Law




Law is a system of rules created and enforced through social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and the art of justice. State-enforced laws can be made by a collective legislature or by a single legislator, resulting in statutes; by the executive through decrees and regulations; or established by judges through precedent, normally in common law jurisdictions. Private individuals can create legally binding contracts, including arbitration agreements that may elect to accept alternative arbitration to the normal court process. The formation of laws themselves may be influenced by a constitution, written or tacit, and the rights encoded therein. The law shapes politics, economics, history, and society in various ways and serves as a mediator of relations between people.
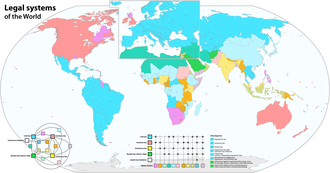
Legal systems[edit]
There are several types of legal systems, each with their own sets of laws and ways of being interpreted and enforced. These include:
- Civil law, which is the most widespread system of law in the world, codified into legal codes.
- Common law, which is based on precedent – decisions made in previous legal cases.
- Statutory law, which is written law passed by a body of legislature.
- Religious law, which is based on the scriptures of a particular religion, such as Islamic law (Sharia) and Jewish law (Halakha).
- Customary law, which is unwritten and based on cultural or societal norms.
- Hybrid systems, which combine elements of various legal systems.
Functions of law[edit]
Law serves several important functions in society, including:
- Establishing standards and ethics that are to be followed by individuals and societies.
- Maintaining order by providing a basis for resolving disputes and punishing actions that threaten the well-being of society.
- Protecting liberties and rights through constitutions and other legal documents.
- Regulating industry and business practices to ensure fairness and safety.
- Facilitating planning and the realization of reasonable expectations by providing a framework within which people can plan their futures and businesses can make economic decisions.
Branches of law[edit]
Law is divided into various branches, such as:
- Criminal law, which deals with behavior that is or can be construed as an offense against the public, society, or the state—even if the immediate victim is an individual.
- Civil law, which addresses the resolution of lawsuits between individuals or organizations.
- Constitutional law, which involves the principles and structures of a government and its relationship with the people it governs.
- Administrative law, which governs the activities of administrative agencies of government.
- International law, which concerns the treaties, customs, and agreements between nations.
Legal profession[edit]
The practice of law is typically overseen by either a government or independent regulating body such as a bar association, bar council, or law society. Modern lawyers achieve distinct professional identity through specified legal procedures (e.g., successfully passing a qualifying examination), are required by law to have a special qualification (a legal education earning the student a Bachelor of Laws, a Bachelor of Civil Law, or a Juris Doctor degree), and are constituted in office by legal forms of appointment (being admitted to the bar). There are civil law and common law legal systems.
Challenges and criticisms[edit]
The law faces criticism and challenges in various aspects, including issues of justice, fairness, and equality. Critics argue that the law can be manipulated or abused by those with power, leading to injustices. Additionally, the complexity of the law can make it difficult for individuals to understand their rights and obligations.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
