Vitreous body: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{Eye anatomy}} | {{Eye anatomy}} | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Schematic_diagram_of_the_human_eye_en.svg|Schematic diagram of the human eye | |||
File:Three_Main_Layers_of_the_Eye.png|Three main layers of the eye | |||
File:Three_Internal_chambers_of_the_Eye.svg|Three internal chambers of the eye | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:08, 18 February 2025
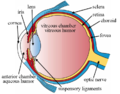
Vitreous Body
The Vitreous Body is a clear, jelly-like substance that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eye. It makes up approximately two-thirds of the eye's volume, giving it a round shape. The vitreous body is composed mostly of water, but also contains proteins and hyaluronic acid.
Structure[edit]
The vitreous body is a clear, gel-like substance that fills the space between the lens and the retina. It is composed of about 99% water, with the remaining 1% consisting of collagen, hyaluronic acid, inorganic salts, sugars, and a network of collagen type II fibers. The vitreous body is not connected to the blood vessels and does not contain any cells, except for some scattered phagocytes which are likely to be remnants from an earlier developmental stage.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the vitreous body is to provide structural support to the eye. It helps to maintain the shape of the eye and keep the retina in place. The vitreous body also acts as a shock absorber, protecting the retina from damage caused by sudden movements or impacts.
Clinical significance[edit]
Changes in the vitreous body can lead to a number of eye conditions. For example, the vitreous body can shrink and pull away from the retina, a condition known as posterior vitreous detachment. This can lead to retinal detachment, a serious condition that can cause blindness if not treated promptly. Other conditions related to the vitreous body include vitreous hemorrhage and vitreous floaters.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
| Anatomy of the globe of the human eye | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|