Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | MASLD |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Often asymptomatic, fatigue, right upper quadrant pain |
| Complications | Cirrhosis, liver cancer, cardiovascular disease |
| Onset | Typically in adulthood |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Metabolic syndrome, obesity, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia |
| Risks | Insulin resistance, hypertension, sedentary lifestyle |
| Diagnosis | Liver function tests, ultrasound, liver biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis |
| Prevention | Weight loss, dietary changes, physical activity |
| Treatment | Lifestyle modification, medication, bariatric surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on stage and treatment |
| Frequency | Increasing worldwide, common in developed countries |
| Deaths | N/A |

File:Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.webm


Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MAFLD), previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a type of liver disease characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver of people who drink little to no alcohol. It is closely associated with metabolic syndrome, which is why the name was changed to reflect its metabolic dysfunction origin.
Definition[edit]
MAFLD is defined by the presence of steatosis in patients who have overweight or obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, or evidence of metabolic dysregulation. The term MAFLD can be applied to both non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH).
Epidemiology[edit]
MAFLD is the most common liver disorder in Western countries, affecting about 25% of the population. It is also increasingly recognized in developing countries due to the global epidemic of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Pathophysiology[edit]
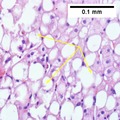
The pathogenesis of MAFLD is complex and involves multiple parallel hits, including insulin resistance, secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. The disease progresses from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of MAFLD is usually made by imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, which can detect fat in the liver. Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing MAFLD, but it is invasive and has potential complications.
Treatment[edit]
The mainstay of treatment for MAFLD is lifestyle modification, including diet, exercise, and weight loss. Pharmacological therapies are also available, but their long-term efficacy and safety are still under investigation.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis of MAFLD varies depending on the stage of the disease. Patients with simple steatosis have a relatively benign course, while those with NASH, fibrosis, or cirrhosis have a higher risk of liver-related morbidity and mortality.
-
NASH stage 6
-
NASH stage 2
-
Histopathology of inflammatory foci in MASH
-
NAFLD liver progression
-
MRI Liver steatosis
-
Human liver biopsy sample
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
-
Bariatric surgery in NAFLD
See also[edit]
| Liver diseases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This liver disease related article is a stub.
|
| Metabolic disorders | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This metabolic disorder related article is a stub.
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian