Brodie abscess: Difference between revisions
From WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia
No edit summary Tag: visualeditor-wikitext |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Brodie abscess | {{SI}} {{Infobox medical condition | ||
[[ | | name = Brodie abscess | ||
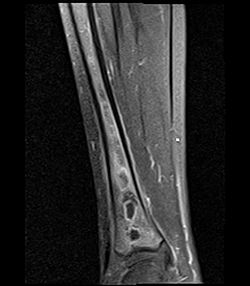
| image = [[File:BrodieAbscessSagT1FSMRI.jpg|250px]] | |||
| caption = MRI image showing a Brodie abscess | |||
| field = [[Infectious disease]], [[Orthopedic surgery]] | |||
| synonyms = Subacute osteomyelitis | |||
| symptoms = Localized bone pain, swelling, tenderness | |||
| complications = Chronic osteomyelitis, bone destruction | |||
| onset = Gradual | |||
| duration = Persistent if untreated | |||
| causes = [[Staphylococcus aureus]] infection | |||
| risks = Trauma, previous infection, immunocompromised state | |||
| diagnosis = [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]], [[X-ray]], [[Bone scan]] | |||
| differential = [[Bone tumor]], [[Osteoid osteoma]], [[Ewing's sarcoma]] | |||
| treatment = [[Antibiotics]], [[Surgical drainage]] | |||
| medication = [[Antibiotics]] such as [[clindamycin]], [[vancomycin]] | |||
| prognosis = Good with treatment | |||
| frequency = Rare | |||
}} | |||
==Incidence== | ==Incidence== | ||
It that accounts for 2.5%–42% of primary bone infections. | It that accounts for 2.5%–42% of primary bone infections. | ||
==Patient characteristics== | ==Patient characteristics== | ||
The patients are younger than 25 years of age. They usually present with joint pain and localized swelling. | The patients are younger than 25 years of age. They usually present with joint pain and localized swelling. | ||
==Signs and symptoms== | ==Signs and symptoms== | ||
Signs and symptoms of systemic disease are frequently absent and usually only have joint pain and swelling. | Signs and symptoms of systemic disease are frequently absent and usually only have joint pain and swelling. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 30: | ||
* Klebsiella (5%) and | * Klebsiella (5%) and | ||
* Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (5%) are causative organisms. | * Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (5%) are causative organisms. | ||
===Culture negative=== | ===Culture negative=== | ||
20% of cultures are negative for these organisms. | 20% of cultures are negative for these organisms. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 35: | ||
==Radiology== | ==Radiology== | ||
* Radiographically, an intramedullary area of central lucency with sclerotic margins is characteristic. | * Radiographically, an intramedullary area of central lucency with sclerotic margins is characteristic. | ||
==Differential diagnosis== | ==Differential diagnosis== | ||
* Differential diagnosis of Brodie abscess includes many forms of benign and malignant bone lesions including but not limited to [[bone cysts]], [[osteoid osteoma]], [[giant cell tumor]], [[chondroblastoma]] and [[Ewing sarcoma]]. | * Differential diagnosis of Brodie abscess includes many forms of benign and malignant bone lesions including but not limited to [[bone cysts]], [[osteoid osteoma]], [[giant cell tumor]], [[chondroblastoma]] and [[Ewing sarcoma]]. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
[[X-rays]], [[CT scan]], [[MRI]], [[blood culture]]s etc. | [[X-rays]], [[CT scan]], [[MRI]], [[blood culture]]s etc. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
* A course of systemic antibiotics, surgical [[ | * A course of systemic antibiotics, surgical [[débridement]]. | ||
* Sometimes bone grafting maybe required a large cavity requires stabilization. | * Sometimes bone grafting maybe required a large cavity requires stabilization. | ||
{{Osteochondropathy}} | {{Osteochondropathy}} | ||
[[Category:Bacterial diseases]] | [[Category:Bacterial diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Osteopathies]] | [[Category:Osteopathies]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:18, 5 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Brodie abscess | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Subacute osteomyelitis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Localized bone pain, swelling, tenderness |
| Complications | Chronic osteomyelitis, bone destruction |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Persistent if untreated |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Staphylococcus aureus infection |
| Risks | Trauma, previous infection, immunocompromised state |
| Diagnosis | MRI, X-ray, Bone scan |
| Differential diagnosis | Bone tumor, Osteoid osteoma, Ewing's sarcoma |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, Surgical drainage |
| Medication | Antibiotics such as clindamycin, vancomycin |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Incidence[edit]
It that accounts for 2.5%–42% of primary bone infections.
Patient characteristics[edit]
The patients are younger than 25 years of age. They usually present with joint pain and localized swelling.
Signs and symptoms[edit]
Signs and symptoms of systemic disease are frequently absent and usually only have joint pain and swelling.

Cause[edit]
- Staphylococcus aureus (30%–60%)
- Pseudomonas (5%)
- Klebsiella (5%) and
- Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (5%) are causative organisms.
Culture negative[edit]
20% of cultures are negative for these organisms.

Radiology[edit]
- Radiographically, an intramedullary area of central lucency with sclerotic margins is characteristic.
Differential diagnosis[edit]
- Differential diagnosis of Brodie abscess includes many forms of benign and malignant bone lesions including but not limited to bone cysts, osteoid osteoma, giant cell tumor, chondroblastoma and Ewing sarcoma.
Diagnosis[edit]
X-rays, CT scan, MRI, blood cultures etc.
Treatment[edit]
- A course of systemic antibiotics, surgical débridement.
- Sometimes bone grafting maybe required a large cavity requires stabilization.
| Bone and joint disease | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|