Acrania: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Acrania | |||
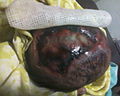
| image =[[File:Acrania.jpg]] | |||
| caption = An infant with acrania | |||
| field = [[Neurology]], [[Pediatrics]] | |||
| synonyms = Exencephaly | |||
| symptoms = Absence of the [[skull]] | |||
| complications = [[Anencephaly]], [[stillbirth]] | |||
| onset = [[Congenital disorder|Congenital]] | |||
| duration = [[Permanent]] | |||
| causes = [[Neural tube defect]] | |||
| risks = [[Genetic predisposition]], [[environmental factors]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Ultrasound]], [[MRI]] | |||
| differential = [[Anencephaly]], [[encephalocele]] | |||
| prevention = [[Folic acid]] supplementation | |||
| treatment = [[Supportive care]] | |||
| prognosis = [[Poor prognosis|Poor]] | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
{{Short description|A rare congenital disorder characterized by the absence of the cranial vault}} | {{Short description|A rare congenital disorder characterized by the absence of the cranial vault}} | ||
{{Medical condition}} | {{Medical condition}} | ||
Latest revision as of 02:56, 4 April 2025
| Acrania | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Exencephaly |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Absence of the skull |
| Complications | Anencephaly, stillbirth |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Permanent |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Neural tube defect |
| Risks | Genetic predisposition, environmental factors |
| Diagnosis | Ultrasound, MRI |
| Differential diagnosis | Anencephaly, encephalocele |
| Prevention | Folic acid supplementation |
| Treatment | Supportive care |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Poor |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
A rare congenital disorder characterized by the absence of the cranial vault
| Medical conditions | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This medical condition related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
|
Acrania is a rare congenital disorder characterized by the partial or complete absence of the cranial vault, the protective bony structure that encases the brain. This condition is often associated with other neural tube defects, such as anencephaly.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Acrania occurs due to a failure in the closure of the neural tube during embryonic development. The neural tube is the precursor to the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. In acrania, the mesenchyme that forms the skull does not develop properly, leading to the absence of the cranial bones.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Infants with acrania are typically born with a malformed head due to the absence of the cranial bones. The brain is exposed or covered only by a thin membrane. This condition is often detected during prenatal ultrasound examinations.
Diagnosis[edit]
Acrania can be diagnosed prenatally through ultrasound imaging, which can reveal the absence of the cranial vault. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be used to assess the extent of the defect and any associated anomalies.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for infants with acrania is extremely poor. The condition is often incompatible with life due to the severe exposure and damage to the brain. Most affected pregnancies result in stillbirth or early neonatal death.
Management[edit]
There is no cure for acrania. Management is supportive and focuses on providing comfort care. In some cases, parents may choose to terminate the pregnancy upon diagnosis due to the poor prognosis.
Related Conditions[edit]
Acrania is often associated with other neural tube defects, such as:
Related pages[edit]
Gallery[edit]
-
Acrania
-
Anencephaly
-
Acrania
-
Anencefalia