Tachypnea: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
= Tachypnea = | {{Infobox medical condition | ||
| name = Tachypnea | |||
== | | image = [[File:Diafragma_ademhaling.gif|250px]] | ||
| caption = Animation showing the diaphragm's role in breathing | |||
| field = [[Pulmonology]] | |||
| synonyms = Rapid breathing | |||
| symptoms = [[Increased respiratory rate]] | |||
| complications = [[Respiratory alkalosis]], [[Hypoxemia]] | |||
| onset = Sudden or gradual | |||
| duration = Variable, depending on underlying cause | |||
| causes = [[Fever]], [[Anxiety]], [[Lung infection]], [[Heart failure]], [[Asthma]], [[Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease|COPD]] | |||
| risks = [[Respiratory disease]], [[Cardiac disease]], [[Infection]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Physical examination]], [[Respiratory rate measurement]] | |||
| differential = [[Hyperventilation]], [[Dyspnea]], [[Bradypnea]] | |||
| treatment = Address underlying cause, [[Oxygen therapy]] | |||
| medication = [[Bronchodilators]], [[Antibiotics]] (if infection is present) | |||
| frequency = Common in [[acute illness]] | |||
| deaths = Rarely directly fatal, but can indicate serious underlying conditions | |||
}} | |||
'''Tachypnea''' refers to an abnormally rapid [[Breathing|breathing]] rate. It is a medical term used to describe accelerated respiration in patients, which can be a symptom of various underlying health conditions. | '''Tachypnea''' refers to an abnormally rapid [[Breathing|breathing]] rate. It is a medical term used to describe accelerated respiration in patients, which can be a symptom of various underlying health conditions. | ||
== Definition and Characteristics == | == Definition and Characteristics == | ||
Tachypnea is characterized by a breathing rate that is faster than the normal range for a person's age and activity level. The condition is particularly noticeable in resting states, where the number of breaths per minute exceeds the typical range. | Tachypnea is characterized by a breathing rate that is faster than the normal range for a person's age and activity level. The condition is particularly noticeable in resting states, where the number of breaths per minute exceeds the typical range. | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
| Line 20: | Line 32: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
==Normal breathing rate== | ==Normal breathing rate== | ||
A normal breathing rate for an adult at rest is 8 to 16 breaths per minute. For an infant, a normal rate is up to 44 breaths per minute. | A normal breathing rate for an adult at rest is 8 to 16 breaths per minute. For an infant, a normal rate is up to 44 breaths per minute. | ||
==Tachypnea breathing rate== | ==Tachypnea breathing rate== | ||
Tachypnea is the term that your health care provider uses to describe your breathing if it is too fast, especially if you have fast, shallow breathing from a lung disease or other medical cause. | Tachypnea is the term that your health care provider uses to describe your breathing if it is too fast, especially if you have fast, shallow breathing from a lung disease or other medical cause. | ||
==Hyperventilation== | ==Hyperventilation== | ||
The term hyperventilation is usually used if you are taking rapid, deep breaths. This can be due to lung disease or because of anxiety or panic. The terms are sometimes used interchangeably. | The term hyperventilation is usually used if you are taking rapid, deep breaths. This can be due to lung disease or because of anxiety or panic. The terms are sometimes used interchangeably. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Shallow, rapid breathing has many possible medical causes, including: | Shallow, rapid breathing has many possible medical causes, including: | ||
* [[Asthma]] | * [[Asthma]] | ||
* Blood clot in an artery in the lung | * Blood clot in an artery in the lung | ||
| Line 44: | Line 50: | ||
* [[Anxiety]] and panic | * [[Anxiety]] and panic | ||
* Other serious lung disease | * Other serious lung disease | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
The diagnosis is made clinically by measuring the breathing rate. However, additional tests, including blood tests, X-ray of the chest, CT scan and MRI might be needed to look for underlying causes. | The diagnosis is made clinically by measuring the breathing rate. However, additional tests, including blood tests, X-ray of the chest, CT scan and MRI might be needed to look for underlying causes. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Treatment of tachypnea depends on the underlying cause. | Treatment of tachypnea depends on the underlying cause. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 60: | ||
* '''[[Fever]]''': Increased body temperature can accelerate breathing. | * '''[[Fever]]''': Increased body temperature can accelerate breathing. | ||
* '''[[Anxiety Disorders|Anxiety]] and [[Panic attack|Panic Attacks]]''': Psychological stress can result in rapid breathing. | * '''[[Anxiety Disorders|Anxiety]] and [[Panic attack|Panic Attacks]]''': Psychological stress can result in rapid breathing. | ||
== Diagnosis and Evaluation == | == Diagnosis and Evaluation == | ||
Diagnosis of tachypnea involves: | Diagnosis of tachypnea involves: | ||
| Line 62: | Line 65: | ||
* Assessing the patient's overall clinical presentation. | * Assessing the patient's overall clinical presentation. | ||
* Conducting tests to determine the underlying cause, such as chest X-rays or blood tests. | * Conducting tests to determine the underlying cause, such as chest X-rays or blood tests. | ||
== Treatment and Management == | == Treatment and Management == | ||
Treatment of tachypnea focuses on addressing the underlying cause. This may involve: | Treatment of tachypnea focuses on addressing the underlying cause. This may involve: | ||
| Line 68: | Line 70: | ||
* Oxygen therapy for conditions like COPD. | * Oxygen therapy for conditions like COPD. | ||
