Macular degeneration

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Macular degeneration | |
|---|---|
| File:Intermediate age related macular degeneration.jpg | |
| Synonyms | Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Blurred vision, central vision loss |
| Complications | Blindness |
| Onset | Typically after age 50 |
| Duration | Long-term |
| Types | Dry macular degeneration, Wet macular degeneration |
| Causes | Genetics, smoking, diet, high blood pressure |
| Risks | Age, family history, smoking, obesity |
| Diagnosis | Eye examination, optical coherence tomography, fluorescein angiography |
| Differential diagnosis | Diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, glaucoma |
| Prevention | Healthy diet, smoking cessation, regular exercise |
| Treatment | Anti-VEGF therapy, laser coagulation, vitamin supplements |
| Medication | Ranibizumab, Aflibercept, Bevacizumab |
| Prognosis | Variable, can lead to vision loss |
| Frequency | Affects millions worldwide, more common in Caucasians |
| Deaths | Rarely directly causes death |
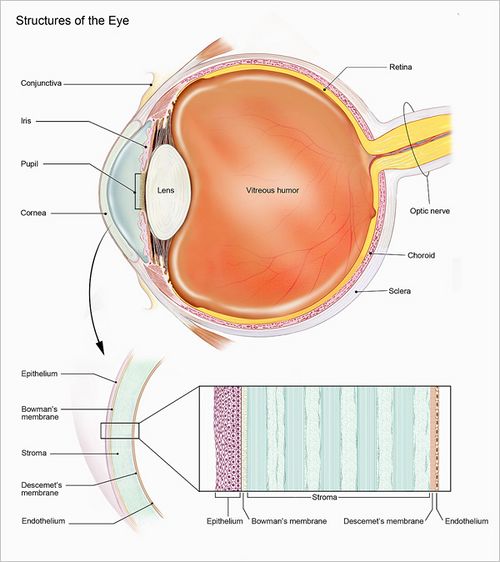
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is a medical condition that leads to blurred or loss of vision in the center field of view. This condition usually affects older adults and results from damage to the macula, a small area near the center of the retina.
Classification[edit]
AMD is typically classified into two types: dry (atrophic) and wet (neovascular or exudative). The dry form is more common and is characterized by small yellow deposits, known as drusen, in the macula. Wet AMD, on the other hand, is less common but more serious, and it is characterized by the growth of abnormal blood vessels under the retina, which leak fluid and blood.
Dry AMD[edit]
Dry AMD is the initial phase and affects 85-90% of individuals with AMD. Its cause is due to aging and thinning of macular tissues, depositing of pigment in the macula or a combination of the two.
Wet AMD[edit]
Wet AMD is more severe and affects 10-15% of individuals with AMD. Despite its rarity, it accounts for a significant proportion of all cases of severe vision loss in AMD.
Signs and Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of AMD include difficulty recognizing faces, distortion of straight lines, and a dark or empty area appearing in the center of vision.
Risk Factors[edit]
Several factors may increase the risk of developing AMD, including age, genetics, race, smoking, and diet.
Pathophysiology[edit]
AMD is believed to be a complex disorder that is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. The condition is characterized by the presence of drusen and changes in the pigment of the retina.
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis of AMD can often be made based on the patient's symptoms and findings during an eye examination. Other tests, such as fluorescein angiography and optical coherence tomography, can also be useful in confirming the diagnosis and determining the severity of the disease.
Management[edit]
While there is currently no cure for AMD, treatments can help slow its progression and improve quality of life. These treatments may include anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) drugs, laser therapy, and photodynamic therapy. For those with advanced disease, low-vision aids, such as special eyeglasses or electronic systems, can help to improve vision.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with AMD varies widely. Some people may retain good vision for a long time, while others may experience a rapid decline in vision.
Prevention[edit]
While AMD cannot be completely prevented, certain lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, a diet high in fruits and vegetables, and avoiding smoking, can reduce the risk.
Epidemiology[edit]
AMD is a leading cause of vision loss in the elderly, affecting an estimated 8.7% of the worldwide population.
Images[edit]
-
Macular degeneration
-
Macular degeneration and other sense organ diseases world map
-
Retinal pigment epithelium
References[edit]
- Mayo Clinic - Macular DegenerationOverview of Age-Related Macular Degeneration</ref>
- National Eye Institute - Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Topics in Ophthalmology[edit]
- Macular degeneration (AMD)
- Amblyopia
- Anophthalmia and * Microphthalmia
- Astigmatism
- Blepharitis
- Cataract
- Color blindness
- Cornea and Corneal disease
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Dry eye
- Floaters
- Glaucoma
- Hyperopia
- Intracranial hypertension
- Low vision
- Macular edema
- Myopia
- Pink Eye or Conjunctivitis
- Presbyopia
- Refractive errors
- Retinal detachment
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Retinoblastoma
- Retinopathy of prematurity
- Uveitis
- Vitreous detachment
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


