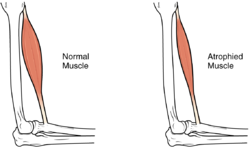
Muscle atrophy

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Muscle atrophy | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Muscle wasting |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Muscle weakness, decreased muscle mass |
| Complications | Disability, reduced mobility |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Disuse, malnutrition, aging, disease |
| Risks | Sedentary lifestyle, immobilization, chronic illness |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Muscle dystrophy, neuropathy |
| Prevention | Exercise, nutrition |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, occupational therapy, nutritional support |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on underlying cause |
| Frequency | Common in elderly and immobilized individuals |
| Deaths | N/A |
Muscle atrophy, often termed "muscle wastage," is a medical condition characterized by the loss of muscle tissue. This condition results in diminished muscle strength, which can significantly affect an individual's quality of life. The extent of muscle wastage can vary, ranging from partial to complete muscle loss.

Causes and Risk Factors[edit]
While the exact cause of muscle atrophy remains undetermined, several factors and conditions have been associated with its onset:
- Aging: Many elderly individuals experience a degree of muscle atrophy as a natural consequence of aging.
- Disuse: Extended periods of inactivity, such as prolonged bed rest or immobilization due to casts, can lead to muscle wastage.
- Medical conditions: Several diseases can lead to muscle atrophy, including cancer, AIDS, congestive heart failure, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, renal failure, Dejerine Sottas syndrome, cachexia, liver failure, and starvation.
- Cellular Changes: The degeneration of "satellite cells," responsible for regenerating skeletal muscle fibers, may play a role. Additionally, a decrease in the sensitivity or availability of growth factors vital for muscle mass and satellite cell survival might be implicated.
- Protein Imbalance: In muscle atrophy, the equilibrium between protein synthesis and degradation shifts. Protein synthesis pathways are down-regulated, whereas protein breakdown pathways, such as the ATP-dependent ubiquitin/proteasome pathway, become activated.
Clinical Implications[edit]
Muscular atrophy poses significant challenges to affected individuals:
- Loss of Functionality: As muscles weaken, the range of activities an individual can undertake is restricted.
- Increased Accident Risk: Weakened muscles make individuals prone to accidents when attempting certain tasks.
- Falls: The risk of falls is notably heightened among individuals with conditions like IBM (inclusion body myositis) in the context of muscle atrophy.
Treatment Approaches[edit]
Several treatment methods have demonstrated efficacy in addressing muscle atrophy:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can enhance muscle mass, countering atrophy. Exercise specifically downregulates the pathways responsible for muscle hypertrophy.
- Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): FES has been beneficial in stimulating muscles, especially in rehabilitating paraplegic patients.
- Amino acid therapy: Certain muscle-building amino acids, like branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs - leucine, isoleucine, and valine), as well as lysine, are essential for regenerating damaged or atrophied muscle tissue.
Summary[edit]
Muscle atrophy, while often associated with aging, can be triggered by various factors, from prolonged inactivity to specific medical conditions. Understanding its causes, implications, and potential treatments is essential for medical professionals, ensuring patients receive the best care possible.
|
|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


