Microphthalmia: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| deaths = | | deaths = | ||
}} | }} | ||
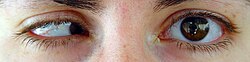
'''Microphthalmia''' (Greek: μικρός ''mikros'' = small; ὀφθαλμός ''ophthalmos'' = eye), also referred as microphthalmos, is a developmental disorder of the eye in which one (unilateral microphthalmia) or both (bilateral microphthalmia) eyes are abnormally small and have anatomic malformations. It is different from [[nanophthalmos]] in which the eye is small in size but has no anatomical alterations. | [[File:Goddard 11 (bottom).jpg|Microphthalmia|thumb]] | ||
[[File:Microphthalmus congenitus.jpg|Microphthalmia|thumb|left]] | |||
[[File:Microphthalmia-500px.jpg|Microphthalmia|thumb]] | |||
'''Microphthalmia''' (Greek: μικρός ''mikros'' = small; ὀφθαλμός ''ophthalmos'' = eye), also referred as microphthalmos, is a developmental disorder of the eye in which one (unilateral microphthalmia) or both (bilateral microphthalmia) eyes are abnormally small and have anatomic malformations. It is different from [[nanophthalmos]] in which the eye is small in size but has no anatomical alterations. | |||
==Presentation== | ==Presentation== | ||
The presence of a small eye within the orbit can be a normal incidental finding but in most cases it is abnormal and results in blindness. The incidence is 14 per 100,000 and the condition affects 3-11% of blind children. | The presence of a small eye within the orbit can be a normal incidental finding but in most cases it is abnormal and results in blindness. The incidence is 14 per 100,000 and the condition affects 3-11% of blind children. | ||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Microphthalmia in newborns is sometimes associated with [[fetal alcohol syndrome]] | Microphthalmia in newborns is sometimes associated with [[fetal alcohol syndrome]] or infections during pregnancy, particularly [[herpes simplex virus]], [[rubella]] and [[cytomegalovirus]] (CMV), but the evidence is inconclusive. Genetic causes of microphthalmia include chromosomal abnormalities ([[Trisomy 13]] ([[Patau syndrome]]), [[Triploid Syndrome]], [[13q deletion syndrome]], and [[Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome]]) or monogenetic Mendelian disorders. The latter may be autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive or X linked. | ||
The following genes have been implicated in microphthalmia, many of which are transcription and regulatory factors: | The following genes have been implicated in microphthalmia, many of which are transcription and regulatory factors: | ||
| Line 35: | Line 39: | ||
| [[BCL-6 corepressor|BCOR]] || [[BCL6]] corepressor || {{OMIM2|300166}} || MCOPS2 | | [[BCL-6 corepressor|BCOR]] || [[BCL6]] corepressor || {{OMIM2|300166}} || MCOPS2 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[BMP4]] | | [[BMP4]] || Induces cartilage and bone formation || {{OMIM2|607932}} || MCOPS6 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[CRYBA4]] || crystallin, beta A4 | | [[CRYBA4]] || crystallin, beta A4 | ||
| Line 41: | Line 45: | ||
| [[FOXE3]] || [[forkhead box]] E3 | | [[FOXE3]] || [[forkhead box]] E3 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[GDF3]] | | [[GDF3]] || [[growth differentiation factor]] 3 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[GDF6]]<ref name=GHR/> || [[growth differentiation factor]] 6 | | [[GDF6]]<ref name=GHR/> || [[growth differentiation factor]] 6 | ||
| Line 68: | Line 72: | ||
|} | |} | ||
How these genes result in the eye disorder is unknown but it has been postulated that interference with the process of eye growth after birth may be involved in contrast to anophthalmia (absence of eyeball) which originates much earlier during foetal development. SOX2 has been implicated in a substantial number (10-15%) of cases and in many other cases failure to develop the ocular lens often results in microphthalmia. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) located on chromosome 14q32 is associated with one form of isolated microphthalmia (MCOP1. In [[mammal]]s the failure of expression of the transcription factor, MITF ([[microphthalmia-associated transcription factor]]), in the pigmented [[retina]] prevents this structure from fully differentiating. This in turn causes a malformation of the [[choroid fissure]] of the eye, resulting in the drainage of [[vitreous humor]] fluid. Without this fluid, the eye fails to enlarge, thus the name microphthalmia.The gene encoding the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) is a member of the [[basic helix-loop-helix]]-leucine zipper (bHLH-ZIP) family. [[Waardenburg syndrome]] type 2 (WS type 2) in humans is also a type of microphthalmia syndrome. [[Mutations]] in MITF gene are thought to be responsible for this syndrome. The human MITF gene is [[Homology (biology)|homologous]] to the mouse MITF gene (aka mouse mi or microphthalmia gene); [[mouse]] with mutations in this gene are [[hypopigmentation|hypopigmented]] in their fur. The identification of the genetics of WS type 2 owes a lot to observations of [[phenotype]]s of MITF mutant mice. | How these genes result in the eye disorder is unknown but it has been postulated that interference with the process of eye growth after birth may be involved in contrast to anophthalmia (absence of eyeball) which originates much earlier during foetal development. SOX2 has been implicated in a substantial number (10-15%) of cases and in many other cases failure to develop the ocular lens often results in microphthalmia. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) located on chromosome 14q32 is associated with one form of isolated microphthalmia (MCOP1. | ||
In [[mammal]]s the failure of expression of the transcription factor, MITF ([[microphthalmia-associated transcription factor]]), in the pigmented [[retina]] prevents this structure from fully differentiating. This in turn causes a malformation of the [[choroid fissure]] of the eye, resulting in the drainage of [[vitreous humor]] fluid. Without this fluid, the eye fails to enlarge, thus the name microphthalmia.The gene encoding the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) is a member of the [[basic helix-loop-helix]]-leucine zipper (bHLH-ZIP) family. | |||
