Jaundice: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[ | {{SI}} | ||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Jaundice | |||
Jaundice | | image = [[File:Old_jaundice.jpg|250px]] | ||
| caption = A person with jaundice | |||
| field = [[Hepatology]] | |||
| synonyms = Icterus | |||
| symptoms = [[Yellowing of the skin]], [[yellowing of the eyes]], [[dark urine]], [[pale stools]], [[itching]] | |||
| complications = [[Kernicterus]], [[liver failure]] | |||
== | | onset = Can occur at any age | ||
| duration = Varies depending on cause | |||
* | | causes = [[Liver disease]], [[bile duct obstruction]], [[hemolysis]] | ||
* | | risks = [[Alcohol use disorder]], [[hepatitis]], [[gallstones]] | ||
* | | diagnosis = [[Blood test]], [[liver function test]], [[imaging studies]] | ||
| differential = [[Carotenemia]], [[hepatitis]], [[Gilbert's syndrome]] | |||
| treatment = Depends on the underlying cause (e.g., [[medication]], [[surgery]], [[lifestyle changes]]) | |||
| medication = [[Cholestyramine]], [[ursodeoxycholic acid]] | |||
==Symptoms== | | frequency = Common | ||
| deaths = Varies depending on underlying cause | |||
The symptoms of jaundice | }} | ||
* | [[File:Jaundice phototherapy.jpg|left|thumb|220px|right|New born baby being treated for jaundice]] | ||
* | [[File:Old_jaundice.jpg|Old jaundice|left|thumb]] | ||
* | [[File:Jaundice.jpg|Jaundice|thumb]] | ||
* | [[File:Heme_Breakdown.png|Heme Breakdown|thumb]] | ||
* | [[File:Jaundice-types.png|Jaundice types|left|thumb]] | ||
* | [[File:Bilirubin_pigment_in_cholestatic_liver_40X.jpg|Bilirubin pigment in cholestatic liver 40X|left|thumb]] | ||
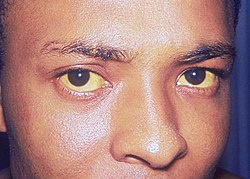
* | '''Jaundice''' (also called '''icterus''') is a medical condition characterized by the yellowing of the [[skin]], the [[sclera]] (whites of the eyes), and sometimes other tissues due to elevated levels of [[bilirubin]] in the blood. This yellow discoloration occurs when the [[liver]] is unable to effectively process and remove bilirubin, a byproduct of the breakdown of [[red blood cells]]. Jaundice is commonly associated with liver diseases but can also result from infections, bile duct obstruction, or increased red blood cell destruction. | ||
* | [[File:Jaundice eye.jpg|left|thumb|250px|Yellowing of the eyes caused by jaundice from hepatitis.]] | ||
== Causes of Jaundice == | |||
* | Jaundice is caused by an imbalance in the production, processing, or elimination of bilirubin. Common causes include: | ||
=== Liver Disorders === | |||
* '''Hepatitis''' – Viral or autoimmune inflammation of the liver. | |||
* '''Cirrhosis''' – Liver scarring due to long-term damage (e.g., from alcohol, fatty liver disease, or infections). | |||
* '''Liver cancer''' – Malignancies affecting liver function. | |||
* '''Liver failure''' – Severe liver dysfunction preventing bilirubin processing. | |||
=== Increased Red Blood Cell Breakdown === | |||
* '''Hemolytic anemia''' – Rapid breakdown of red blood cells due to inherited disorders, infections, or immune reactions. | |||
* '''Sickle cell disease''' – A genetic disorder that causes red blood cells to break down prematurely. | |||
* '''Malaria''' – A parasitic infection that destroys red blood cells. | |||
=== Bile Duct Obstruction === | |||
* '''Gallstones''' – Hardened deposits blocking the bile ducts. | |||
* '''Pancreatic tumors''' – Growths that obstruct bile flow. | |||
* '''Biliary atresia''' – A congenital defect affecting bile duct formation. | |||
=== Neonatal Jaundice === | |||
Newborns frequently experience jaundice due to immature liver function. This type of jaundice often resolves on its own or with phototherapy. | |||
== Symptoms == | |||
The signs and symptoms of jaundice vary based on the underlying cause but may include: | |||
=== Primary Symptoms === | |||
* Yellow discoloration of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes | |||
* Dark-colored urine | |||
* Pale or clay-colored stools | |||
=== Additional Symptoms === | |||
* Fatigue – Weakness and lack of energy | |||
* Fever – If caused by infection | |||
* Loss of appetite – Often seen in liver diseases | |||
* Nausea & vomiting – Common in hepatobiliary disorders | |||
* Abdominal pain – Particularly with gallstones or liver inflammation | |||
* Itching (pruritus) – Seen in obstructive jaundice due to bile acid buildup | |||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Doctors diagnose jaundice through a combination of clinical examination and laboratory tests: | |||
=== Physical Examination === | |||
* | * Checking for yellowing of the skin and eyes. | ||
* Examining the abdomen for liver or spleen enlargement. | |||
== Types of Jaundice == | |||
* Liver function tests to | {| class="wikitable" style="width:100%; text-align:center;" | ||
! Type | |||
! Cause | |||
! Features | |||
|- | |||
| '''Hemolytic Jaundice''' | |||
| Excessive destruction of red blood cells leading to increased bilirubin production. | |||
| Associated with anemia, dark urine, and pale stools. | |||
|- | |||
| '''Hepatocellular Jaundice''' | |||
| Liver diseases that impair bilirubin metabolism (e.g., hepatitis, cirrhosis). | |||
| Liver dysfunction symptoms, such as fatigue and abdominal pain. | |||
|- | |||
| '''Obstructive Jaundice''' | |||
| Blocked bile ducts preventing bilirubin excretion. | |||
| Dark urine, pale stools, and intense itching. | |||
|} | |||
=== Laboratory Tests === | |||
* '''Bilirubin test''' – Measures levels of direct and indirect bilirubin. | |||
* '''Liver function tests (LFTs)''' – Assess liver enzyme levels. | |||
* '''Complete blood count (CBC)''' – Detects infections or anemia. | |||
* '''Hepatitis panel''' – Identifies viral liver infections. | |||
* '''Coagulation tests''' – Checks for clotting issues linked to liver disease. | |||
=== Imaging Tests === | |||
* '''Ultrasound''' – Evaluates liver and bile ducts. | |||
* '''CT scan or MRI''' – Detects tumors or obstructions. | |||
* '''Liver biopsy''' – Identifies liver damage or disease. | |||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
The treatment of jaundice depends on the underlying cause. Some common approaches include: | |||
=== Medications === | |||
* ''' | * '''Antiviral drugs''' – For hepatitis B or C. | ||
* ''' | * '''Steroids''' – For autoimmune liver diseases. | ||
* '''Phototherapy''' | * '''Antibiotics''' – If jaundice is due to bacterial infections. | ||
* ''' | === Surgery or Procedures === | ||
* '''Gallstone removal''' – If bile duct obstruction is present. | |||
== ''' | * '''Liver transplant''' – In severe cases of liver failure. | ||
* '''Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)''' – Removes bile duct obstructions. | |||
=== Phototherapy for Newborns === | |||
* '''Blue light therapy''' – Helps break down excess bilirubin in neonatal jaundice. | |||
=== Lifestyle and Dietary Management === | |||
* '''Avoid alcohol''' – To prevent liver damage. | |||
* '''Maintain hydration''' – Helps flush out toxins. | |||
* '''Eat a balanced diet''' – Supports liver health. | |||
== Prevention == | |||
Preventative measures vary depending on the type of jaundice: | |||
* '''Vaccination''' – Against hepatitis A and B | |||
* '''Avoid excessive alcohol consumption''' – To protect liver function | |||
* '''Safe food and water practices''' – Prevents infections like hepatitis | |||
* '''Regular medical check-ups''' – Early detection of liver diseases | |||
* '''Manage underlying conditions''' – Such as gallstones or anemia | |||
== Jaundice Gallery == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Obstructivebiliarydilation.png|Obstructive biliary dilation | |||
[File:Obstructivebiliarydilation2.png|Obstructive biliary dilation (ultrasound) | |||
File:Kayser-Fleischer_ring.jpg|Kayser-Fleischer ring, associated with liver disease | |||
</gallery> | |||
== See Also == | |||
* [[Hepatitis]] | * [[Hepatitis]] | ||
* [[Cirrhosis]] | * [[Cirrhosis]] | ||
* [[Gallstones]] | * [[Gallstones]] | ||
* [[Hemolytic anemia]] | * [[Hemolytic anemia]] | ||
* [[Liver function tests]] | |||
{{Medical condition classification and resources | |||
| ICD10 = {{ICD10|R|17||r|10}} | |||
| ICD9 = {{ICD9|782.4}} | |||
| OMIM = | |||
| MedlinePlus = 003243 | |||
| eMedicineSubj = | |||
| eMedicineTopic = | |||
| DiseasesDB = 7038 | |||
| MeshID = D007565 | |||
}} | |||
{{Digestive system and abdomen symptoms and signs}} | |||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[Category:Symptoms and signs: Digestive system and abdomen]] | |||
[[Category:Medical conditions]] | [[Category:Medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Gastroenterology]] | [[Category:Gastroenterology]] | ||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | [[Category:Hepatology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:13, 9 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Jaundice | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Icterus |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Yellowing of the skin, yellowing of the eyes, dark urine, pale stools, itching |
| Complications | Kernicterus, liver failure |
| Onset | Can occur at any age |
| Duration | Varies depending on cause |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Liver disease, bile duct obstruction, hemolysis |
| Risks | Alcohol use disorder, hepatitis, gallstones |
| Diagnosis | Blood test, liver function test, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Carotenemia, hepatitis, Gilbert's syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Depends on the underlying cause (e.g., medication, surgery, lifestyle changes) |
| Medication | Cholestyramine, ursodeoxycholic acid |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | Varies depending on underlying cause |






Jaundice (also called icterus) is a medical condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin, the sclera (whites of the eyes), and sometimes other tissues due to elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood. This yellow discoloration occurs when the liver is unable to effectively process and remove bilirubin, a byproduct of the breakdown of red blood cells. Jaundice is commonly associated with liver diseases but can also result from infections, bile duct obstruction, or increased red blood cell destruction.
