Auditory system
File:Journey of Sound to the Brain.ogv
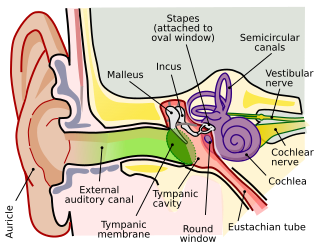

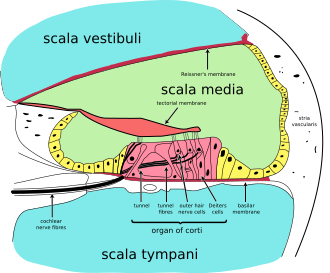
Auditory System
The auditory system is a complex network of structures and processes that enable the perception of sound. It encompasses both peripheral and central components, each playing a crucial role in the detection, transmission, and interpretation of auditory information. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the auditory system, detailing its anatomy, physiology, and associated functions.
Anatomy of the Auditory System[edit]
The auditory system can be divided into the peripheral auditory system and the central auditory system.
Peripheral Auditory System[edit]
The peripheral auditory system includes the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
Outer Ear[edit]
The outer ear consists of the pinna (or auricle) and the external auditory canal. The pinna is the visible part of the ear that helps to collect sound waves and direct them into the ear canal. The external auditory canal is a tube-like structure that channels sound waves towards the tympanic membrane (eardrum).
Middle Ear[edit]
The middle ear is an air-filled cavity that contains three small bones known as the ossicles: the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones form a chain that transmits sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the oval window of the cochlea. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, helping to equalize pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane.
Inner Ear[edit]
The inner ear contains the cochlea, a spiral-shaped organ responsible for converting sound vibrations into neural signals. The cochlea is filled with fluid and lined with hair cells that detect sound-induced vibrations. The vestibular system, also located in the inner ear, is involved in balance and spatial orientation.
Central Auditory System[edit]
The central auditory system includes the auditory pathways and centers in the brain that process auditory information.
Auditory Nerve[edit]
The auditory nerve, also known as the cochlear nerve, carries electrical signals from the hair cells in the cochlea to the brainstem.
Brainstem[edit]
In the brainstem, the auditory signals are processed by several nuclei, including the cochlear nucleus, superior olivary complex, and inferior colliculus. These structures are involved in sound localization and the integration of auditory information from both ears.
Auditory Cortex[edit]
The auditory cortex, located in the temporal lobe of the brain, is the primary center for processing auditory information. It is responsible for interpreting the complex aspects of sound, such as pitch, volume, and rhythm.
Physiology of Hearing[edit]
Hearing involves the conversion of sound waves into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain. This process begins with the collection of sound waves by the outer ear and their transmission through the middle ear to the cochlea. In the cochlea, hair cells transduce mechanical vibrations into electrical signals, which are then transmitted via the auditory nerve to the brainstem and ultimately to the auditory cortex.
Disorders of the Auditory System[edit]
Disorders of the auditory system can lead to hearing loss, tinnitus, and balance issues. Common conditions include:
- Conductive Hearing Loss: Caused by problems in the outer or middle ear that prevent sound from reaching the inner ear.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Results from damage to the hair cells in the cochlea or the auditory nerve.
- Tinnitus: The perception of sound, such as ringing, in the absence of external stimuli.
Also see[edit]
| Anatomy of hearing and balance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian