Hemothorax: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Hemothorax | |||
| image = [[File:PMC2567296_1757-1626-1-225-2.png|250px]] | |||
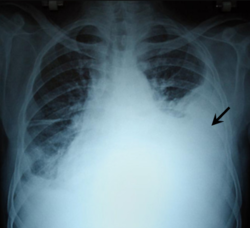
| caption = Chest X-ray showing a hemothorax on the right side | |||
| field = [[Pulmonology]], [[Emergency medicine]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Chest pain]], [[dyspnea]], [[tachycardia]], [[hypotension]] | |||
| complications = [[Respiratory failure]], [[shock (circulatory)|shock]], [[infection]] | |||
| onset = Sudden | |||
| duration = Variable | |||
| causes = [[Trauma]], [[surgery]], [[cancer]], [[blood clotting disorders]] | |||
| risks = [[Rib fracture]], [[anticoagulation therapy]] | |||
| diagnosis = [[Chest X-ray]], [[CT scan]], [[ultrasound]] | |||
| differential = [[Pneumothorax]], [[pleural effusion]], [[pulmonary embolism]] | |||
| treatment = [[Chest tube]], [[thoracotomy]], [[blood transfusion]] | |||
| prognosis = Depends on cause and treatment | |||
| frequency = Common in trauma cases | |||
}} | |||
= Hemothorax = | = Hemothorax = | ||
[[File:Hemothorax complicating rheumatoid arthritis.png|left|thumb|An X-ray showing the presence of a hemothorax.]] | |||
[[File:Hemothorax complicating rheumatoid arthritis.png|thumb | '''Hemothorax''' is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of [[blood]] in the pleural cavity—the space between the [[Lung anatomy|lungs]] and the chest wall. This condition is a type of [[Pleural effusion]] and is considered a medical emergency. Hemothorax can compromise breathing and, if left untreated, can lead to serious health complications, including [[Respiratory failure|respiratory failure]] and [[Shock (circulatory)|shock]]. | ||
'''Hemothorax''' is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of [[blood]] in the pleural | |||
== Definition and Pathophysiology == | == Definition and Pathophysiology == | ||
Hemothorax occurs when blood collects in the pleural space, which normally contains a small amount of fluid to facilitate lung movement during breathing. The presence of blood in this space can be due to trauma, medical procedures, or pathological processes that disrupt the blood vessels within the chest cavity. | Hemothorax occurs when blood collects in the pleural space, which normally contains a small amount of fluid to facilitate lung movement during breathing. The presence of blood in this space can be due to trauma, medical procedures, or pathological processes that disrupt the blood vessels within the chest cavity. | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
<youtube> | <youtube> | ||
title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | title='''{{PAGENAME}}''' | ||
movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/oqO83Loqt04 | movie_url=http://www.youtube.com/v/oqO83Loqt04 | ||
&rel=1 | &rel=1 | ||
| Line 20: | Line 33: | ||
height=600 | height=600 | ||
</youtube> | </youtube> | ||
The most common causes of hemothorax include: | The most common causes of hemothorax include: | ||
; [[Chest trauma]]: | ; [[Chest trauma]]: | ||
: Such as from a motor vehicle accident, fall, or penetrating injury, which can damage the blood vessels of the lung or chest wall. | : Such as from a motor vehicle accident, fall, or penetrating injury, which can damage the blood vessels of the lung or chest wall. | ||
; [[Surgery]]: | ; [[Surgery]]: | ||
: Complications from chest or heart surgery may lead to a hemothorax. | : Complications from chest or heart surgery may lead to a hemothorax. | ||
; [[Pulmonary embolism]]: | ; [[Pulmonary embolism]]: | ||
: A [[Pulmonary embolism|pulmonary embolism]] with infarction can lead to bleeding into the pleural space. | : A [[Pulmonary embolism|pulmonary embolism]] with infarction can lead to bleeding into the pleural space. | ||
; [[Malignancy]]: | ; [[Malignancy]]: | ||
: Tumors in the chest can erode into blood vessels, causing a hemothorax. | : Tumors in the chest can erode into blood vessels, causing a hemothorax. | ||
; [[Coagulopathy]]: | ; [[Coagulopathy]]: | ||
: Disorders of blood clotting can predispose an individual to bleeding, including into the pleural cavity. | : Disorders of blood clotting can predispose an individual to bleeding, including into the pleural cavity. | ||
