Cephalic vein: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Sobo 1909 597.png| | {{SI}} | ||
[[File:Sobo 1909 597.png|thumb|400px|Illustration showing the cephalic vein and its common anatomical variations.]] | |||
== '''Cephalic Vein''' == | |||
In [[human anatomy]], the '''cephalic vein''' (Latin: ''vena cephalica'') is a prominent [[superficial vein]] of the [[upper limb]], located along the anterolateral aspect of the arm. It is a key structure involved in superficial venous return from the hand and forearm and is often used clinically for [[venipuncture]], [[intravenous therapy]], and [[pacemaker]] lead insertion. | |||
== '''Anatomical Course''' == | |||
The cephalic vein originates from the '''[[dorsal venous network of the hand]]''', specifically on the [[radial]] (thumb) side of the wrist. It ascends along the: | |||
* '''Lateral forearm''', passing over the [[radius (bone)|radius]] and deep to the skin within the superficial [[fascia]] | |||
* '''Anterior surface of the [[biceps brachii muscle]]''', where it is often clearly visible beneath the skin | |||
==Additional | At the level of the [[cubital fossa]], the cephalic vein communicates with the [[basilic vein]] via the prominent [[median cubital vein]], which is a common site for venipuncture. | ||
It then continues superiorly through the '''[[deltopectoral groove]]''', the interval between the [[deltoid muscle]] and [[pectoralis major]], and pierces the '''[[clavipectoral fascia]]''' within the [[deltopectoral triangle]]. From there, it empties into the deep venous system via the [[axillary vein]]. | |||
== '''Anatomical Relations and Variations''' == | |||
* The cephalic vein lies in close proximity to the '''[[cephalic artery]] (when present)''' and the '''[[lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm]]''' | |||
* Its location is '''superficial and consistent''', making it ideal for cannulation | |||
* The diameter, course, and communications of the vein may vary among individuals | |||
== '''Clinical Significance''' == | |||
The cephalic vein is frequently used in: | |||
* '''[[Intravenous access]]''', especially when veins in the [[antecubital fossa]] are not usable | |||
* '''Placement of large-bore [[cannulae]]''' or [[peripherally inserted central catheters]] (PICC lines) | |||
* '''Insertion of [[permanent pacemaker]] leads''' through the deltopectoral groove | |||
Due to its accessibility and visibility, the cephalic vein is nicknamed the '''"Houseman's Friend"'''—a reference to its use by medical trainees for venous cannulation. | |||
== '''Etymology''' == | |||
The term "cephalic" typically pertains to the [[head]]. However, in this context, the usage is a result of a '''translation error'''. When the Arabic term ''al-kífal'' (meaning "outer") from [[Avicenna]]’s ''[[Canon of Medicine]]'' was translated into [[medieval Latin]], it was mistakenly rendered as ''cephalicus'', implying an incorrect association with the head. | |||
== '''Additional Images''' == | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Image:Gray417_color.PNG|Cross-section through the middle of the forearm showing superficial and deep veins | |||
Image:Gray573.png|Superficial veins on the dorsum of the hand | |||
Image:Gray575.png|Deep veins of the upper extremity | |||
Image:Gray413_color.png|Cross-section | Image:Gray413_color.png|Cross-section of the upper arm (cephalic vein labeled at upper left) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
{| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | {| class="wikitable collapsible collapsed" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 23: | Line 47: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <gallery> | | <gallery> | ||
File:Slide7yyy.JPG| | File:Slide7yyy.JPG|Dissection showing the cephalic vein | ||
File:Slide16yyy.JPG|Cephalic vein | File:Slide16yyy.JPG|Cephalic vein in the arm | ||
</gallery | </gallery> | ||
|} | |} | ||
== See also == | == '''See also''' == | ||
*[[ | * [[Basilic vein]] | ||
*[[ | * [[Median cubital vein]] | ||
* [[Axillary vein]] | |||
* [[Venipuncture]] | |||
* [[Deltopectoral triangle]] | |||
