Cell


In biology, the cell is the basic structure of organisms. All cells are made by the division of other cells.
The cell is the fundamental unit of life. It is the smallest structure of the body capable of performing all of the processes that define life. Each of the organs in the body, such as the lung, breast, colon, and brain, consists of specialized cells that carry out the organ's functions such as the transportation of oxygen, digestion of nutrients, excretion of waste materials, locomotion, reproduction, thinking, etc.
Kinds of cells[edit]
There are two basic kinds of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes, bacteria and archaea, are simple cells that have no cell nucleus. They do have bacterial microcompartments.
Eukaryotes are complex cells with many organelles and other structures in the cell. They are larger than prokaryote cells: they can be as much as 1000 times greater in volume. Eukaryotes store their genetic information (DNA) on chromosomes in the cell nucleus. Organisms (living things) which are made up of multiple cells are eukaryotes.
Kinds of prokaryotic organisms[edit]
The only kinds of prokaryotic organisms alive at present are bacteria and archaea. Prokaryotic organisms evolved before eukaryotic organisms, so at one point the world consisted of nothing but prokaryotic organisms. There are also viruses, which are hard to classify, but cause some important diseases. Viruses are made of RNA, or DNA, and protein, and they reproduce themselves inside the cells of bacteria or eukaryotes.
Kinds of eukaryotic organisms[edit]
Unicellular[edit]


Unicellular organisms are made up of one cell. Examples of unicellular organisms are:
Unicellular organisms need to:
All unicellular organisms must:
- get rid of waste (discard)
- reproduce (make more of itself)
- grow
Some may:
- move
- sense their environment
- get their energy from the sun (e.g., cyanobacteria)
- ferment (e.g., yeasts)
- use anaerobic respiration (e.g. Clostridium botulinum)
Multicellular[edit]
Multicellular organisms are made from many cells. They are complex organisms. This can be a small number of cells, or millions or trillions of cells. All plants and animals are multicellular organisms. The cells of a multicellular organism are not all the same. They have different shapes and sizes, and do different work in the organism. The cells are specialized. This means they do only some kinds of work. By themselves, they cannot do everything that the organism needs to live. They need other cells to do other work. They live together, but cannot live alone.
To assure the proper performance of each organ, worn out or injured cells must be replaced, and particular types of cells must increase in response to environmental changes. For example, the bone marrow increases its production of oxygen-carrying red blood cells sevenfold or greater in response to bleeding or high altitude. Certain white blood cells are produced more rapidly during an infection. Similarly, the liver or endocrine organs frequently respond to injury by regenerating damaged cells.
Cell reproduction[edit]
The body cells of metazoans divide by simple mitotic cell division. Sexual reproduction is ancestral in eukaryotes, and in metazoa it is carried out by specialized sex cells. They are produced by a process called meiosis.
Prokaryotic cells reproduce using binary fission, where the cell simply splits in half. For both mitosis and binary fission the cell must replicate (copy) all its genetic information (DNA) so that each new cell will have a copy.
Cells have long been recognized as the simplest units of living matter that can maintain life and reproduce themselves. The human body, which is made up of numerous cells, begins as a single, newly fertilized cell. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells. They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body’s hereditary material and can make copies of themselves.
Cell organelles[edit]
Cells have many parts, each with a different function. Some of these parts, called organelles, are specialized structures that perform certain tasks within the cell. Human cells contain the following major parts, listed in alphabetical order:
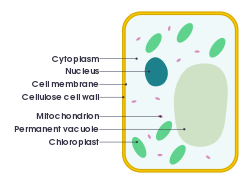
Cytoplasm[edit]
Within cells, the cytoplasm is made up of a jelly-like fluid (called the cytosol) and other structures that surround the nucleus.
Cytoskeleton[edit]
The cytoskeleton is a network of long fibers that make up the cell’s structural framework. The cytoskeleton has several critical functions, including determining cell shape, participating in cell division, and allowing cells to move. It also provides a track-like system that directs the movement of organelles and other substances within cells.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)[edit]
This organelle helps process molecules created by the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum also transports these molecules to their specific destinations either inside or outside the cell.
Golgi apparatus[edit]
The Golgi apparatus packages molecules processed by the endoplasmic reticulum to be transported out of the cell.
Lysosomes and peroxisomes[edit]
These organelles are the recycling center of the cell. They digest foreign bacteria that invade the cell, rid the cell of toxic substances, and recycle worn-out cell components. Mitochondria
Mitochondria are complex organelles that convert energy from food into a form that the cell can use. They have their own genetic material, separate from the DNA in the nucleus, and can make copies of themselves.
Nucleus[edit]
The nucleus serves as the cell’s command center, sending directions to the cell to grow, mature, divide, or die. It also houses DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), the cell’s hereditary material. The nucleus is surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope, which protects the DNA and separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell.
Plasma membrane[edit]
The plasma membrane is the outer lining of the cell. It separates the cell from its environment and allows materials to enter and leave the cell.
Ribosomes[edit]
Ribosomes are organelles that process the cell’s genetic instructions to create proteins. These organelles can float freely in the cytoplasm or be connected to the endoplasmic reticulum (see above).
Also see[edit]
- Cellular metabolism
- Cell cortex
- Cell culture
- Cellular model
- Cytoneme
- Cytorrhysis
- Cytotoxicity
- Cell death
|
|
|
| Structures of the cell / organelles | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Hierarchy of life |
|---|
|
|
| Biotechnology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


