Sustainable energy
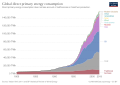
Sustainable energy refers to the practice of using energy in a way that meets current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It encompasses a broad range of energy sources and technologies that are environmentally friendly, economically viable, and socially responsible. Sustainable energy sources are often renewable, meaning they are naturally replenished on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat.
Definition and Importance[edit]
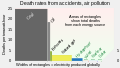
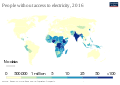
Sustainable energy is defined by its ability to be sustainably produced, consumed, and conserved. It plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and decreasing the dependency on fossil fuels. Additionally, sustainable energy promotes energy security, reduces pollution, and supports economic development and job creation in new industries.
Types of Sustainable Energy[edit]
Solar Energy[edit]
Solar energy is harnessed from the sun's rays and can be converted into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells or used to heat water or air.
Wind Energy[edit]
Wind energy involves generating electricity by converting the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical power, which can then be converted into electricity using wind turbines.
Hydroelectric Power[edit]
Hydroelectric power is generated by capturing the energy of falling or fast-running water. It's one of the oldest and most widely used forms of renewable energy.
Geothermal Energy[edit]
Geothermal energy is derived from the natural heat of the earth. It can be used for heating, cooling, and electricity generation.
Biomass[edit]
Biomass refers to organic materials, such as wood, agricultural crops, or waste, that can be used as fuel to produce energy.
Tidal and Wave Energy[edit]
Tidal energy and wave energy harness the power of water movements in oceans and seas to generate electricity.
Challenges and Solutions[edit]
While sustainable energy offers numerous benefits, there are challenges to its widespread adoption, including high initial costs, technological barriers, and the need for supportive policy frameworks. Solutions include investing in research and development, implementing policies that encourage the use of sustainable energy, and increasing public awareness and education on the importance of energy sustainability.
Future Directions[edit]
The future of sustainable energy is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and increasing global commitment to reducing carbon emissions. Innovations in energy storage, smart grid technology, and energy efficiency are expected to further enhance the viability and adoption of sustainable energy sources.
See Also[edit]
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
-
Sustainable energy
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $49.99


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $49.99 for the starting dose of Semaglutide and $65.00 for Tirzepatide.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian