Methylprednisolone: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Replaced content with "{{Short description|Corticosteroid medication}} {{Use dmy dates|date=March 2022}} {{cs1 config |name-list-style=vanc |display-authors=6}} {{Infobox drug | verifiedrevid =..." Tag: Replaced |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Short description|Corticosteroid medication}} | ||
{{Use dmy dates|date=March 2022}} | |||
{{cs1 config |name-list-style=vanc |display-authors=6}} | |||
== | {{Infobox drug | ||
| verifiedrevid = 4771699945 | |||
| image = Methylprednisolone.svg | |||
| image_class = skin-invert-image | |||
| width = 250 | |||
| tradename = Medrol, Depo-Medrol, Solu-Medrol | |||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|methylprednisolone}} | |||
| MedlinePlus = a682795 | |||
| DailyMedID = Methylprednisolone | |||
| pregnancy_AU = A | |||
| pregnancy_US = C | |||
| routes_of_administration = [[Oral administration|By mouth]], [[intramuscular]], [[intra-articular]], [[intravenous]] | |||
| ATC_prefix = D07 | |||
| ATC_suffix = AA01 | |||
| legal_CA = Rx-only | |||
| legal_UK = POM | |||
| legal_US = Rx-only | |||
| metabolism = [[Liver]] (CYP3A4) | |||
| elimination_half-life = 1.8–2.6 hours | |||
| excretion = [[Urine]] | |||
| CAS_number = 83-43-2 | |||
| DrugBank = DB00959 | |||
| PubChem = 6741 | |||
| ChEBI = 6888 | |||
| ChEMBL = 650 | |||
}} | |||
Methylprednisolone | '''Methylprednisolone''' is a synthetic glucocorticoid primarily used for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. | ||
Methylprednisolone is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines. | |||
Methylprednisolone is | == Medical Uses == | ||
Methylprednisolone is prescribed for a variety of conditions, including: | |||
Inflammatory and Autoimmune Disorders | |||
* [[Rheumatoid arthritis]] | |||
* [[Systemic lupus erythematosus]] (SLE) | |||
* [[Psoriatic arthritis]] | |||
* [[Multiple sclerosis]] (MS) | |||
* [[Ulcerative colitis]] | |||
* [[Crohn’s disease]] | |||
Allergic and Respiratory Conditions | |||
* Severe allergies – including angioedema and anaphylaxis. | |||
* Asthma and COPD exacerbations – Used as an oral or IV corticosteroid in severe cases. | |||
Endocrine and Oncological Uses | |||
* Adrenal insufficiency – As an alternative to hydrocortisone when mineralocorticoid activity is not required. | |||
* Cancer therapy – Used in the management of leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. | |||
Neurological Disorders | |||
* | * Multiple sclerosis (MS) relapses – Administered as high-dose IV methylprednisolone. | ||
* | * Spinal cord injury (off-label) – Used to reduce inflammation in acute cases. | ||
Ophthalmic Conditions | |||
* Optic neuritis (often linked to MS) | |||
* Uveitis, iritis, and scleritis | |||
== | == Administration and Dosage == | ||
Methylprednisolone is available in oral tablets, intramuscular, intra-articular, and intravenous formulations. Dosage depends on the condition being treated: | |||
* Mild to moderate inflammation – 4–16 mg/day (oral) | |||
* Severe inflammation or autoimmune flares – IV pulse therapy (e.g., 500–1000 mg IV) | |||
* Acute asthma exacerbation – 40–80 mg/day PO or IV | |||
{{ | == Side Effects == | ||
Common Side Effects | |||
* Weight gain | |||
* Mood changes (insomnia, agitation) | |||
* Increased blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) | |||
* Fluid retention | |||
Serious Adverse Effects | |||
Long-term or high-dose use may lead to: | |||
* Osteoporosis and fractures | |||
* Adrenal suppression (requiring tapering) | |||
* Glaucoma and cataracts | |||
* Cushing’s syndrome (moon face, buffalo hump) | |||
* Infections due to immune suppression | |||
== Pharmacology == | |||
Mechanism of Action | |||
Methylprednisolone is a glucocorticoid receptor agonist that: | |||
1. Suppresses inflammation by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, TNF-alpha). | |||
2. Suppresses the immune response by reducing T-cell activation. | |||
3. Regulates metabolism by increasing glucose levels and altering fat distribution. | |||
Metabolism and Elimination | |||
* Metabolized in the liver (CYP3A4 pathway). | |||
* Eliminated via the kidneys. | |||
* Half-life: 1.8–2.6 hours. | |||
== Contraindications == | |||
Methylprednisolone should not be used in: | |||
* Systemic fungal infections | |||
* Uncontrolled infections | |||
* Hypersensitivity to corticosteroids | |||
* Live vaccine administration | |||
== Drug Interactions == | |||
* NSAIDs – Increased risk of gastric ulcers. | |||
* Diabetes medications – May require higher insulin doses. | |||
