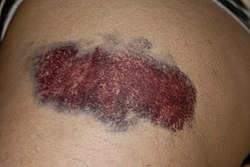
Bruise

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Bruise | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Contusion, ecchymosis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Skin discoloration, pain, swelling |
| Complications | Hematoma, compartment syndrome |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Days to weeks |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma, blunt force |
| Risks | Coagulopathy, anticoagulant use |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, medical history |
| Differential diagnosis | Fracture, hematoma, deep vein thrombosis |
| Prevention | Protective gear, fall prevention |
| Treatment | RICE, pain management |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good |
| Frequency | Very common |
| Deaths | N/A |




Bruise (also known as a contusion) is a common type of soft tissue injury resulting from blunt trauma. It occurs when small blood vessels (capillaries) are damaged, leading to blood leakage into the surrounding tissues. Bruises can appear on the skin, muscles, bones, or internal organs, with varying degrees of severity.
Pathophysiology[edit]
A bruise occurs due to:
- Blunt trauma causing damage to the capillaries beneath the skin or tissue.
- Extravasation of blood from damaged capillaries into interstitial spaces.
- Inflammatory response involving immune cells that clear the leaked blood over time.
Causes[edit]
Bruises can result from various factors, including:
- Trauma – Accidental falls, sports injuries, motor vehicle accidents.
- Medical conditions – Hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, leukemia, and thrombocytopenia.
- Medications – Blood thinners such as aspirin, warfarin, heparin, and corticosteroids.
- Nutritional deficiencies – Vitamin C (scurvy) and Vitamin K deficiency can lead to increased bruising.
- Age-related factors – Older adults have thinner skin and more fragile capillaries, leading to easier bruising.
Clinical Presentation[edit]
Bruises typically progress through the following color changes due to hemoglobin breakdown:
- Red/Purple (0-2 days) – Fresh extravasated blood rich in oxygenated hemoglobin.
- Blue/Purple (2-5 days) – Breakdown of hemoglobin to deoxygenated forms.
- Green (5-7 days) – Conversion of hemoglobin to biliverdin.
- Yellow/Brown (7-14 days) – Final breakdown to bilirubin, before reabsorption.
Bruises may also present with:
- Swelling – Due to localized inflammation.
- Tenderness – Pain around the affected area.
- Skin discoloration – Depending on depth and severity.
- Limited movement – If the bruise affects muscles or joints.
Types of Bruises[edit]
Bruises are classified based on location and severity:
- Subcutaneous bruise – Located under the skin, often superficial.
- Intramuscular bruise – Deeper, affecting muscle tissue.
- Periosteal bruise – Affects the outer layer of bones, causing prolonged pain.
- Hematoma – More severe form with significant blood accumulation, often forming a lump.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on history and physical examination. Additional tests may be required in unexplained or frequent bruising:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) – To evaluate for thrombocytopenia or leukemia.
- Coagulation tests – Prothrombin time (PT), Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT), International Normalized Ratio (INR), and Factor assays to assess clotting function.
- Imaging (Ultrasound or MRI) – In cases of deep tissue or periosteal bruises.
Management[edit]
Most bruises resolve spontaneously. However, management can include:
- Immediate Care (R.I.C.E. protocol):
- Rest – Avoid further trauma.
- Ice – Apply cold compresses (15-20 min every 2-3 hours) to reduce swelling.
- Compression – Use elastic bandages if swelling is present.
- Elevation – Keep the affected area elevated to minimize blood pooling.
- Pain management:
- NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen) – Reduce inflammation and pain.
- Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) – Alternative pain reliever, avoiding anticoagulant effects.
- Topical treatments:
- Arnica gel – Herbal remedy believed to reduce inflammation.
- Vitamin K cream – May help with faster resolution in some cases.
- Medical intervention:
- If an underlying bleeding disorder is suspected, hematologic evaluation is necessary.
- Large hematomas may require needle aspiration or surgical drainage.
Complications[edit]
Although most bruises heal without complications, severe cases can lead to:
- Compartment syndrome – Increased pressure within a muscle compartment causing ischemia.
- Myositis ossificans – Abnormal calcification of muscle after repeated trauma.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) – In rare cases of significant vascular injury.
- Persistent ecchymosis – May indicate an underlying systemic disorder.
Prevention[edit]
Preventive measures include:
- Avoiding trauma – Wearing protective gear in sports and using safety precautions.
- Optimizing nutrition – Ensuring adequate intake of Vitamin C, Vitamin K, and Iron.
- Managing medications – Monitoring anticoagulant use under medical supervision.
- Regular medical check-ups – Especially for individuals with frequent unexplained bruising.
When to Seek Medical Attention[edit]
Seek medical care if:
- Bruising occurs spontaneously without trauma.
- Excessive or frequent bruising is noticed.
- Bruises do not heal within 2 weeks.
- Pain and swelling worsen over time.
- Signs of systemic bleeding (nosebleeds, gum bleeding, blood in urine/stool) appear.
Related Conditions[edit]
- Ecchymosis – Larger bruises covering a broader area.
- Petechiae – Small pinpoint hemorrhages in the skin.
- Hematoma – Localized blood accumulation forming a palpable lump.
- Purpura – Widespread bruising associated with bleeding disorders.
- Hemophilia – Genetic clotting disorder leading to excessive bruising.
| General wounds and injuries | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Disorders of bleeding and clotting | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian