Cyst: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The word ''' | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Cyst | |||
| image = [[File:bronchogenic_cyst_high_mag.jpg|250px]] | |||
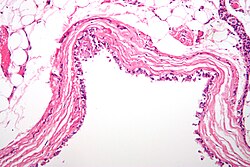
| caption = Micrograph of a [[bronchogenic cyst]], a type of cyst. | |||
| field = [[Dermatology]], [[Pathology]] | |||
| synonyms = | |||
| symptoms = [[Lump]], [[swelling]], [[pain]] | |||
| complications = [[Infection]], [[rupture]] | |||
| onset = | |||
| duration = | |||
| causes = [[Blockage]] of ducts, [[infection]], [[genetic conditions]] | |||
| risks = | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[imaging studies]] | |||
| differential = [[Abscess]], [[tumor]] | |||
| prevention = | |||
| treatment = [[Surgical removal]], [[drainage]] | |||
| medication = [[Antibiotics]] if infected | |||
| prognosis = Generally good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
| deaths = Rare | |||
}} | |||
The word '''‘cyst’''' is derived from Greek word kystitis meaningbladder. Kramer (1974) defined cyst as a pathological cavity having fluid, semifluid or gaseous contents and which is not created by the accumulation of pus. It is frequently, but not always, lined by the epithelium. Cysts may arise due to trauma, inflammation and degeneration or retention. | |||
===True cyst=== | ===True cyst=== | ||
True cysts are lined by epithelium. | True cysts are lined by epithelium. | ||
[[File:Bronchogenic_cyst_high_mag.jpg|alt=|thumb|300x300px|True cyst]] | [[File:Bronchogenic_cyst_high_mag.jpg|alt=|left|thumb|300x300px|True cyst]] | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
| Line 15: | Line 35: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
===Pseudo/False cyst=== | ===Pseudo/False cyst=== | ||
Pseudo/False cyst are not lined by epithelium. | Pseudo/False cyst are not lined by epithelium. | ||
During the initial stages, when the cysts are small they are usually asymptomatic. Secondary infection may result in the formation of abscess, cellulitis, osteomyelitis and subsequent sinus formation. As the cyst enlarges it may cause displacement of roots of teeth, resorption of roots, paresthesia, expansion of the cortical plates and eventually result in pathologic fracture of the jaw. | During the initial stages, when the cysts are small they are usually asymptomatic. Secondary infection may result in the formation of abscess, cellulitis, osteomyelitis and subsequent sinus formation. As the cyst enlarges it may cause displacement of roots of teeth, resorption of roots, paresthesia, expansion of the cortical plates and eventually result in pathologic fracture of the jaw. | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{Tumors}} | {{Tumors}} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:37, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Cyst | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Lump, swelling, pain |
| Complications | Infection, rupture |
| Onset | |
| Duration | |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Blockage of ducts, infection, genetic conditions |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Abscess, tumor |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Surgical removal, drainage |
| Medication | Antibiotics if infected |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | Rare |
The word ‘cyst’ is derived from Greek word kystitis meaningbladder. Kramer (1974) defined cyst as a pathological cavity having fluid, semifluid or gaseous contents and which is not created by the accumulation of pus. It is frequently, but not always, lined by the epithelium. Cysts may arise due to trauma, inflammation and degeneration or retention.
True cyst[edit]
True cysts are lined by epithelium.

Pseudo/False cyst[edit]
Pseudo/False cyst are not lined by epithelium. During the initial stages, when the cysts are small they are usually asymptomatic. Secondary infection may result in the formation of abscess, cellulitis, osteomyelitis and subsequent sinus formation. As the cyst enlarges it may cause displacement of roots of teeth, resorption of roots, paresthesia, expansion of the cortical plates and eventually result in pathologic fracture of the jaw.
|
|
|
| Overview of tumors, cancer and oncology | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Cystic diseases | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|