[[Waardenburg syndrome]] type 2 (WS type 2) in humans is also a type of microphthalmia syndrome. [[Mutations]] in MITF gene are thought to be responsible for this syndrome. The human MITF gene is [[Homology (biology)|homologous]] to the mouse MITF gene (aka mouse mi or microphthalmia gene); [[mouse]] with mutations in this gene are [[hypopigmentation|hypopigmented]] in their fur. The identification of the genetics of WS type 2 owes a lot to observations of [[phenotype]]s of MITF mutant mice. | |||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
==Epidemiology== | ==Epidemiology== | ||
The most extensive epidemiological survey on this congenital malformation has been carried out by Dharmasena et al | The most extensive epidemiological survey on this congenital malformation has been carried out by Dharmasena et al and using English National Hospital Episode Statistics, they calculated the annual incidence of anophthalmia, microphthalmia and congenital malformations of orbit/lacrimal apparatus from 1999 to 2011. | ||
According to this study the annual incidence of congenital microphthalmia in the United Kingdom was 10.8 (8.2 to 13.5) in 1999 and 10.0 (7.6 to 12.4) in 2011. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 103: | Line 112: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of eye, ear, face and neck}} | {{Congenital malformations and deformations of eye, ear, face and neck}} | ||
{{stub}} | |||
[[Category:Genetic disorders by system]] | [[Category:Genetic disorders by system]] | ||
[[Category:Congenital disorders of eyes]] | [[Category:Congenital disorders of eyes]] | ||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
Revision as of 20:51, 2 April 2025
Developmental disorder of the eye



Microphthalmia (Greek: μικρός mikros = small; ὀφθαλμός ophthalmos = eye), also referred as microphthalmos, is a developmental disorder of the eye in which one (unilateral microphthalmia) or both (bilateral microphthalmia) eyes are abnormally small and have anatomic malformations. It is different from nanophthalmos in which the eye is small in size but has no anatomical alterations.
Presentation
The presence of a small eye within the orbit can be a normal incidental finding but in most cases it is abnormal and results in blindness. The incidence is 14 per 100,000 and the condition affects 3-11% of blind children.
Causes
Microphthalmia in newborns is sometimes associated with fetal alcohol syndrome or infections during pregnancy, particularly herpes simplex virus, rubella and cytomegalovirus (CMV), but the evidence is inconclusive. Genetic causes of microphthalmia include chromosomal abnormalities (Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome), Triploid Syndrome, 13q deletion syndrome, and Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome) or monogenetic Mendelian disorders. The latter may be autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive or X linked.
The following genes have been implicated in microphthalmia, many of which are transcription and regulatory factors:
| HGNC symbol | Description | OMIM | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCOR | BCL6 corepressor | 300166 | MCOPS2 |
| BMP4 | Induces cartilage and bone formation | 607932 | MCOPS6 |
| CRYBA4 | crystallin, beta A4 | ||
| FOXE3 | forkhead box E3 | ||
| GDF3 | growth differentiation factor 3 | ||
| GDF6<ref name=GHR/> | growth differentiation factor 6 | ||
| MITF | microphthalmia-associated transcription factor | ||
| OTX2 | orthodenticle homeobox 2 | ||
| PAX6 | paired box 6 | ||
| PITX3 | Paired-like homeodomain transcription factor 3 | ||
| RAX | retina and anterior neural fold homeobox | ||
| SHH | sonic hedgehog homolog | ||
| SIX6 | SIX homeobox 6 | ||
| SOX2 | SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 2 | 206900 | MCOPS3 |
| VSX1 | visual system homeobox 1 VSX1 | visual system homeobox 1 | |
| RAB18 | Ras-related protein 18 | ||
| VSX2 (CHX10) | visual system homeobox 2 |
How these genes result in the eye disorder is unknown but it has been postulated that interference with the process of eye growth after birth may be involved in contrast to anophthalmia (absence of eyeball) which originates much earlier during foetal development. SOX2 has been implicated in a substantial number (10-15%) of cases and in many other cases failure to develop the ocular lens often results in microphthalmia. Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) located on chromosome 14q32 is associated with one form of isolated microphthalmia (MCOP1.
In mammals the failure of expression of the transcription factor, MITF (microphthalmia-associated transcription factor), in the pigmented retina prevents this structure from fully differentiating. This in turn causes a malformation of the choroid fissure of the eye, resulting in the drainage of vitreous humor fluid. Without this fluid, the eye fails to enlarge, thus the name microphthalmia.The gene encoding the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) is a member of the basic helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper (bHLH-ZIP) family.
Waardenburg syndrome type 2 (WS type 2) in humans is also a type of microphthalmia syndrome. Mutations in MITF gene are thought to be responsible for this syndrome. The human MITF gene is homologous to the mouse MITF gene (aka mouse mi or microphthalmia gene); mouse with mutations in this gene are hypopigmented in their fur. The identification of the genetics of WS type 2 owes a lot to observations of phenotypes of MITF mutant mice.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Epidemiology
The most extensive epidemiological survey on this congenital malformation has been carried out by Dharmasena et al and using English National Hospital Episode Statistics, they calculated the annual incidence of anophthalmia, microphthalmia and congenital malformations of orbit/lacrimal apparatus from 1999 to 2011.
According to this study the annual incidence of congenital microphthalmia in the United Kingdom was 10.8 (8.2 to 13.5) in 1999 and 10.0 (7.6 to 12.4) in 2011.
See also
References
<references group="" responsive="1"></references>
Further reading
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Anophthalmia / Microphthalmia Overview
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Microphthalmia with Linear Skin Defects Syndrome
- OMIM-Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man
External links
| Congenital malformations and deformations of eyes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|