Perilymph: Difference between revisions
CSV import Tags: mobile edit mobile web edit |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{short description|Extracellular fluid located within the inner ear}} | |||
[[File:Cochlea-crosssection.svg|thumb]] | |||
{{Infobox anatomy | |||
|Name = Perilymph | |||
|Latin = perilympha | |||
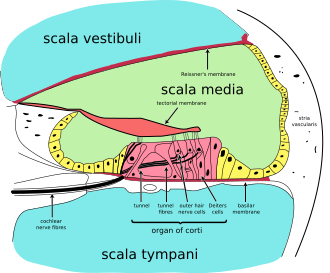
|Caption = Cross-section of [[cochlea]]. Perilymph is located in the [[scala vestibuli]] and [[scala tympani]] - the aqua regions at the top and bottom of the diagram. | |||
|Image2 =Cross section of semi circular canal svg hariadhi.svg | |||
|Caption2 = Cross-section of semi-circular canal and duct showing perilymphatic space | |||
}} | |||
'''Perilymph''' is a fluid located within the [[inner ear]] of many vertebrates, including humans. It is an extracellular fluid that fills the [[cochlea]] and [[vestibular system]] of the inner ear, playing a crucial role in the function of these structures. | '''Perilymph''' is a fluid located within the [[inner ear]] of many vertebrates, including humans. It is an extracellular fluid that fills the [[cochlea]] and [[vestibular system]] of the inner ear, playing a crucial role in the function of these structures. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 24: | ||
* [[Vestibular system]] | * [[Vestibular system]] | ||
* [[Perilymph fistula]] | * [[Perilymph fistula]] | ||
==External links== | |||
== | * [https://web.archive.org/web/19970401200140/http://oto.wustl.edu/cochlea/intro3.htm] | ||
{{Auditory and vestibular systems}} | |||
[[Category:Ear]] | [[Category:Ear]] | ||
[[Category:Body fluids]] | [[Category:Body fluids]] | ||
[[Category:Auditory system]] | [[Category:Auditory system]] | ||
{{ENT-stub}} | |||
{{stub}} | |||
Latest revision as of 02:11, 13 January 2025
Extracellular fluid located within the inner ear
| General Information | |
|---|---|
| Latin | perilympha |
| Greek | |
| TA98 | |
| TA2 | |
| FMA | |
| Details | |
| System | |
| Artery | |
| Vein | |
| Nerve | |
| Lymphatic drainage | |
| Precursor | |
| Function | |
| Identifiers | |
| Clinical significance | |
| Notes | |
Perilymph is a fluid located within the inner ear of many vertebrates, including humans. It is an extracellular fluid that fills the cochlea and vestibular system of the inner ear, playing a crucial role in the function of these structures.
Composition[edit]
Perilymph is similar in composition to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and is rich in sodium ions. It is different from the endolymph, another fluid found in the inner ear, which is high in potassium ions. The unique ionic compositions of these fluids are essential for the proper functioning of the inner ear.
Function[edit]
The primary function of perilymph is to transmit sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane (eardrum) to the sensory cells of the inner ear. It also serves to protect these cells and maintain the ionic balance necessary for the generation of electrical signals in response to sound.
Clinical significance[edit]
Abnormalities in the perilymph, such as changes in its volume or composition, can lead to hearing loss and balance disorders. For example, perilymph fistula is a condition where there is an abnormal communication between the perilymph-filled space and the middle ear, leading to symptoms such as hearing loss, tinnitus, and vertigo.
See also[edit]
External links[edit]
| Anatomy of hearing and balance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
This ENT-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.