Anatomical snuffbox: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
File:Schematic_drawing_of_anatomical_snuffbox.png|Schematic drawing of anatomical snuffbox | File:Schematic_drawing_of_anatomical_snuffbox.png|Schematic drawing of anatomical snuffbox | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Anatomical Snuffbox == | |||
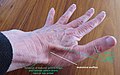
The '''anatomical snuffbox''' is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand, at the level of the carpal bones. It is visible when the thumb is fully extended, creating a concavity between the tendons of the [[extensor pollicis longus]] and [[extensor pollicis brevis]]. | |||
== Structure == | |||
The anatomical snuffbox is bordered by: | |||
* The [[extensor pollicis longus]] tendon medially. | |||
* The [[extensor pollicis brevis]] and [[abductor pollicis longus]] tendons laterally. | |||
* The proximal border is formed by the [[styloid process of the radius]]. | |||
* The distal border is the apex of the triangle, which points towards the base of the thumb. | |||
* The floor of the snuffbox is formed by the [[scaphoid]] and [[trapezium]] bones. | |||
The roof of the snuffbox is made up of the skin and superficial fascia, which contains the branches of the [[superficial branch of the radial nerve]]. | |||
== Contents == | |||
The anatomical snuffbox contains several important structures: | |||
* The [[radial artery]] passes obliquely through the snuffbox, making it a site for palpating the radial pulse. | |||
* The [[cephalic vein]] originates in the anatomical snuffbox. | |||
* The [[superficial branch of the radial nerve]] provides sensory innervation to the skin overlying the snuffbox. | |||
== Clinical Significance == | |||
The anatomical snuffbox is clinically significant for several reasons: | |||
* '''Fracture of the Scaphoid:''' The scaphoid bone, which forms part of the floor of the snuffbox, is the most commonly fractured carpal bone. Tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox following a fall on an outstretched hand is a classic sign of a scaphoid fracture. | |||
* '''Radial Artery Cannulation:''' The radial artery, which runs through the snuffbox, can be accessed for arterial blood sampling or cannulation. | |||
* '''De Quervain's Tenosynovitis:''' This condition involves inflammation of the tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus, which form the lateral border of the snuffbox. | |||
== History == | |||
The term "snuffbox" originates from the historical use of the area for placing and inhaling snuff, a form of powdered tobacco. The concavity formed by the tendons was convenient for holding a small amount of snuff. | |||
== Related Pages == | |||
* [[Extensor pollicis longus]] | |||
* [[Extensor pollicis brevis]] | |||
* [[Abductor pollicis longus]] | |||
* [[Radial artery]] | |||
* [[Scaphoid fracture]] | |||
{{Anatomy}} | |||
[[Category:Anatomy of the upper limb]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:41, 19 February 2025
-
Anatomical snuffbox
-
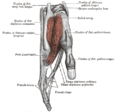
Bones of the left forearm, posterior surface
-
Bones of the left forearm, anterior surface
-
The radial artery
-
The superficial branches of the radial and ulnar nerves
-
Anatomical snuffbox
-
Schematic drawing of anatomical snuffbox
Anatomical Snuffbox[edit]
The anatomical snuffbox is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand, at the level of the carpal bones. It is visible when the thumb is fully extended, creating a concavity between the tendons of the extensor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis.
Structure[edit]
The anatomical snuffbox is bordered by:
- The extensor pollicis longus tendon medially.
- The extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus tendons laterally.
- The proximal border is formed by the styloid process of the radius.
- The distal border is the apex of the triangle, which points towards the base of the thumb.
- The floor of the snuffbox is formed by the scaphoid and trapezium bones.
The roof of the snuffbox is made up of the skin and superficial fascia, which contains the branches of the superficial branch of the radial nerve.
Contents[edit]
The anatomical snuffbox contains several important structures:
- The radial artery passes obliquely through the snuffbox, making it a site for palpating the radial pulse.
- The cephalic vein originates in the anatomical snuffbox.
- The superficial branch of the radial nerve provides sensory innervation to the skin overlying the snuffbox.
Clinical Significance[edit]
The anatomical snuffbox is clinically significant for several reasons:
- Fracture of the Scaphoid: The scaphoid bone, which forms part of the floor of the snuffbox, is the most commonly fractured carpal bone. Tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox following a fall on an outstretched hand is a classic sign of a scaphoid fracture.
- Radial Artery Cannulation: The radial artery, which runs through the snuffbox, can be accessed for arterial blood sampling or cannulation.
- De Quervain's Tenosynovitis: This condition involves inflammation of the tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis longus, which form the lateral border of the snuffbox.
History[edit]
The term "snuffbox" originates from the historical use of the area for placing and inhaling snuff, a form of powdered tobacco. The concavity formed by the tendons was convenient for holding a small amount of snuff.
Related Pages[edit]
- Extensor pollicis longus
- Extensor pollicis brevis
- Abductor pollicis longus
- Radial artery
- Scaphoid fracture
| Anatomy and morphology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|