Hemimegalencephaly: Difference between revisions
m 1 revision imported |
CSV import |
||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Syndromes affecting the nervous system]] | [[Category:Syndromes affecting the nervous system]] | ||
<gallery> | |||
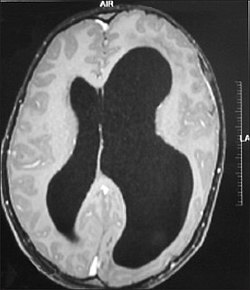
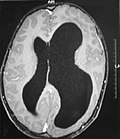
File:OJO-7-43-g005.jpg|Hemimegalencephaly | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 01:31, 20 February 2025
Hemimegalencephaly (HME), or unilateral megalencephaly, is a rare congenital disorder affecting all or a part of a cerebral hemisphere.<ref name="pmid17416820">,
Hemimegalencephaly: a study of abnormalities occurring outside the involved hemisphere., AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, Vol. 28(Issue: 4), pp. 678–82, PMID: 17416820, Full text,</ref> It causes severe seizures, which are often frequent and hard to control. A minority might have seizure control with medicines, but most will need removal or disconnection of the affected hemisphere as the best chance. Uncontrolled, they often cause progressive intellectual disability and brain damage and stop development.<ref>
Hemimegalencephaly - Why hemispherectomy is usually required(link). www.brainrecoveryproject.org.
Accessed 2018-04-12.
</ref>
Symptoms
Seizures are the main symptom. There can be as many as hundreds of seizures a day.<ref name=":0">
Gene Mutations Cause Massive Brain Asymmetry(link). UC Health - UC San Diego.
Accessed 2018-04-12.
</ref> Seizures usually begin days right after birth, though they can be delayed by months or, rarely, start in early childhood.<ref name=":2">
Hemimegalencephaly & Cortical Dysplasia(link). hemifoundation.homestead.com.
Accessed 2018-04-14.
</ref>
Other symptoms
- Asymmetrical or enlarged head<ref name=":2" />
- Developmental delay<ref name=":2" />
- Progressive weakness of half the body<ref name=":2" />
- Progressive blindness of half the body<ref name=":2" />
Genetics
Somatic activation of AKT3 causes hemispheric developmental brain malformations.<ref name="pmid22500628">,
Somatic Activation of AKT3 Causes Hemispheric Developmental Brain Malformations, Neuron, Vol. 74(Issue: 1), pp. 41–48, DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.03.010, PMID: 22500628, PMC: 3460551,</ref>
Pathophysiology
It is a disorder related to excessive neuronal proliferation and hamartomatous overgrowth affecting the cortical formation.<ref name="pmid18687750">,
Disorders of Cortical Formation: MR Imaging Features, American Journal of Neuroradiology, Vol. 30(Issue: 1), pp. 4–11, DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A1223, PMID: 18687750,</ref> The excessive proliferation is postulated to occur early and to possibly continue beyond the normal proliferative period. Epidermal growth factor is thought to play an important role in the excessive proliferation and the pathogenesis of HME.<ref name="SarnatCuratolo2007">, Malformations of the Nervous System. online version, Newnes, ISBN 978-0-08-055984-1, Pages: 154,</ref>
Diagnosis
It should be suspected in infants or children with intractable, frequent seizures.<ref name=":0" /> On a CT scan, the affected part is distorted and enlarged.<ref> Hennessy-Fiske, Molly. Radical surgery offers hope for baby racked by seizures(link). latimes.com.
2012-06-15.
Accessed 2018-04-12.
</ref> It can be diagnosed prenatally, but a lot of cases go undiagnosed until seizures begin. Ultrasound can display asymmetrical brain hemispheres.<ref name=":2" />
Treatment
Although there have been a few reports of medical treatment, the main treatment is radical: remove or disconnect the affected side. However, it has a high mortality, and there have been reports of a vegetative state and seizures resuming, this time in the healthy hemisphere.<ref name=":1">Bonioli, Eugenio,
Surgical vs. medical treatment of seizures in hemimegalencephaly, Brain and Development, Vol. 16(Issue: 2), pp. 169, DOI: 10.1016/0387-7604(94)90060-4, Full text,</ref>
Surgery should be done as early as possible to minimize damage caused by seizures. However, a trial with drugs can be attempted for a few months before surgery, and there is a slim chance of it succeeding.<ref name=":1" /> The earlier surgery be done, the more the remaining side will do the missing side's job.
Benzodiazepines might control the seizures.<ref>
Hemimegalencephaly: diagnosis and treatment. - Semantic Scholar(link). {{{website}}}.
Accessed 2018-04-12.
</ref>
References
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
External links
| Congenital malformations and deformations of nervous system | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Congenital abnormality syndromes (Q87, 759.7) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
-
Hemimegalencephaly