Causes of Jaundice[edit]
Jaundice is caused by an imbalance in the production, processing, or elimination of bilirubin. Common causes include:
Liver Disorders[edit]
- Hepatitis – Viral or autoimmune inflammation of the liver.
- Cirrhosis – Liver scarring due to long-term damage (e.g., from alcohol, fatty liver disease, or infections).
- Liver cancer – Malignancies affecting liver function.
- Liver failure – Severe liver dysfunction preventing bilirubin processing.
Increased Red Blood Cell Breakdown[edit]
- Hemolytic anemia – Rapid breakdown of red blood cells due to inherited disorders, infections, or immune reactions.
- Sickle cell disease – A genetic disorder that causes red blood cells to break down prematurely.
- Malaria – A parasitic infection that destroys red blood cells.
Bile Duct Obstruction[edit]
- Gallstones – Hardened deposits blocking the bile ducts.
- Pancreatic tumors – Growths that obstruct bile flow.
- Biliary atresia – A congenital defect affecting bile duct formation.
Neonatal Jaundice[edit]
Newborns frequently experience jaundice due to immature liver function. This type of jaundice often resolves on its own or with phototherapy.
Symptoms[edit]
The signs and symptoms of jaundice vary based on the underlying cause but may include:
Primary Symptoms[edit]
- Yellow discoloration of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes
- Dark-colored urine
- Pale or clay-colored stools
Additional Symptoms[edit]
- Fatigue – Weakness and lack of energy
- Fever – If caused by infection
- Loss of appetite – Often seen in liver diseases
- Nausea & vomiting – Common in hepatobiliary disorders
- Abdominal pain – Particularly with gallstones or liver inflammation
- Itching (pruritus) – Seen in obstructive jaundice due to bile acid buildup
Diagnosis[edit]
Doctors diagnose jaundice through a combination of clinical examination and laboratory tests:
Physical Examination[edit]
- Checking for yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Examining the abdomen for liver or spleen enlargement.
Types of Jaundice[edit]
| Type | Cause | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Hemolytic Jaundice | Excessive destruction of red blood cells leading to increased bilirubin production. | Associated with anemia, dark urine, and pale stools. |
| Hepatocellular Jaundice | Liver diseases that impair bilirubin metabolism (e.g., hepatitis, cirrhosis). | Liver dysfunction symptoms, such as fatigue and abdominal pain. |
| Obstructive Jaundice | Blocked bile ducts preventing bilirubin excretion. | Dark urine, pale stools, and intense itching. |
Laboratory Tests[edit]
- Bilirubin test – Measures levels of direct and indirect bilirubin.
- Liver function tests (LFTs) – Assess liver enzyme levels.
- Complete blood count (CBC) – Detects infections or anemia.
- Hepatitis panel – Identifies viral liver infections.
- Coagulation tests – Checks for clotting issues linked to liver disease.
Imaging Tests[edit]
- Ultrasound – Evaluates liver and bile ducts.
- CT scan or MRI – Detects tumors or obstructions.
- Liver biopsy – Identifies liver damage or disease.
Treatment[edit]
The treatment of jaundice depends on the underlying cause. Some common approaches include:
Medications[edit]
- Antiviral drugs – For hepatitis B or C.
- Steroids – For autoimmune liver diseases.
- Antibiotics – If jaundice is due to bacterial infections.
Surgery or Procedures[edit]
- Gallstone removal – If bile duct obstruction is present.
- Liver transplant – In severe cases of liver failure.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) – Removes bile duct obstructions.
Phototherapy for Newborns[edit]
- Blue light therapy – Helps break down excess bilirubin in neonatal jaundice.
Lifestyle and Dietary Management[edit]
- Avoid alcohol – To prevent liver damage.
- Maintain hydration – Helps flush out toxins.
- Eat a balanced diet – Supports liver health.
Prevention[edit]
Preventative measures vary depending on the type of jaundice:
- Vaccination – Against hepatitis A and B
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption – To protect liver function
- Safe food and water practices – Prevents infections like hepatitis
- Regular medical check-ups – Early detection of liver diseases
- Manage underlying conditions – Such as gallstones or anemia
Jaundice Gallery[edit]
-
Obstructive biliary dilation
-
Kayser-Fleischer ring, associated with liver disease
See Also[edit]
| Signs and symptoms relating to the human digestive system or abdomen | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|




