Liver failure: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Liver failure | |||
| image = [[File:Hepaticfailure.jpg|250px]] | |||
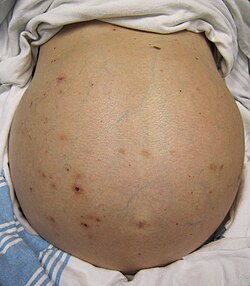
| caption = Liver failure can lead to [[jaundice]], [[ascites]], and [[hepatic encephalopathy]]. | |||
| field = [[Hepatology]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Jaundice]], [[ascites]], [[hepatic encephalopathy]], [[coagulopathy]], [[hypoglycemia]] | |||
| complications = [[Hepatorenal syndrome]], [[hepatic coma]], [[sepsis]] | |||
| onset = Acute or chronic | |||
| duration = Varies | |||
| causes = [[Viral hepatitis]], [[alcoholic liver disease]], [[non-alcoholic fatty liver disease]], [[drug-induced liver injury]] | |||
| risks = [[Chronic alcohol use]], [[obesity]], [[hepatitis B]], [[hepatitis C]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Liver function tests]], [[imaging studies]], [[liver biopsy]] | |||
| treatment = [[Supportive care]], [[liver transplantation]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on cause and treatment | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|Overview of liver failure}} | {{Short description|Overview of liver failure}} | ||
'''Liver failure''' is a life-threatening condition that occurs when large parts of the [[liver]] become damaged beyond repair and the liver is no longer able to function. It is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate attention. | '''Liver failure''' is a life-threatening condition that occurs when large parts of the [[liver]] become damaged beyond repair and the liver is no longer able to function. It is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate attention. | ||
==Types== | ==Types== | ||
Liver failure can be classified into two main types: | Liver failure can be classified into two main types: | ||
===Acute liver failure=== | ===Acute liver failure=== | ||
Acute liver failure, also known as fulminant hepatic failure, occurs when the liver rapidly loses its ability to function. This can happen within days or weeks and is often caused by factors such as [[acetaminophen]] overdose, viral [[hepatitis]], or ingestion of toxic substances. | Acute liver failure, also known as fulminant hepatic failure, occurs when the liver rapidly loses its ability to function. This can happen within days or weeks and is often caused by factors such as [[acetaminophen]] overdose, viral [[hepatitis]], or ingestion of toxic substances. | ||
===Chronic liver failure=== | ===Chronic liver failure=== | ||
Chronic liver failure, or end-stage liver disease, develops more slowly over months or years. It is often the result of long-term liver damage due to conditions such as [[cirrhosis]], chronic [[hepatitis B]] or [[hepatitis C]], and [[alcoholic liver disease]]. | Chronic liver failure, or end-stage liver disease, develops more slowly over months or years. It is often the result of long-term liver damage due to conditions such as [[cirrhosis]], chronic [[hepatitis B]] or [[hepatitis C]], and [[alcoholic liver disease]]. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
The causes of liver failure can vary depending on whether it is acute or chronic. Common causes include: | The causes of liver failure can vary depending on whether it is acute or chronic. Common causes include: | ||
* [[Viral hepatitis]] (A, B, C, D, and E) | * [[Viral hepatitis]] (A, B, C, D, and E) | ||
* [[Drug-induced liver injury]], particularly from acetaminophen | * [[Drug-induced liver injury]], particularly from acetaminophen | ||
| Line 24: | Line 33: | ||
* [[Genetic disorders]] such as [[Wilson's disease]] and [[hemochromatosis]] | * [[Genetic disorders]] such as [[Wilson's disease]] and [[hemochromatosis]] | ||
* [[Toxins]] and [[poisons]], including certain [[mushrooms]] and [[herbal supplements]] | * [[Toxins]] and [[poisons]], including certain [[mushrooms]] and [[herbal supplements]] | ||
==Symptoms== | ==Symptoms== | ||
Symptoms of liver failure can include: | Symptoms of liver failure can include: | ||
* [[Jaundice]] (yellowing of the skin and eyes) | * [[Jaundice]] (yellowing of the skin and eyes) | ||
* [[Fatigue]] | * [[Fatigue]] | ||
| Line 35: | Line 42: | ||
* [[Confusion]] or [[encephalopathy]] | * [[Confusion]] or [[encephalopathy]] | ||
* [[Bleeding]] easily | * [[Bleeding]] easily | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of liver failure involves a combination of [[medical history]], [[physical examination]], and [[laboratory tests]]. Key tests include: | Diagnosis of liver failure involves a combination of [[medical history]], [[physical examination]], and [[laboratory tests]]. Key tests include: | ||
* [[Liver function tests]] | * [[Liver function tests]] | ||
* [[Blood tests]] to check for viral hepatitis | * [[Blood tests]] to check for viral hepatitis | ||
* [[Imaging studies]] such as [[ultrasound]] or [[CT scan]] | * [[Imaging studies]] such as [[ultrasound]] or [[CT scan]] | ||
* [[Liver biopsy]] in some cases | * [[Liver biopsy]] in some cases | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment for liver failure depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Options may include: | Treatment for liver failure depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Options may include: | ||
