Carbon footprint: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
CSV import |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
{{Sustainability}} | {{Sustainability}} | ||
{{medicine-stub}} | {{medicine-stub}} | ||
== Carbon_footprint == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Environmental-impact-of-food-by-life-cycle-stage.png|Environmental impact of food by life cycle stage | |||
File:Carbon_Footprint_simple-explanation_EN.webm|Carbon Footprint simple explanation EN | |||
File:Carbon-footprint-of-protein-foods-2.png|Carbon footprint of protein foods 2 | |||
File:Scope3_Calculation_Guidance_-updated.png|Scope 3 Calculation Guidance updated | |||
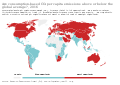
File:Are_consumption-based_CO₂_per_capita_emissions_above_or_below_the_global_average.,_OWID.svg|Are consumption-based CO₂ per capita emissions above or below the global average, OWID | |||
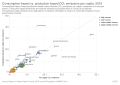
File:Consumption-based_vs._production-based_CO₂_emissions_per_capita,_OWID.svg|Consumption-based vs. production-based CO₂ emissions per capita, OWID | |||
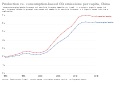
File:Production_vs._consumption-based_CO₂_emissions,_OWID.svg|Production vs. consumption-based CO₂ emissions, OWID | |||
File:Production_vs._consumption-based_CO₂_emissions_per_capita,_OWID.svg|Production vs. consumption-based CO₂ emissions per capita, OWID | |||
File:Life_cycle_analysis_and_GHG_carbon_accounting.jpg|Life cycle analysis and GHG carbon accounting | |||
File:Carbon-footprint-of-EU-diets-by-supply-chain.png|Carbon footprint of EU diets by supply chain | |||
File:Carbon-footprint-travel-mode.png|Carbon footprint travel mode | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 21:39, 23 February 2025
Carbon Footprint
A carbon footprint is the total amount of greenhouse gases (GHG) emissions caused directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, event, or product. It is measured in units of carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e) and includes gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), which contribute to global warming and climate change. Understanding and reducing carbon footprints is crucial for mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Overview[edit]
The concept of a carbon footprint is a subset of the broader concept of ecological footprints, introduced in the 1990s. The carbon footprint focuses specifically on the emissions of greenhouse gases that are associated with human activity. It can be categorized into two parts: the primary footprint and the secondary footprint. The primary footprint measures the direct emissions of CO2 from the burning of fossil fuels, including domestic energy consumption and transportation. The secondary footprint measures indirect CO2 emissions from the whole lifecycle of products used by an individual or organization, from their manufacture to their eventual disposal.
Calculation[edit]
Calculating a carbon footprint can be complex, as it involves various factors and requires data on the amount of greenhouse gases emitted by different activities and processes. Several online calculators and professional services can help individuals and organizations estimate their carbon footprints. These calculations often involve assessing energy consumption, transportation methods, diet, and the consumption of goods and services.
Reduction Strategies[edit]
Reducing a carbon footprint involves adopting practices that limit greenhouse gas emissions. Strategies include:
- Energy efficiency: Improving the energy efficiency of buildings and appliances.
- Renewable energy: Switching to renewable energy sources such as solar power, wind power, and hydroelectric power.
- Sustainable transportation: Using public transportation, biking, walking, or driving fuel-efficient or electric vehicles.
- Dietary changes: Adopting a diet with a lower environmental impact, such as reducing meat consumption.
- Waste reduction: Reducing, reusing, and recycling to minimize waste and consumption.
Impact[edit]
The carbon footprint concept has influenced both policy and personal behavior. Governments and organizations have set targets for reducing emissions, and many individuals are becoming more conscious of their environmental impact. However, achieving significant reductions in global carbon footprints requires coordinated action across all sectors of society.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
<references/>
| Carbon neutrality | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This carbon neutrality related article is a stub.
|
Carbon_footprint[edit]
-
Environmental impact of food by life cycle stage
-
Carbon Footprint simple explanation EN
-
Carbon footprint of protein foods 2
-
Scope 3 Calculation Guidance updated
-
Are consumption-based CO₂ per capita emissions above or below the global average, OWID
-
Consumption-based vs. production-based CO₂ emissions per capita, OWID
-
Production vs. consumption-based CO₂ emissions, OWID
-
Production vs. consumption-based CO₂ emissions per capita, OWID
-
Life cycle analysis and GHG carbon accounting
-
Carbon footprint of EU diets by supply chain
-
Carbon footprint travel mode