== Symptoms == | == Symptoms == | ||
Symptoms of a hemothorax can vary depending on the volume of blood accumulated and may include: | Symptoms of a hemothorax can vary depending on the volume of blood accumulated and may include: | ||
* [[Chest pain]] | * [[Chest pain]] | ||
* [[Dyspnea|Shortness of breath]] | * [[Dyspnea|Shortness of breath]] | ||
| Line 46: | Line 51: | ||
* [[Tachycardia|Rapid heartbeat]] | * [[Tachycardia|Rapid heartbeat]] | ||
* [[Cyanosis|Bluish skin]] due to lack of oxygen | * [[Cyanosis|Bluish skin]] due to lack of oxygen | ||
== Diagnosis == | == Diagnosis == | ||
Diagnosis of hemothorax generally includes: | Diagnosis of hemothorax generally includes: | ||
* [[Physical examination]], which may reveal reduced breath sounds on the affected side | * [[Physical examination]], which may reveal reduced breath sounds on the affected side | ||
* [[Chest X-ray]]s showing a fluid level in the pleural space | * [[Chest X-ray]]s showing a fluid level in the pleural space | ||
| Line 55: | Line 58: | ||
* [[Computed tomography|CT scan]] of the chest for a more detailed assessment | * [[Computed tomography|CT scan]] of the chest for a more detailed assessment | ||
* [[Thoracentesis]], where a needle is inserted into the pleural space to obtain a sample of the fluid for analysis | * [[Thoracentesis]], where a needle is inserted into the pleural space to obtain a sample of the fluid for analysis | ||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
Treatment of hemothorax typically involves: | Treatment of hemothorax typically involves: | ||
* Immediate stabilization of the patient's airway, breathing, and circulation | * Immediate stabilization of the patient's airway, breathing, and circulation | ||
* [[Thoracostomy|Chest tube insertion]] to drain the blood from the pleural space | * [[Thoracostomy|Chest tube insertion]] to drain the blood from the pleural space | ||
| Line 64: | Line 65: | ||
* Treatment of the underlying cause of the hemothorax | * Treatment of the underlying cause of the hemothorax | ||
* [[Blood transfusion]]s if a significant amount of blood is lost | * [[Blood transfusion]]s if a significant amount of blood is lost | ||
== Prognosis and Complications == | == Prognosis and Complications == | ||
The prognosis for individuals with hemothorax depends on the cause and the promptness of treatment. Potential complications include: | The prognosis for individuals with hemothorax depends on the cause and the promptness of treatment. Potential complications include: | ||
* [[Infection]] leading to [[Empyema]] | * [[Infection]] leading to [[Empyema]] | ||
* [[Fibrothorax]] due to scarring and entrapped lung | * [[Fibrothorax]] due to scarring and entrapped lung | ||
* [[Pneumonia]] | * [[Pneumonia]] | ||
== Preventive Measures == | == Preventive Measures == | ||
Preventive measures for hemothorax focus on minimizing chest trauma and managing underlying health conditions that could contribute to bleeding. | Preventive measures for hemothorax focus on minimizing chest trauma and managing underlying health conditions that could contribute to bleeding. | ||
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
* [[Pleural cavity]] | * [[Pleural cavity]] | ||
* [[Thoracic surgery]] | * [[Thoracic surgery]] | ||
* [[Trauma surgery]] | * [[Trauma surgery]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
* ''Clinical Aspects of Hemothorax''. Thoracic Medicine, 2023. | * ''Clinical Aspects of Hemothorax''. Thoracic Medicine, 2023. | ||
* ''Emergency Management of Hemothorax''. Trauma Care, 2023. | * ''Emergency Management of Hemothorax''. Trauma Care, 2023. | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
* [https://www.thoracic.org/patients/patient-resources/resources/hemothorax.pdf American Thoracic Society: Hemothorax Patient Information] | * [https://www.thoracic.org/patients/patient-resources/resources/hemothorax.pdf American Thoracic Society: Hemothorax Patient Information] | ||
* [https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2047916-overview eMedicine: Hemothorax Overview] | * [https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2047916-overview eMedicine: Hemothorax Overview] | ||
[[Category:Respiratory diseases]] | [[Category:Respiratory diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Emergency medical conditions]] | [[Category:Emergency medical conditions]] | ||
[[Category:Thoracic surgery]] | [[Category:Thoracic surgery]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:04, 7 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hemothorax | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Chest pain, dyspnea, tachycardia, hypotension |
| Complications | Respiratory failure, shock, infection |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma, surgery, cancer, blood clotting disorders |
| Risks | Rib fracture, anticoagulation therapy |
| Diagnosis | Chest X-ray, CT scan, ultrasound |
| Differential diagnosis | Pneumothorax, pleural effusion, pulmonary embolism |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Chest tube, thoracotomy, blood transfusion |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on cause and treatment |
| Frequency | Common in trauma cases |
| Deaths | N/A |
Hemothorax[edit]

Hemothorax is a medical condition characterized by the accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity—the space between the lungs and the chest wall. This condition is a type of Pleural effusion and is considered a medical emergency. Hemothorax can compromise breathing and, if left untreated, can lead to serious health complications, including respiratory failure and shock.
Definition and Pathophysiology[edit]
Hemothorax occurs when blood collects in the pleural space, which normally contains a small amount of fluid to facilitate lung movement during breathing. The presence of blood in this space can be due to trauma, medical procedures, or pathological processes that disrupt the blood vessels within the chest cavity.
Causes[edit]
The most common causes of hemothorax include:
- Chest trauma
- Such as from a motor vehicle accident, fall, or penetrating injury, which can damage the blood vessels of the lung or chest wall.
- Surgery
- Complications from chest or heart surgery may lead to a hemothorax.
- Pulmonary embolism
- A pulmonary embolism with infarction can lead to bleeding into the pleural space.
- Malignancy
- Tumors in the chest can erode into blood vessels, causing a hemothorax.
- Coagulopathy
- Disorders of blood clotting can predispose an individual to bleeding, including into the pleural cavity.
Symptoms[edit]
Symptoms of a hemothorax can vary depending on the volume of blood accumulated and may include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Low blood pressure
- Rapid heartbeat
- Bluish skin due to lack of oxygen
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of hemothorax generally includes:
- Physical examination, which may reveal reduced breath sounds on the affected side
- Chest X-rays showing a fluid level in the pleural space
- Ultrasound of the chest, which can detect fluid accumulation
- CT scan of the chest for a more detailed assessment
- Thoracentesis, where a needle is inserted into the pleural space to obtain a sample of the fluid for analysis
Treatment[edit]
Treatment of hemothorax typically involves:
- Immediate stabilization of the patient's airway, breathing, and circulation
- Chest tube insertion to drain the blood from the pleural space
- Surgery in cases of ongoing bleeding or large, clotted hemothorax
- Treatment of the underlying cause of the hemothorax
- Blood transfusions if a significant amount of blood is lost
Prognosis and Complications[edit]
The prognosis for individuals with hemothorax depends on the cause and the promptness of treatment. Potential complications include:
- Infection leading to Empyema
- Fibrothorax due to scarring and entrapped lung
- Pneumonia
Preventive Measures[edit]
Preventive measures for hemothorax focus on minimizing chest trauma and managing underlying health conditions that could contribute to bleeding.
See Also[edit]
References[edit]
- Clinical Aspects of Hemothorax. Thoracic Medicine, 2023.
- Emergency Management of Hemothorax. Trauma Care, 2023.