* [[Superficial veins of the upper limb]] | |||
== | == '''External Links''' == | ||
* {{SUNYAnatomyLabs|07|st|07|02}} | * {{SUNYAnatomyLabs|07|st|07|02}} | ||
* {{SUNYRadiology|UpperLimb|18VenoFo}} | * {{SUNYRadiology|UpperLimb|18VenoFo}} | ||
{{grays}} | {{Human anatomy}} | ||
{{Circulatory system}} | |||
{{grays adapted}} | |||
[[Category:Anatomy]] | [[Category:Anatomy]] | ||
[[Category:Veins of the upper limb]] | [[Category:Veins of the upper limb]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:12, 30 March 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
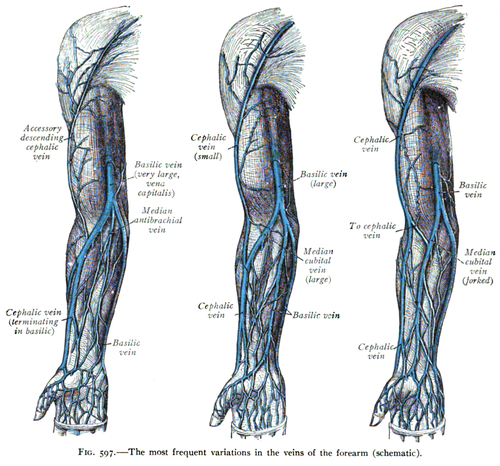
Cephalic Vein[edit]
In human anatomy, the cephalic vein (Latin: vena cephalica) is a prominent superficial vein of the upper limb, located along the anterolateral aspect of the arm. It is a key structure involved in superficial venous return from the hand and forearm and is often used clinically for venipuncture, intravenous therapy, and pacemaker lead insertion.
Anatomical Course[edit]
The cephalic vein originates from the dorsal venous network of the hand, specifically on the radial (thumb) side of the wrist. It ascends along the:
- Lateral forearm, passing over the radius and deep to the skin within the superficial fascia
- Anterior surface of the biceps brachii muscle, where it is often clearly visible beneath the skin
At the level of the cubital fossa, the cephalic vein communicates with the basilic vein via the prominent median cubital vein, which is a common site for venipuncture.
It then continues superiorly through the deltopectoral groove, the interval between the deltoid muscle and pectoralis major, and pierces the clavipectoral fascia within the deltopectoral triangle. From there, it empties into the deep venous system via the axillary vein.
Anatomical Relations and Variations[edit]
- The cephalic vein lies in close proximity to the cephalic artery (when present) and the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm
- Its location is superficial and consistent, making it ideal for cannulation
- The diameter, course, and communications of the vein may vary among individuals
Clinical Significance[edit]
The cephalic vein is frequently used in:
- Intravenous access, especially when veins in the antecubital fossa are not usable
- Placement of large-bore cannulae or peripherally inserted central catheters (PICC lines)
- Insertion of permanent pacemaker leads through the deltopectoral groove
Due to its accessibility and visibility, the cephalic vein is nicknamed the "Houseman's Friend"—a reference to its use by medical trainees for venous cannulation.
Etymology[edit]
The term "cephalic" typically pertains to the head. However, in this context, the usage is a result of a translation error. When the Arabic term al-kífal (meaning "outer") from Avicenna’s Canon of Medicine was translated into medieval Latin, it was mistakenly rendered as cephalicus, implying an incorrect association with the head.
Additional Images[edit]
-
Cross-section through the middle of the forearm showing superficial and deep veins
-
Superficial veins on the dorsum of the hand
-
Deep veins of the upper extremity
-
Cross-section of the upper arm (cephalic vein labeled at upper left)
| Dissection images |
|---|
|
See also[edit]
- Basilic vein
- Median cubital vein
- Axillary vein
- Venipuncture
- Deltopectoral triangle
- Superficial veins of the upper limb
External Links[edit]
- Anatomy photo:07:st-0702 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Radiology image: UpperLimb:18VenoFo from Radiology Atlas at SUNY Downstate Medical Center (need to enable Java)
| Anatomy and morphology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Circulatory system | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Gray's Anatomy[edit]
- Gray's Anatomy Contents
- Gray's Anatomy Subject Index
- About Classic Gray's Anatomy
- Glossary of anatomy terms
Anatomy atlases (external)[edit]
[1] - Anatomy Atlases
| Human systems and organs | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Adapted from the Classic Grays Anatomy of the Human Body 1918 edition (public domain)





