Arcturus Therapeutics: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Short description|Anatomical structure in the cardiovascular system}} | |||
{{Anatomy}} | |||
The '''aortic body''' is a small cluster of [[chemoreceptor]]s, [[baroreceptor]]s, and supporting cells located along the [[aortic arch]]. It plays a crucial role in the regulation of respiratory and cardiovascular functions by monitoring changes in blood chemistry and pressure. | |||
== | ==Structure== | ||
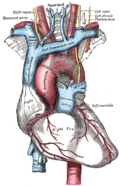
The aortic body is situated near the heart, specifically at the arch of the [[aorta]], which is the major artery that carries blood away from the heart to the rest of the body. It is composed of a collection of cells that are sensitive to changes in the partial pressure of [[oxygen]] (pO2), carbon dioxide (pCO2), and the pH of the blood. | |||
== | ==Function== | ||
The primary function of the aortic body is to detect changes in the blood's chemical composition. It is particularly sensitive to hypoxia (low oxygen levels), hypercapnia (high carbon dioxide levels), and acidosis (low pH). When such changes are detected, the aortic body sends signals to the [[medulla oblongata]] in the brainstem, which in turn adjusts the rate and depth of [[respiration]] to maintain homeostasis. | |||
The aortic body also contains baroreceptors that help regulate blood pressure by detecting changes in the stretch of the aortic wall. These receptors send signals to the brain to modulate heart rate and vascular resistance, thus maintaining stable blood pressure. | |||
== | ==Clinical significance== | ||
Dysfunction of the aortic body can lead to impaired respiratory and cardiovascular responses. Conditions such as [[chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]] (COPD) and [[heart failure]] can affect the sensitivity of the aortic body, leading to inadequate responses to changes in blood gases. | |||
== | ==Related pages== | ||
* [[Carotid body]] | |||
* [[Chemoreceptor]] | |||
* [[Baroreceptor]] | |||
* [[Aorta]] | |||
==Gallery== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray505.png|Location of the aortic body in relation to the aortic arch. | |||
</gallery> | |||
[[Category:Cardiovascular system]] | |||
[[Category:Respiratory physiology]] | |||
Revision as of 17:43, 11 February 2025
Anatomical structure in the cardiovascular system
| Anatomy and morphology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The aortic body is a small cluster of chemoreceptors, baroreceptors, and supporting cells located along the aortic arch. It plays a crucial role in the regulation of respiratory and cardiovascular functions by monitoring changes in blood chemistry and pressure.
Structure
The aortic body is situated near the heart, specifically at the arch of the aorta, which is the major artery that carries blood away from the heart to the rest of the body. It is composed of a collection of cells that are sensitive to changes in the partial pressure of oxygen (pO2), carbon dioxide (pCO2), and the pH of the blood.
Function
The primary function of the aortic body is to detect changes in the blood's chemical composition. It is particularly sensitive to hypoxia (low oxygen levels), hypercapnia (high carbon dioxide levels), and acidosis (low pH). When such changes are detected, the aortic body sends signals to the medulla oblongata in the brainstem, which in turn adjusts the rate and depth of respiration to maintain homeostasis.
The aortic body also contains baroreceptors that help regulate blood pressure by detecting changes in the stretch of the aortic wall. These receptors send signals to the brain to modulate heart rate and vascular resistance, thus maintaining stable blood pressure.
Clinical significance
Dysfunction of the aortic body can lead to impaired respiratory and cardiovascular responses. Conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and heart failure can affect the sensitivity of the aortic body, leading to inadequate responses to changes in blood gases.
Related pages
Gallery
-
Location of the aortic body in relation to the aortic arch.