Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism[edit]
| Hypopituitarism | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | |
| Field | Endocrinology |
| Symptoms | |
| Complications | |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | |
| Causes | |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | |
| Frequency | |
| Deaths | |
Hypopituitarism is the decreased (hypo) secretion of one or more of the eight hormones normally produced by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain.
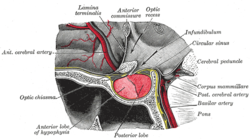
Anatomy[edit]
The pituitary gland is a small structure that is located just below the brain. It is attached by a stalk to the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is the area of the brain that controls the pituitary gland's function.
Pituitary hormones[edit]
The hormones released by the pituitary gland (and their functions) are: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) -- stimulates the adrenal gland to release cortisol; cortisol helps to maintain blood pressure and blood sugar Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) -- controls water loss by the kidneys Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) -- controls sexual function and fertility in males and females Growth hormone (GH) -- stimulates growth of tissues and bone Luteinizing hormone (LH) -- controls sexual function and fertility in males and females Oxytocin -- stimulates the uterus to contract during labor and the breasts to release milk Prolactin -- stimulates female breast development and milk production Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) -- stimulates the thyroid gland to release hormones that affect the body's metabolism
Pathophysiology[edit]
In hypopituitarism, there is a lack of one or more pituitary hormones. Lack of a hormone leads to loss of function in the gland or organ the hormone controls. For example, lack of TSH leads to loss of normal function of the thyroid gland.
Causes[edit]
- Brain surgery
- Brain tumor
- Head trauma (traumatic brain injury)
- Infections or inflammation of the brain and the tissues that support the brain
- Death of an area of tissue in the pituitary gland (pituitary apoplexy)
- Radiation therapy to the brain
- Stroke
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (from a burst aneurysm)
- Tumors of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus
- Too much iron in the body (hemochromatosis)
- Abnormal increase in immune cells called histiocytes (histiocytosis X)
- Autoimmune condition that causes inflammation of the pituitary (lymphocytic hypophysitis)
- Inflammation of various tissues and organs (sarcoidosis)
- Infections of the pituitary, such as primary pituitary tuberculosis
During pregnancy[edit]
- Hypopituitarism is also a rare complication caused by severe bleeding during pregnancy.
The loss of blood leads to tissue death in the pituitary gland. This condition is called Sheehan syndrome.
Medications[edit]
Certain medicines can also suppress pituitary function. The most common drugs are glucocorticoids (such as prednisone and dexamethasone), which are taken for inflammatory and immune conditions. Drugs used to treat prostate cancer can also lead to low pituitary function.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of hypopituitarism include any of the following:
- Abdominal pain
- Decreased appetite
- Lack of sex drive (in men or women)
- Dizziness or fainting
- Excessive urination and thirst
- Failure to release milk (in women)
- Fatigue, weakness
- Headache
- Infertility (in women) or stopping of menstrual periods
- Loss of armpit or pubic hair
- Loss of body or facial hair (in men)
- Low blood pressure
- Low blood sugar
- Sensitivity to cold
- Short height (less than 5 feet or 1.5 meters) if onset is during a growth period
- Slowed growth and sexual development (in children)
- Vision problems
- Weight loss
Other symptoms[edit]
Symptoms may develop slowly and may vary greatly, depending upon:
The number of hormones that are missing and the organs they affect The severity of the disorder Other symptoms that may occur with this disease:
- Face swelling
- Hair loss
- Hoarseness or changing voice
- Joint stiffness
- Weight gain
Management[edit]
To diagnose hypopituitarism, there must be low hormone levels due to a problem with the pituitary gland. The diagnosis must also rule out diseases of the organ that is affected by this hormone.
Tests[edit]
- Brain CT scan
- Pituitary MRI
- ACTH
- Cortisol
- Estradiol (estrogen)
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Osmolality tests for blood and urine
- Testosterone level
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Thyroid hormone (T4)
- Biopsy of the pituitary
Level of a pituitary hormone may be high in the bloodstream if you have a pituitary tumor that is producing too much of that hormone. The tumor may crush other cells of the pituitary, leading to low levels of other hormones.
Treatment[edit]
If hypopituitarism is caused by a tumor, you may need surgery to remove the tumor. Radiation therapy may also be needed.
You will need lifelong hormone medicines to replace hormones that are no longer made by organs under the control of the pituitary gland. These may include:
- Corticosteroids (cortisol)
- Growth hormone
- Sex hormones (testosterone for men and estrogen for women)
- Thyroid hormone
- Desmopressin
Drugs are also available to treat related infertility in men and women.
If you take glucocorticoid medicines for pituitary ACTH deficiency, be sure you know when to take a stress dose of your medicine. Discuss this with your health care provider.
Always carry medical ID (card, bracelet, or necklace) that says you have adrenal insufficiency. The ID should also say the type of medicine and dosage you need in case of an emergency caused by adrenal insufficiency.
Prognosis[edit]
Hypopituitarism is usually permanent. It requires lifelong treatment with one or more medicines. But you can expect a normal life span.
In children, hypopituitarism may improve if the tumor is removed during surgery.
Complications[edit]
Side effects of medicines to treat hypopituitarism can develop. However, do not stop any medicine on your own without talking with your provider first.
| Pituitary disease | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


