Carbon sink
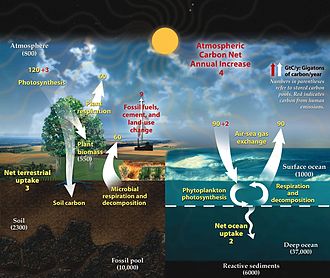


Carbon sink refers to natural or artificial reservoirs that accumulate and store some carbon-containing chemical compound for an indefinite period, thus removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. The concept of carbon sinks is a critical aspect of the global carbon cycle, which is a natural process by which carbon is exchanged among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals. The understanding and management of carbon sinks are vital for climate change mitigation efforts.
Types of Carbon Sinks[edit]
There are two main types of carbon sinks: natural and artificial.
Natural Carbon Sinks[edit]
- Forests: Trees and plants absorb CO2 through photosynthesis, converting it into biomass. Forests are the largest terrestrial carbon sinks.
- Oceans: The ocean is the largest carbon sink in the world. It absorbs CO2 from the atmosphere and stores it in various forms, such as dissolved in water, in the bodies of marine organisms, and in sediments on the ocean floor.
- Soils: Soil acts as a carbon sink through the storage of organic matter. Plants transfer carbon to the soil through their roots and by leaving behind dead organic material, which decomposes into soil organic matter.
Artificial Carbon Sinks[edit]
- Carbon sequestration: This is the process of capturing and storing atmospheric CO2. It can be done through biological processes, such as afforestation (planting trees on land not previously forested) or through technological processes, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS), where CO2 is captured from large point sources like power plants and then stored underground in geological formations.
Importance of Carbon Sinks[edit]
Carbon sinks play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by reducing the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere. Enhancing carbon sinks is a significant strategy in efforts to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement, which aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
Challenges and Threats[edit]
Carbon sinks face several challenges and threats that can reduce their capacity to absorb CO2. These include:
- Deforestation: The removal of forests for agriculture, logging, and development reduces the number of trees available to absorb CO2.
- Ocean acidification: Increased CO2 levels in the ocean change the water's chemistry, leading to ocean acidification, which can harm marine life and reduce the ocean's ability to absorb CO2.
- Climate change: Rising temperatures can reduce the effectiveness of forests and other ecosystems as carbon sinks. For example, increased temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can lead to more frequent and severe wildfires, releasing stored carbon back into the atmosphere.
Future Directions[edit]
To enhance the capacity of carbon sinks and combat climate change, efforts are being made in several areas, including:
- Reforestation and afforestation: Planting trees to restore deforested areas or to create new forests.
- Improved land management: Practices such as reduced tillage farming, restoration of degraded lands, and protection of wetlands can enhance soil carbon storage.
- Advancements in carbon capture and storage technology: Developing more efficient and cost-effective technologies for capturing and storing CO2.
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
