Neuron




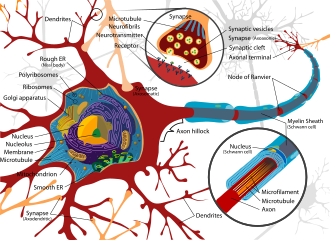

A neuron, traditionally referred to as a neurone in British English, is an electrically excitable cell that constitutes the foundational unit of the nervous system. Its primary function is to relay information across the body using electrical and chemical processes. These cells are intricate in design, with complex mechanisms allowing them to communicate with other cells through unique structures named synapses.
Overview[edit]
The significance of neurons is evident in almost all animals, with the notable exception of sponges and placozoans. Interestingly, while animals possess these intricate cells, other multicellular organisms, like plants, do not have neurons. A collection of interconnected neurons forms what is commonly referred to as a neural circuit.
Anatomy and Histology[edit]
The neuron's structure consists of several vital components:
- Cell Body (Soma): This is the central part of the neuron, typically compact in nature.
- Dendrites: Resembling tree branches, these protrude from the soma and can spread out extensively. They play a crucial role in receiving signals from other neurons.
- Axon: Extending from a region of the soma known as the axon hillock, this long, filamentous structure can span distances as vast as a meter in humans. The axon is instrumental in transmitting signals to other cells.
- Axon terminals: These are situated at the furthest tips of the axon branches, acting as transmission points where signals are sent across the synapse to another cell.
Though most neurons possess both dendrites and an axon, some may lack one or the other. The term neurite is employed to describe either dendrites or axons, especially in cases where differentiation is challenging.
Membrane[edit]
The neuron membrane is responsible for maintaining voltage gradients, rendering the neuron electrically excitable. This excitability paves the way for the neuron to produce a rapid, all-or-nothing electrochemical pulse termed an action potential.
Histology and Internal Structure[edit]
Neurons have a specialized internal structure, allowing them to effectively process and transmit signals. Synapses are critical junctures that facilitate communication between neurons or between a neuron and another type of cell. They can be both chemical and electrical, dictating whether a neuron gets excited or inhibited.
Classification[edit]
Neurons are typically categorized based on function and structure:
Structural Classification[edit]
This categorization is based on the number of protruding structures from the neuron's cell body.
Functional Classification[edit]
Functionally, neurons fall into three main categories:
- Sensory Neurons: These neurons react to external stimuli, such as light, sound, or touch, and relay this information to the brain or spinal cord.
- Motor Neurons: They are involved in receiving signals from the brain or spinal cord, subsequently controlling functions ranging from muscle movements to gland activity.
- Interneurons: These facilitate communication between neurons within the same area of the brain or spinal cord.
Connectivity and Neural Circuits[edit]
A network of interconnected neurons is called a neural circuit. Most neurons receive signals through their dendrites and soma and dispatch signals via their axon. Although the majority of synapses involve signals transitioning from one neuron's axon to another's dendrite, axon-to-axon and dendrite-to-dendrite synapses also exist.
Nervous System: The Grand Network[edit]
The nervous system, comprising both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), is the primary residence of neurons. The CNS encompasses the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS consists of autonomic and somatic systems.
Neurons, along with glial cells, are the main components of the nervous system. In vertebrates, the majority of neurons are housed within the CNS, though some are located in peripheral ganglia. Numerous sensory neurons are also embedded in organs like the retina and cochlea. Axons in the PNS group together to form nerves, while those in the CNS cluster into tracts.
|
|
|
| Tumours of the nervous system | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Note: Not all brain tumors are of nervous tissue, and not all nervous tissue tumors are in the brain (see brain metastasis).
|
| Nervous tissue | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
![]() Error creating thumbnail: Error creating thumbnail:
Error creating thumbnail: Error creating thumbnail:
![]()
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian

