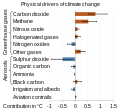
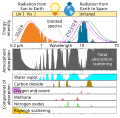
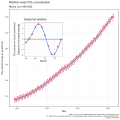
Greenhouse gas
Greenfield Site
A Greenfield site is a term used in urban planning to describe land that has not been previously developed or built upon. This can include agricultural fields, forests, or any other undeveloped space in an urban environment. Greenfield sites are often sought after for new development projects due to their untouched nature, which allows for maximum flexibility in design and construction.
Definition[edit]
The term "greenfield" originates from the image of a green field, untouched by development. In the context of urban development, a greenfield site refers to an area of land that has not been previously used for construction or industry. This is in contrast to a brownfield site, which refers to land that has been previously developed, often for industrial purposes, and may be contaminated with hazardous waste or pollution.
Advantages and Disadvantages[edit]
There are several advantages to developing on a greenfield site. These include the ability to design and build from scratch, without having to work around existing structures or infrastructure. This can result in more efficient and sustainable designs. Additionally, greenfield sites are often located in desirable areas, such as near major transportation routes or in rapidly growing communities.
However, there are also disadvantages to greenfield development. These include the potential for increased urban sprawl, which can lead to a loss of agricultural land, natural habitats, and open space. Additionally, greenfield development can result in increased traffic and air pollution, as well as a greater demand for public services such as schools and emergency services.
Greenfield Development and Sustainability[edit]
Greenfield development can have significant environmental impacts, particularly if it results in the loss of open space or natural habitats. However, it also presents opportunities for sustainable development. For example, greenfield sites can be designed to incorporate green building practices, such as energy-efficient buildings, renewable energy sources, and sustainable landscaping. Additionally, greenfield development can be planned to minimize impacts on local ecosystems and to preserve open space.
See Also[edit]
This urban-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
-
Greenhouse gas
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian