Amblyopia

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Amblyopia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Lazy eye |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Ophthalmology |
| Symptoms | Poor vision in one eye |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Early childhood |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Strabismus, refractive error, cataract |
| Risks | Family history, premature birth |
| Diagnosis | Eye examination |
| Differential diagnosis | Refractive error, strabismus |
| Prevention | Early detection and treatment |
| Treatment | Corrective lenses, eye patching, atropine drops |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Good with early treatment |
| Frequency | 1-5% of the population |
| Deaths | N/A |
Amblyopia, commonly referred to as lazy eye, represents the most frequent cause of vision impairment in children. It is a medical condition in which the brain and one eye fail to work together effectively, despite the eye appearing normal. This results in diminished vision in the affected eye as the brain favors the other eye.


Causes of Amblyopia[edit]
Amblyopia is typically brought about by conditions such as:
- Strabismus: A condition where the eyes do not align correctly, with one or both eyes turning inward, outward, upward, or downward.
- Refractive Anisometropia: This is when there's a significant difference in the refractive errors of the two eyes, leading to one eye being more nearsighted (myopia), farsighted, or having more astigmatism than the other.
- Other Eye Conditions: Less frequently, conditions such as cataract (a clouding of the eye's lens) can cause amblyopia.
Diagnosis and Treatment[edit]
Early detection and treatment of amblyopia are crucial for successful outcomes, as the condition typically persists into adulthood if left untreated during childhood. Screening for amblyopia is a routine part of pediatric eye exams. Treatment strategies aim to stimulate the affected eye and encourage the brain to utilize it. This can be achieved by:
- Corrective Eyewear: Glasses or contact lenses may be used to correct refractive errors.
- Patching: Covering the stronger eye with a patch to force the brain to rely on the weaker one.
- Pharmacological Therapy: Atropine eye drops may be used to blur the vision in the stronger eye, encouraging use of the weaker one.
Epidemiology[edit]
Amblyopia affects approximately 2%–3% of the population, making it a prevalent cause of monocular vision impairment among children and adults in their young and middle ages.
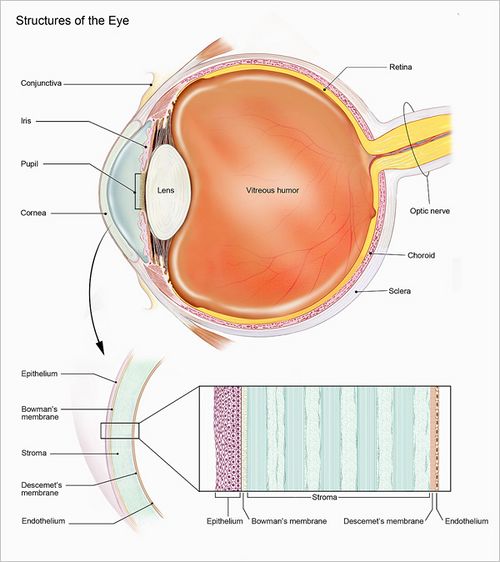
Topics in Ophthalmology[edit]
- Macular degeneration (AMD)
- Amblyopia
- Anophthalmia and * Microphthalmia
- Astigmatism
- Blepharitis
- Cataract
- Color blindness
- Cornea and Corneal disease
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Dry eye
- Floaters
- Glaucoma
- Hyperopia
- Intracranial hypertension
- Low vision
- Macular edema
- Myopia
- Pink Eye or Conjunctivitis
- Presbyopia
- Refractive errors
- Retinal detachment
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Retinoblastoma
- Retinopathy of prematurity
- Uveitis
- Vitreous detachment
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian


