Toxoplasmosis: Difference between revisions
m Text replacement - "Category:Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate" to "" |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
[[File:Toxoplasma gondii | {{Infobox medical condition | ||
| name = Toxoplasmosis | |||
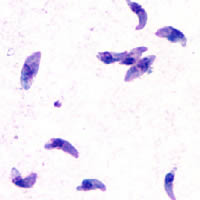
| image = [[File:Toxoplasma_gondii_tachy.jpg|alt=Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites]] | |||
| caption = ''[[Toxoplasma gondii]]'' tachyzoites | |||
| field = [[Infectious disease]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Flu-like symptoms]], [[lymphadenopathy]], [[muscle aches]] | |||
| complications = [[Congenital toxoplasmosis]], [[encephalitis]], [[chorioretinitis]] | |||
| onset = 1-3 weeks after exposure | |||
| duration = Weeks to months | |||
| causes = ''[[Toxoplasma gondii]]'' | |||
| risks = [[Pregnancy]], [[immunocompromised]] individuals | |||
| diagnosis = [[Serology]], [[PCR]], [[biopsy]] | |||
| differential = [[Mononucleosis]], [[cytomegalovirus infection]], [[lymphoma]] | |||
| prevention = [[Proper food handling]], [[avoiding cat feces]] | |||
| treatment = [[Pyrimethamine]], [[sulfadiazine]], [[folinic acid]] | |||
| prognosis = Generally good in healthy individuals | |||
| frequency = Common | |||
}} | |||
'''Toxoplasmosis''' is a common [[protozoan]] infection caused by the parasite ''Toxoplasma gondii''<ref>https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/toxoplasmosis/index.html</ref>. It is usually contracted through ingestion of contaminated food, water, or soil, or through contact with infected cat feces<ref>https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/toxoplasmosis</ref>. While the infection is generally mild and asymptomatic in healthy individuals, it can pose a significant risk to a fetus during early pregnancy and to immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS or organ transplant recipients<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3499757/</ref>. | '''Toxoplasmosis''' is a common [[protozoan]] infection caused by the parasite ''Toxoplasma gondii''<ref>https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/toxoplasmosis/index.html</ref>. It is usually contracted through ingestion of contaminated food, water, or soil, or through contact with infected cat feces<ref>https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/toxoplasmosis</ref>. While the infection is generally mild and asymptomatic in healthy individuals, it can pose a significant risk to a fetus during early pregnancy and to immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS or organ transplant recipients<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3499757/</ref>. | ||
[[File:Toxoplasmosis life cycle en.svg|thumb|Toxoplasmosis life cycle en]] | [[File:Toxoplasmosis life cycle en.svg|left|thumb|Toxoplasmosis life cycle en]] | ||
=== Infection and Transmission === | === Infection and Transmission === | ||
''Toxoplasma gondii'' is primarily transmitted through ingestion of oocysts, which are shed in the feces of infected cats<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731335/</ref>. Humans can become infected by: | ''Toxoplasma gondii'' is primarily transmitted through ingestion of oocysts, which are shed in the feces of infected cats<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731335/</ref>. Humans can become infected by: | ||
| Line 9: | Line 26: | ||
* Handling contaminated cat litter or soil and inadvertently ingesting oocysts | * Handling contaminated cat litter or soil and inadvertently ingesting oocysts | ||
* Vertical transmission from mother to fetus during pregnancy | * Vertical transmission from mother to fetus during pregnancy | ||
=== Risk to Fetus and Immunocompromised Individuals === | === Risk to Fetus and Immunocompromised Individuals === | ||
* In healthy individuals, toxoplasmosis is often asymptomatic or presents with mild, flu-like symptoms. However, the infection can be severe in two specific groups: fetuses during early pregnancy and immunocompromised individuals<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731335/</ref>. | * In healthy individuals, toxoplasmosis is often asymptomatic or presents with mild, flu-like symptoms. However, the infection can be severe in two specific groups: fetuses during early pregnancy and immunocompromised individuals<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731335/</ref>. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 36: | ||
[[Category:Protozoan Infections]] | [[Category:Protozoan Infections]] | ||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
Toxoplasmosis is a | Toxoplasmosis is a common protozoan [[infection]] that is usually only dangerous to a [[fetus]] in early [[pregnancy]] or a person who is [[immunocompromised]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
{{Chromalveolate diseases}} | {{Chromalveolate diseases}} | ||
| Line 31: | Line 47: | ||
[[Category:Protozoal diseases]] | [[Category:Protozoal diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Zoonoses]] | [[Category:Zoonoses]] | ||
[[Category:Disorders causing seizures]] | [[Category:Disorders causing seizures]] | ||
[[Category:Biology of bipolar disorder]] | [[Category:Biology of bipolar disorder]] | ||
[[Category:Biology of obsessive–compulsive disorder]] | [[Category:Biology of obsessive–compulsive disorder]] | ||
[[Category:Medical triads]] | [[Category:Medical triads]] | ||
Revision as of 20:21, 8 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Toxoplasmosis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Flu-like symptoms, lymphadenopathy, muscle aches |
| Complications | Congenital toxoplasmosis, encephalitis, chorioretinitis |
| Onset | 1-3 weeks after exposure |
| Duration | Weeks to months |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Toxoplasma gondii |
| Risks | Pregnancy, immunocompromised individuals |
| Diagnosis | Serology, PCR, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus infection, lymphoma |
| Prevention | Proper food handling, avoiding cat feces |
| Treatment | Pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, folinic acid |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Generally good in healthy individuals |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Toxoplasmosis is a common protozoan infection caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii<ref>https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/toxoplasmosis/index.html</ref>. It is usually contracted through ingestion of contaminated food, water, or soil, or through contact with infected cat feces<ref>https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/toxoplasmosis</ref>. While the infection is generally mild and asymptomatic in healthy individuals, it can pose a significant risk to a fetus during early pregnancy and to immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS or organ transplant recipients<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3499757/</ref>.

Infection and Transmission
Toxoplasma gondii is primarily transmitted through ingestion of oocysts, which are shed in the feces of infected cats<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731335/</ref>. Humans can become infected by:
- Consuming undercooked or raw meat containing tissue cysts
- Ingesting oocysts from contaminated food, water, or soil
- Handling contaminated cat litter or soil and inadvertently ingesting oocysts
- Vertical transmission from mother to fetus during pregnancy
Risk to Fetus and Immunocompromised Individuals
- In healthy individuals, toxoplasmosis is often asymptomatic or presents with mild, flu-like symptoms. However, the infection can be severe in two specific groups: fetuses during early pregnancy and immunocompromised individuals<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731335/</ref>.
- Fetus: If a pregnant woman becomes infected with T. gondii for the first time during pregnancy, the parasite can cross the placenta and infect the fetus. This can result in miscarriage, stillbirth, or severe congenital abnormalities, such as hydrocephalus, cerebral calcifications, and chorioretinitis<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731335/</ref>. The risk of congenital toxoplasmosis and its severity depend on the timing of infection during pregnancy; the earlier the infection, the greater the potential harm to the fetus<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731335/</ref>.
- Immunocompromised individuals: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or organ transplant recipients, are at a higher risk of developing severe toxoplasmosis. In these cases, the infection can reactivate and cause life-threatening complications, such as encephalitis, myocarditis, pneumonitis, or disseminated infection<ref>https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2731335/</ref>.
References
<references />
Summary
Toxoplasmosis is a common protozoan infection that is usually only dangerous to a fetus in early pregnancy or a person who is immunocompromised
|
|
|
| Protozoan infection: SAR and Archaeplastida | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
- Infectious Diseases
- Parasitic Diseases
- Protozoan Infections
- Conoidasida
- Cat diseases
- Health issues in pregnancy
- Mind-altering parasites
- Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin
- Poultry diseases
- Protozoal diseases
- Zoonoses
- Disorders causing seizures
- Biology of bipolar disorder
- Biology of obsessive–compulsive disorder
- Medical triads


