Indinavir: Difference between revisions
Created page with " {{intro}} Indinavir is an antiretroviral protease inhibitor used in the therapy and prevention of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and the acquired immunodefi..." |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
{{antiviral agents}} | {{antiviral agents}} | ||
{{coststubd}} | {{coststubd}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Indinavir_structure.svg|Chemical structure of Indinavir | |||
File:Indinavir_ball-and-stick.png|Ball-and-stick model of Indinavir | |||
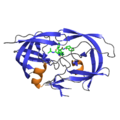
File:2avo_Indinavir.png|Indinavir bound to HIV protease (PDB: 2AVO) | |||
File:HIV_protease-indinavir_complex.jpg|HIV protease complexed with Indinavir | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:59, 18 February 2025
[edit]
Indinavir is an antiretroviral protease inhibitor used in the therapy and prevention of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
[edit]
Indinavir can cause transient and usually asymptomatic elevations in serum aminotransferase levels and mild elevations in indirect bilirubin concentration. Indinavir is a rare cause of clinically apparent, acute liver injury. In HBV or HCV coinfected patients, antiretroviral therapy with indinavir may result in an exacerbation of the underlying chronic hepatitis B or C.
[edit]
Indinavir (in din' a vir) is an antiretroviral protease inhibitor that acts by binding to the catalytic site of the HIV protease, thereby preventing the cleavage of viral polyprotein precursors into mature, functional proteins that are necessary for viral replication.
[edit]
Indinavir was approved for use in the United States in 1996 and continues to be commonly used in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV infection. Indinavir is available under the brand name Crixivan in capsules of 100, 200 and 400 mg. Indinavir is typically used in combination with a low dose of ritonavir, which improves its pharmacokinetics.
[edit]
The recommended dosage of indinavir is 800 mg orally every 8 hours with or without ritonavir (usually 100 to 200 mg twice daily).
[edit]
Side effects can include gastrointestinal upset, nausea, diarrhea, back pain, fatigue and, with long term use, hyperlipidemia and lipodystrophy.
Antiviral agents[edit]
Drugs for HIV Infection, in the Subclass Antiretroviral Agents
- Fusion Inhibitors (HIV)
- Integrase Inhibitors (HIV)
- Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (HIV)
- Interferon Based Therapies
HCV NS5A Inhibitors
HCV NS5B (Polymerase) Inhibitors
- Asunaprevir, Boceprevir, Glecaprevir, Grazoprevir, Paritaprevir, Simeprevir, Telaprevir, Voxilaprevir
Combination Therapies
Drugs for Herpes Virus Infections (HSV, CMV, others)
Drugs for Influenza
-
Chemical structure of Indinavir
-
Ball-and-stick model of Indinavir
-
Indinavir bound to HIV protease (PDB: 2AVO)
-
HIV protease complexed with Indinavir