Science: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
{{Scientific method}} | {{Scientific method}} | ||
{{Science-stub}} | {{Science-stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Plimpton 322.jpg|Plimpton 322 | |||
File:MANNapoli 124545 plato's academy mosaic.jpg|Plato's Academy Mosaic | |||
File:ViennaDioscoridesEndpaperPeacock.jpg|Vienna Dioscorides Peacock | |||
File:De Revolutionibus manuscript p9b.jpg|De Revolutionibus Manuscript | |||
File:Newton's Principia title page.png|Newton's Principia Title Page | |||
File:Darwin Tree 1837.png|Darwin Tree 1837 | |||
File:Carte trou ozone Antarctique.jpg|Ozone Hole over Antarctica | |||
File:Apjlab0e85f4 EHT-images-M87-four-teams.jpg|EHT Images of M87 | |||
File:Supply-demand-equilibrium.svg|Supply and Demand Equilibrium | |||
File:The Scientific Method.svg|The Scientific Method | |||
File:Nature cover, November 4, 1869.jpg|Nature Cover, November 4, 1869 | |||
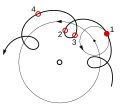
File:Epicycle and deferent.svg|Epicycle and Deferent | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 01:36, 20 February 2025
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. The earliest roots of science can be traced to Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3500 to 3000 BCE.
History of Science[edit]
The history of science involves the study of the development of science and scientific knowledge, including both the natural and social sciences. The history of the physical sciences such as physics and chemistry, biological sciences such as biology and medicine, and social sciences such as psychology and economics are all part of the larger history of science.
Branches of Science[edit]
Science is divided into three major branches: Natural science, Social science, and Formal science. Each of these branches comprise various specialized yet overlapping scientific disciplines that often possess their own nomenclature and expertise.
Natural Science[edit]
Natural science is a branch of science concerned with the description, prediction, and understanding of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. It can be divided into two main branches: Life science and Physical science.
Social Science[edit]
Social science is a branch of science devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. It includes disciplines such as Anthropology, Sociology, Psychology, and Economics.
Formal Science[edit]
Formal science is a branch of science concerned with formal systems, such as logic, mathematics, information theory, systems theory, decision theory, statistics, and theoretical computer science.
Scientific Method[edit]
The Scientific method is an empirical method of acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century. It involves careful observation, applying rigorous skepticism about what is observed, given that cognitive assumptions can distort how one interprets the observation.
Impact of Science[edit]
Science has had a profound impact on society, and its applications are continually reshaping the world. From the development of technology to the understanding of the natural world, science has provided us with a way to understand the universe and our place in it.
| Part of a series on |
| Science |
|---|
 |
| General |
| Branches |
| In society |
| History of science | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Natural science |
|---|
|
|
| Social sciences | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This social science related article is a stub.
|
| Formal sciences | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This Formal science related article is a stub.
|
| Scientific method | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This Scientific method related article is a stub.
|
-
Plimpton 322
-
Plato's Academy Mosaic
-
Vienna Dioscorides Peacock
-
De Revolutionibus Manuscript
-
Newton's Principia Title Page
-
Darwin Tree 1837
-
Ozone Hole over Antarctica
-
EHT Images of M87
-
Supply and Demand Equilibrium
-
The Scientific Method
-
Nature Cover, November 4, 1869
-
Epicycle and Deferent