* [[Medications]] to treat infections or reduce liver inflammation | * [[Medications]] to treat infections or reduce liver inflammation | ||
* [[Supportive care]] to manage symptoms | * [[Supportive care]] to manage symptoms | ||
* [[Liver transplantation]] for severe cases | * [[Liver transplantation]] for severe cases | ||
==Prevention== | ==Prevention== | ||
Preventing liver failure involves addressing the risk factors and causes. This can include: | Preventing liver failure involves addressing the risk factors and causes. This can include: | ||
* [[Vaccination]] against hepatitis A and B | * [[Vaccination]] against hepatitis A and B | ||
* Avoiding excessive [[alcohol consumption]] | * Avoiding excessive [[alcohol consumption]] | ||
* Using medications responsibly | * Using medications responsibly | ||
* Maintaining a healthy [[diet]] and [[weight]] | * Maintaining a healthy [[diet]] and [[weight]] | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis for liver failure varies depending on the cause and the timeliness of treatment. Acute liver failure can be fatal without prompt medical intervention, while chronic liver failure may progress slowly but can also lead to life-threatening complications. | The prognosis for liver failure varies depending on the cause and the timeliness of treatment. Acute liver failure can be fatal without prompt medical intervention, while chronic liver failure may progress slowly but can also lead to life-threatening complications. | ||
==See also== | |||
== | |||
* [[Liver transplantation]] | * [[Liver transplantation]] | ||
* [[Cirrhosis]] | * [[Cirrhosis]] | ||
* [[Hepatitis]] | * [[Hepatitis]] | ||
* [[Jaundice]] | * [[Jaundice]] | ||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | [[Category:Hepatology]] | ||
[[Category:Liver disorders]] | [[Category:Liver disorders]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:32, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Liver failure | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Jaundice, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, coagulopathy, hypoglycemia |
| Complications | Hepatorenal syndrome, hepatic coma, sepsis |
| Onset | Acute or chronic |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, drug-induced liver injury |
| Risks | Chronic alcohol use, obesity, hepatitis B, hepatitis C |
| Diagnosis | Liver function tests, imaging studies, liver biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Supportive care, liver transplantation |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on cause and treatment |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Overview of liver failure
Liver failure is a life-threatening condition that occurs when large parts of the liver become damaged beyond repair and the liver is no longer able to function. It is a serious medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
Types[edit]
Liver failure can be classified into two main types:
Acute liver failure[edit]
Acute liver failure, also known as fulminant hepatic failure, occurs when the liver rapidly loses its ability to function. This can happen within days or weeks and is often caused by factors such as acetaminophen overdose, viral hepatitis, or ingestion of toxic substances.
Chronic liver failure[edit]
Chronic liver failure, or end-stage liver disease, develops more slowly over months or years. It is often the result of long-term liver damage due to conditions such as cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis C, and alcoholic liver disease.
Causes[edit]
The causes of liver failure can vary depending on whether it is acute or chronic. Common causes include:
- Viral hepatitis (A, B, C, D, and E)
- Drug-induced liver injury, particularly from acetaminophen
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Genetic disorders such as Wilson's disease and hemochromatosis
- Toxins and poisons, including certain mushrooms and herbal supplements
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of liver failure can include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain and swelling
- Confusion or encephalopathy
- Bleeding easily
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of liver failure involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Key tests include:
- Liver function tests
- Blood tests to check for viral hepatitis
- Imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scan
- Liver biopsy in some cases
Treatment[edit]
Treatment for liver failure depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Options may include:
- Medications to treat infections or reduce liver inflammation
- Supportive care to manage symptoms
- Liver transplantation for severe cases
Prevention[edit]
Preventing liver failure involves addressing the risk factors and causes. This can include:
- Vaccination against hepatitis A and B
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Using medications responsibly
- Maintaining a healthy diet and weight
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for liver failure varies depending on the cause and the timeliness of treatment. Acute liver failure can be fatal without prompt medical intervention, while chronic liver failure may progress slowly but can also lead to life-threatening complications.