Middle cerebellar peduncle: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{Cerebellum}} | {{Cerebellum}} | ||
{{dictionary-stub1}} | {{dictionary-stub1}} | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Gray677.png|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Gray682.png|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Gray719.png|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Gray792.png|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Gehirn,_basal_-_beschriftet_lat.svg|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Human_brainstem-thalamus_posterior_view_description.JPG|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Lower_pons_horizontal_KB.svg|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Slide8dd.JPG|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Slide2cuc.JPG|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Slide2PITER.JPG|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Slide2MIR.JPG|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
File:Slide3MIR.JPG|Middle cerebellar peduncle | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 12:18, 18 February 2025
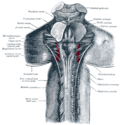
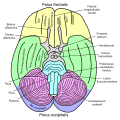
Middle Cerebellar Peduncle
The Middle Cerebellar Peduncle (MCP), also known as brachium pontis, is one of three pairs of cerebellar peduncles. They are the largest of the three and their primary function is to connect the cerebellum to the pons and carry information from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum.
Anatomy[edit]
The Middle Cerebellar Peduncle is located on the sides of the pons, a part of the brainstem. It is formed by fibers that arise from the cells of the pontine nuclei. These fibers cross the midline within the pons, emerge on the opposite side and then enter the cerebellum.
Function[edit]
The primary function of the Middle Cerebellar Peduncle is to carry information from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum. This information is used by the cerebellum to coordinate voluntary movements. The MCP is also involved in the integration of sensory and motor information.
Clinical significance[edit]
Damage to the Middle Cerebellar Peduncle can result in a variety of neurological disorders, including ataxia, nystagmus, and dysarthria. These conditions can affect balance, eye movements, and speech, respectively.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
<references />
|
|
|
| Brainstem Anatomy | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Anatomy of the cerebellum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle
-
Middle cerebellar peduncle