Vertically transmitted infection

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Vertically transmitted infection | |
|---|---|
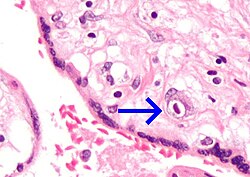
| |
| Synonyms | Mother-to-child transmission |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Congenital anomalies, premature birth, low birth weight, neonatal infection |
| Complications | Developmental delay, neurological disorders, hearing loss |
| Onset | Prenatal, perinatal, postnatal |
| Duration | Varies depending on the infection |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi |
| Risks | Maternal infection, poor prenatal care, HIV, syphilis, rubella |
| Diagnosis | Prenatal screening, ultrasound, amniocentesis, blood tests |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | Vaccination, antiviral therapy, antibiotics, safe childbirth practices |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, antiviral drugs, supportive care |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on the specific infection and timing of intervention |
| Frequency | Common in areas with high rates of infectious diseases |
| Deaths | N/A |
Vertically transmitted infection refers to an infection that is passed from the mother to her baby during the period immediately before and after birth. The transmission can occur across the placenta, in the breast milk, or through direct contact during or after birth. Understanding and managing vertically transmitted infections is a critical aspect of neonatology and obstetrics.
Mechanisms of Transmission[edit]
Vertically transmitted infections can be passed through several mechanisms:
- Transplacental transmission: The pathogen crosses the placenta during pregnancy, infecting the fetus. This can occur at any stage of pregnancy but is more common during the first trimester when the placental barrier is not fully developed.
- Peripartum transmission: Infection occurs during the process of childbirth, either through exposure to maternal blood and bodily fluids or through the passage of the baby through the birth canal.
- Postnatal transmission: This occurs when the infant is exposed to infectious agents in the mother's breast milk or through direct contact after birth.
Common Vertically Transmitted Infections[edit]
Several infections are commonly transmitted from mother to child:
- HIV/AIDS: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) can be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy, delivery, or breastfeeding.
- Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C: These liver infections can be passed from mother to baby, particularly during birth.
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): HSV can be transmitted to the infant if the mother has an active genital herpes infection during delivery.
- Syphilis: This bacterial infection can cross the placenta and infect the fetus during pregnancy.
- Toxoplasmosis: Caused by a parasite, toxoplasmosis can be transmitted if the mother becomes infected during pregnancy.
- Rubella (German measles): If a woman contracts rubella during pregnancy, it can cause serious birth defects or miscarriage.
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV): A common virus that can be passed from a pregnant woman to her fetus, potentially leading to birth defects or developmental delays.
Prevention and Treatment[edit]
Prevention and treatment strategies for vertically transmitted infections include:
- Screening and Vaccination: Pregnant women are often screened for certain infections, such as HIV, hepatitis B, and syphilis, early in their pregnancy. Vaccinations are also recommended for some infections, like hepatitis B and rubella, before or during pregnancy.
- Antiviral or Antibiotic Treatment: In some cases, administering antiviral or antibiotic medications during pregnancy can reduce the risk of transmitting the infection to the baby.
- Cesarean Delivery: For women with active genital herpes or HIV, a cesarean delivery can reduce the risk of transmitting the infection during birth.
- Avoiding Breastfeeding: In cases where the mother has HIV or HTLV-1, avoiding breastfeeding can prevent postnatal transmission of the virus to the infant.
Summary[edit]
Vertically transmitted infections represent a significant risk to neonatal health, but with proper screening, preventive measures, and treatment, the risk of transmission can be greatly reduced. Ongoing research and public health efforts continue to focus on reducing the incidence of these infections and improving outcomes for affected infants.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