* Live vaccines – Risk of severe infection. | |||
* Anticoagulants – May alter warfarin levels. | |||
== History == | |||
Methylprednisolone was first synthesized by The Upjohn Company (now Pfizer) and FDA-approved in 1957. | |||
== Availability == | |||
Methylprednisolone is available under multiple brand names: | |||
* Medrol (oral tablets) | |||
* Depo-Medrol (intramuscular injection) | |||
* Solu-Medrol (intravenous formulation) | |||
== See Also == | |||
* [[Glucocorticoid]] | |||
* [[Prednisolone]] | |||
* [[Cushing's syndrome]] | |||
* [[Adrenal insufficiency]] | |||
{{Glucocorticoids and antiglucocorticoids}} | |||
{{stub}} | |||
[[Category:Glucocorticoids]] | [[Category:Glucocorticoids]] | ||
[[Category:Drugs developed by Pfizer]] | |||
[[Category:World Health Organization essential medicines]] | |||
Latest revision as of 01:58, 20 March 2025
Corticosteroid medication
| Methylprednisolone | |
|---|---|
| |
| INN | |
| Drug class | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intramuscular, intra-articular, intravenous |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Bioavailability | |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP3A4) |
| Elimination half-life | 1.8–2.6 hours |
| Excretion | Urine |
| Legal status | |
| CAS Number | 83-43-2 |
| PubChem | 6741 |
| DrugBank | DB00959 |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
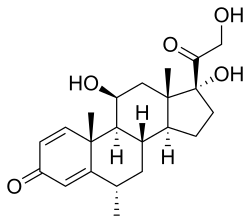
Methylprednisolone is a synthetic glucocorticoid primarily used for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties.
Methylprednisolone is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
Medical Uses[edit]
Methylprednisolone is prescribed for a variety of conditions, including:
Inflammatory and Autoimmune Disorders
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn’s disease
Allergic and Respiratory Conditions
- Severe allergies – including angioedema and anaphylaxis.
- Asthma and COPD exacerbations – Used as an oral or IV corticosteroid in severe cases.
Endocrine and Oncological Uses
- Adrenal insufficiency – As an alternative to hydrocortisone when mineralocorticoid activity is not required.
- Cancer therapy – Used in the management of leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
Neurological Disorders
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) relapses – Administered as high-dose IV methylprednisolone.
- Spinal cord injury (off-label) – Used to reduce inflammation in acute cases.
Ophthalmic Conditions
- Optic neuritis (often linked to MS)
- Uveitis, iritis, and scleritis
Administration and Dosage[edit]
Methylprednisolone is available in oral tablets, intramuscular, intra-articular, and intravenous formulations. Dosage depends on the condition being treated:
- Mild to moderate inflammation – 4–16 mg/day (oral)
- Severe inflammation or autoimmune flares – IV pulse therapy (e.g., 500–1000 mg IV)
- Acute asthma exacerbation – 40–80 mg/day PO or IV
Side Effects[edit]
Common Side Effects
- Weight gain
- Mood changes (insomnia, agitation)
- Increased blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia)
- Fluid retention
Serious Adverse Effects Long-term or high-dose use may lead to:
- Osteoporosis and fractures
- Adrenal suppression (requiring tapering)
- Glaucoma and cataracts
- Cushing’s syndrome (moon face, buffalo hump)
- Infections due to immune suppression
Pharmacology[edit]
Mechanism of Action Methylprednisolone is a glucocorticoid receptor agonist that: 1. Suppresses inflammation by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, TNF-alpha). 2. Suppresses the immune response by reducing T-cell activation. 3. Regulates metabolism by increasing glucose levels and altering fat distribution.
Metabolism and Elimination
- Metabolized in the liver (CYP3A4 pathway).
- Eliminated via the kidneys.
- Half-life: 1.8–2.6 hours.
Contraindications[edit]
Methylprednisolone should not be used in:
- Systemic fungal infections
- Uncontrolled infections
- Hypersensitivity to corticosteroids
- Live vaccine administration
Drug Interactions[edit]
- NSAIDs – Increased risk of gastric ulcers.
- Diabetes medications – May require higher insulin doses.
- Live vaccines – Risk of severe infection.
- Anticoagulants – May alter warfarin levels.
History[edit]
Methylprednisolone was first synthesized by The Upjohn Company (now Pfizer) and FDA-approved in 1957.
Availability[edit]
Methylprednisolone is available under multiple brand names:
- Medrol (oral tablets)
- Depo-Medrol (intramuscular injection)
- Solu-Medrol (intravenous formulation)
See Also[edit]
| Glucocorticoids and antiglucocorticoids (D07, H02) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|