* Psychological interventions for anxiety-induced tachypnea. | * Psychological interventions for anxiety-induced tachypnea. | ||
== Prevention and Monitoring == | == Prevention and Monitoring == | ||
Preventive measures and regular monitoring are crucial for individuals prone to tachypnea, especially those with chronic respiratory or cardiac conditions. | Preventive measures and regular monitoring are crucial for individuals prone to tachypnea, especially those with chronic respiratory or cardiac conditions. | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
* [https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/tachypnea American Lung Association: Tachypnea] | * [https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/tachypnea American Lung Association: Tachypnea] | ||
* [https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/rapid-breathing/basics/definition/sym-20050637 Mayo Clinic: Rapid Breathing] | * [https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/rapid-breathing/basics/definition/sym-20050637 Mayo Clinic: Rapid Breathing] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
* [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430940/ National Center for Biotechnology Information: Tachypnea] | * [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430940/ National Center for Biotechnology Information: Tachypnea] | ||
* [https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/807277-overview Medscape: Tachypnea] | * [https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/807277-overview Medscape: Tachypnea] | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
* [[Control of respiration]] | * [[Control of respiration]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:33, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Tachypnea | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Rapid breathing |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Increased respiratory rate |
| Complications | Respiratory alkalosis, Hypoxemia |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Variable, depending on underlying cause |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Fever, Anxiety, Lung infection, Heart failure, Asthma, COPD |
| Risks | Respiratory disease, Cardiac disease, Infection |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, Respiratory rate measurement |
| Differential diagnosis | Hyperventilation, Dyspnea, Bradypnea |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Address underlying cause, Oxygen therapy |
| Medication | Bronchodilators, Antibiotics (if infection is present) |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common in acute illness |
| Deaths | Rarely directly fatal, but can indicate serious underlying conditions |
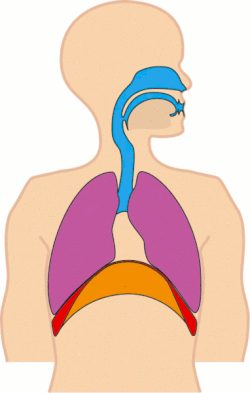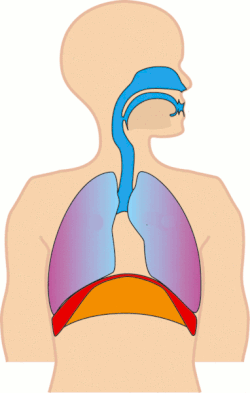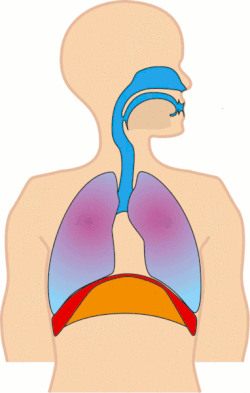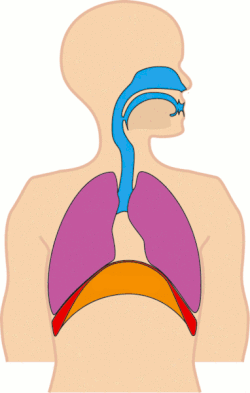
Tachypnea refers to an abnormally rapid breathing rate. It is a medical term used to describe accelerated respiration in patients, which can be a symptom of various underlying health conditions.
Definition and Characteristics[edit]
Tachypnea is characterized by a breathing rate that is faster than the normal range for a person's age and activity level. The condition is particularly noticeable in resting states, where the number of breaths per minute exceeds the typical range.
Normal breathing rate[edit]
A normal breathing rate for an adult at rest is 8 to 16 breaths per minute. For an infant, a normal rate is up to 44 breaths per minute.
Tachypnea breathing rate[edit]
Tachypnea is the term that your health care provider uses to describe your breathing if it is too fast, especially if you have fast, shallow breathing from a lung disease or other medical cause.
Hyperventilation[edit]
The term hyperventilation is usually used if you are taking rapid, deep breaths. This can be due to lung disease or because of anxiety or panic. The terms are sometimes used interchangeably.
Causes[edit]
Shallow, rapid breathing has many possible medical causes, including:
- Asthma
- Blood clot in an artery in the lung
- Choking
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other chronic lung diseases
- Heart failure
- Infection in the smallest air passages of the lungs in children (bronchiolitis)
- Pneumonia or other lung infection
- Transient tachypnea of the newborn
- Anxiety and panic
- Other serious lung disease
Diagnosis[edit]
The diagnosis is made clinically by measuring the breathing rate. However, additional tests, including blood tests, X-ray of the chest, CT scan and MRI might be needed to look for underlying causes.
Treatment[edit]
Treatment of tachypnea depends on the underlying cause.
Causes and Associated Conditions[edit]
Several medical conditions can lead to tachypnea, including:
- Respiratory Disorders: Such as Asthma, COPD, and Pneumonia.
- Cardiac Conditions: Congestive heart failure can cause fluid buildup in the lungs, leading to tachypnea.
- Fever: Increased body temperature can accelerate breathing.
- Anxiety and Panic Attacks: Psychological stress can result in rapid breathing.
Diagnosis and Evaluation[edit]
Diagnosis of tachypnea involves:
- Measuring the respiratory rate.
- Assessing the patient's overall clinical presentation.
- Conducting tests to determine the underlying cause, such as chest X-rays or blood tests.
Treatment and Management[edit]
Treatment of tachypnea focuses on addressing the underlying cause. This may involve:
- Medications, such as bronchodilators for asthma.
- Oxygen therapy for conditions like COPD.
- Psychological interventions for anxiety-induced tachypnea.
Prevention and Monitoring[edit]
Preventive measures and regular monitoring are crucial for individuals prone to tachypnea, especially those with chronic respiratory or cardiac conditions.
External Links[edit]
References[edit]
<references/>
See also[edit]
|
|
|
| Signs and symptoms relating to the respiratory system | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1


