrointestinal diseases (GI diseases) refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, which comprises the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), rectum, and accessory organs of digestion such as the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. These conditions can affect any part of this system and are often grouped by the organ involved.
Classification[edit]
- GI diseases can be broadly classified into infectious, inflammatory, neoplastic, structural, and functional disorders:
- Infectious Diseases: These include conditions such as gastroenteritis, hepatitis, and Helicobacter pylori infection which are caused by bacterial, viral, parasitic, or fungal pathogens.
- Inflammatory Diseases: Conditions such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, together known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), are chronic inflammatory conditions of the GI tract.
- Neoplastic Diseases: This category includes benign and malignant growths such as polyps, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Structural Diseases: These conditions involve physical changes in the structure of the GI tract, such as hiatus hernia, anal fissure, and hemorrhoids.
- Functional Diseases: Disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are functional GI disorders where the GI tract looks normal but does not work properly.

Symptoms[edit]
Common symptoms of gastrointestinal disease include abdominal pain, bloating, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, weight loss, and changes in bowel habits. The nature and severity of symptoms can vary significantly depending on the specific disease and the part of the GI tract affected.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of GI diseases often involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, imaging studies, and endoscopic procedures. Some of the diagnostic tools used in gastroenterology include upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, colonoscopy, abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and various blood and stool tests.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of GI diseases depends on the specific disease. It can involve dietary changes, medications (like antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or proton pump inhibitors), endoscopic procedures, or surgery. Some diseases, such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, may require lifelong management.
Epidemiology and Impact[edit]
GI diseases are prevalent worldwide and have a significant impact on public health. Conditions such as gastroenteritis and hepatitis are more common in regions with poor sanitation. In contrast, IBD and IBS are more prevalent in developed countries. GI diseases can lead to significant morbidity and mortality and have a substantial economic impact due to healthcare costs and loss of productivity.
See Also[edit]
- Digestive system
- Gastroenterology
- Gastroenteritis
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
References[edit]
- Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD, Houghton LA, Mearin F, Spiller RC. (2006). Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology, 130(5), 1480-1491.
- Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. (2012). Crohn's disease. The Lancet, 380(9853), 1590-1605.
Scallan E, Griffin PM, Angulo F.
|
|
|
| Health science - Medicine - Gastroenterology - edit |
|---|
| Diseases of the esophagus - stomach |
| Halitosis | Nausea | Vomiting | GERD | Achalasia | Esophageal cancer | Esophageal varices | Peptic ulcer | Abdominal pain | Stomach cancer | Functional dyspepsia | Gastroparesis |
| Diseases of the liver - pancreas - gallbladder - biliary tree |
| Hepatitis | Cirrhosis | NASH | PBC | PSC | Budd-Chiari | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Acute pancreatitis | Chronic pancreatitis | Pancreatic cancer | Gallstones | Cholecystitis |
| Diseases of the small intestine |
| Peptic ulcer | Intussusception | Malabsorption (e.g. Coeliac, lactose intolerance, fructose malabsorption, Whipple's) | Lymphoma |
| Diseases of the colon |
| Diarrhea | Appendicitis | Diverticulitis | Diverticulosis | IBD (Crohn's, Ulcerative colitis) | IBS | Constipation | Colorectal cancer | Hirschsprung's | Pseudomembranous colitis |
| Major Disease groups |
|---|
|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


