Galactorrhea hyperprolactinemia
| Galactorrhea Hyperprolactinemia | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | |
| Field | N/A |
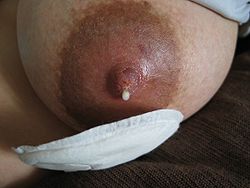
| Symptoms | Galactorrhea, Amenorrhea, Menstrual irregularities, Infertility, Decreased libido, Headaches, Visual disturbances, Erectile dysfunction (in males) |
| Complications | Infertility, Osteoporosis, Pituitary adenoma |
| Onset | Can occur at any age but commonly affects reproductive-age individuals |
| Duration | Chronic if left untreated |
| Types | |
| Causes | Prolactinoma, Pituitary disorders, Hypothyroidism, Medications, Renal failure, Granulomatous diseases, Stress, Pregnancy |
| Risks | Obesity, Chronic stress, Medications (e.g., antipsychotics, dopamine antagonists) |
| Diagnosis | Serum prolactin test, MRI of the pituitary gland, Thyroid function test, Hormonal panel |
| Differential diagnosis | Pregnancy, Breastfeeding, Hypothyroidism, Pituitary tumors, Drug-induced hyperprolactinemia |
| Prevention | Regular hormonal check-ups, avoiding medications that increase prolactin levels unless necessary |
| Treatment | Dopamine agonists, Hormone replacement therapy, Surgery (for tumors), Radiation therapy (rare cases) |
| Medication | Cabergoline, Bromocriptine, Estrogen replacement therapy (for bone health) |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment; risk of recurrence if underlying cause is not addressed |
| Frequency | Considered a rare disease but varies depending on etiology |
| Deaths | Rare, unless associated with a large, untreated pituitary tumor |
Galactorrhea hyperprolactinemia is a condition characterized by abnormal milk secretion (galactorrhea) and elevated blood levels of prolactin (hyperprolactinemia). It can occur in both men and women and may be associated with various underlying medical conditions, including pituitary tumors, hormonal imbalances, and medication side effects.
The disorder is commonly linked to prolactinomas, which are benign pituitary tumors that secrete excess prolactin, leading to menstrual irregularities, infertility, and reduced libido. It may also occur due to conditions that disrupt the normal regulation of prolactin release, such as hypothyroidism, stress, kidney failure, and certain medications.
Signs and Symptoms[edit]
Individuals with galactorrhea hyperprolactinemia may experience the following symptoms:
- Abnormal lactation (Galactorrhea) in non-pregnant or non-breastfeeding individuals
- Menstrual disturbances including amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) or irregular periods
- Infertility due to disrupted ovulation in women and impaired sperm production in men
- Decreased libido and sexual dysfunction
- Erectile dysfunction in males
- Headaches and visual disturbances (in cases of large pituitary tumors)
- Bone loss (osteoporosis) due to prolonged hormonal imbalance
Causes[edit]
Galactorrhea hyperprolactinemia can result from various causes, including:
Pituitary and Hypothalamic Disorders[edit]
- Prolactinoma – A benign tumor of the pituitary gland that secretes excessive prolactin.
- Granulomatous diseases affecting the pituitary gland.
- Hypothalamic dysfunction – Disrupts the normal inhibition of prolactin release.
Hormonal Disorders[edit]
- Hypothyroidism – Low levels of thyroid hormone can trigger increased prolactin secretion.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) – Can be associated with mild hyperprolactinemia.
Medication-Induced Hyperprolactinemia[edit]
Certain medications can increase prolactin levels by blocking dopamine, which normally inhibits prolactin release:
- Antipsychotics (e.g., Risperidone, Haloperidol)
- Antidepressants (e.g., SSRIs, tricyclic antidepressants)
- Dopamine antagonists (e.g., Metoclopramide, Domperidone)
- Opioids and estrogen-containing contraceptives
Other Causes[edit]
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Severe stress (physical or emotional)
- Chronic kidney failure
- Liver cirrhosis
- Ectopic prolactin production (rare)
Diagnosis[edit]
To diagnose galactorrhea hyperprolactinemia, healthcare providers use a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
Laboratory Tests[edit]
- Serum prolactin levels – Elevated levels confirm hyperprolactinemia.
- Thyroid function tests (TSH, T3, T4) – To rule out hypothyroidism.
- Serum estrogen and testosterone levels – Assess hormonal balance.
Imaging Studies[edit]
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pituitary gland – Detects prolactinomas or structural abnormalities.
- Brain CT scan (if MRI is unavailable) – Less detailed but can reveal pituitary tumors.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment of galactorrhea hyperprolactinemia depends on the underlying cause.
Medications[edit]
- Dopamine agonists (first-line treatment for prolactinomas):
- Cabergoline – More effective with fewer side effects.
- Bromocriptine – Used in pregnancy when necessary.
- Estrogen replacement therapy – For women with severe hypogonadism due to hyperprolactinemia.
- Thyroid hormone replacement – If hyperprolactinemia is due to hypothyroidism.
Surgery[edit]
- Transsphenoidal pituitary surgery – Indicated for large tumors that do not respond to medication or cause vision loss.
- Craniotomy – Used in rare cases for aggressive tumors.
Radiation Therapy[edit]
- Considered for large, non-resectable tumors or tumors resistant to medication.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for galactorrhea hyperprolactinemia is generally good, especially when diagnosed early. Most patients respond well to dopamine agonists, with normalization of prolactin levels and resolution of symptoms. However, untreated or large prolactinomas may lead to:
- Permanent infertility
- Severe osteoporosis
- Compression of the optic chiasm, leading to blindness
- Pituitary failure (panhypopituitarism)
Epidemiology[edit]
- More common in women, especially those of reproductive age.
- Prevalence: Approximately 0.4% in the general population, but up to 9-17% in women with reproductive disorders.
- Rare in men, but often diagnosed late due to subtle symptoms.
Prevention[edit]
While some causes of hyperprolactinemia cannot be prevented, the risk can be minimized by:
- Avoiding medications that increase prolactin levels, if possible.
- Managing stress and maintaining hormonal balance.
- Regular screening in individuals with pituitary disorders.
Summary[edit]
Galactorrhea hyperprolactinemia is a hormonal disorder characterized by abnormal milk secretion and elevated prolactin levels. It may result from pituitary tumors, medication use, or hormonal imbalances. The condition can cause menstrual irregularities, infertility, and bone loss if untreated. Diagnosis involves hormone tests and imaging, while treatment options include dopamine agonists, hormone therapy, or surgery in severe cases. With appropriate treatment, most patients can recover normal prolactin levels and fertility.
See Also[edit]
External Links[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


