Fabry disease: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{Infobox medical condition | |||
| name = Fabry disease | |||
| image = [[File:PBB_Protein_GLA_image.jpg|alt=GLA protein structure]] | |||
| caption = Structure of the GLA protein | |||
| synonyms = Anderson-Fabry disease, alpha-galactosidase A deficiency | |||
| pronounce = | |||
| specialty = [[Medical genetics]] | |||
| symptoms = [[Pain]], [[angiokeratoma]], [[hypohidrosis]], [[corneal opacity]], [[tinnitus]], [[hearing loss]], [[kidney failure]], [[heart disease]] | |||
| onset = Childhood to adulthood | |||
| duration = Lifelong | |||
| causes = Mutations in the [[GLA (gene)|GLA gene]] | |||
| risks = Family history | |||
| diagnosis = [[Genetic testing]], [[enzyme assay]] | |||
| differential = [[Rheumatic fever]], [[rheumatoid arthritis]], [[multiple sclerosis]] | |||
| treatment = [[Enzyme replacement therapy]], [[pain management]], [[kidney transplantation]] | |||
| medication = [[Agalsidase alfa]], [[agalsidase beta]], [[migalastat]] | |||
| prognosis = Variable, depends on organ involvement and treatment | |||
| frequency = 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 117,000 males | |||
| deaths = | |||
}} | |||
==Fabry Disease== | ==Fabry Disease== | ||
'''Fabry disease''' is a rare genetic disorder that results from the buildup of a particular type of fat, called globotriaosylceramide, in the body's cells. It is an [[X-linked recessive]] disorder caused by mutations in the ''GLA'' gene, which leads to a deficiency of the enzyme [[alpha-galactosidase A]]. | '''Fabry disease''' is a rare genetic disorder that results from the buildup of a particular type of fat, called globotriaosylceramide, in the body's cells. It is an [[X-linked recessive]] disorder caused by mutations in the ''GLA'' gene, which leads to a deficiency of the enzyme [[alpha-galactosidase A]]. | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
Fabry disease is characterized by the accumulation of [[glycosphingolipids]] in the [[lysosomes]] of various cell types. The deficiency of alpha-galactosidase A enzyme activity results in the progressive deposition of globotriaosylceramide in the [[vascular endothelium]], [[smooth muscle cells]], and other tissues, leading to multi-systemic manifestations. | Fabry disease is characterized by the accumulation of [[glycosphingolipids]] in the [[lysosomes]] of various cell types. The deficiency of alpha-galactosidase A enzyme activity results in the progressive deposition of globotriaosylceramide in the [[vascular endothelium]], [[smooth muscle cells]], and other tissues, leading to multi-systemic manifestations. | ||
==Clinical Manifestations== | ==Clinical Manifestations== | ||
The symptoms of Fabry disease can vary widely among affected individuals, but common manifestations include: | The symptoms of Fabry disease can vary widely among affected individuals, but common manifestations include: | ||
* [[Angiokeratomas]]: Small, dark red spots on the skin, often found in the "bathing trunk" area. | * [[Angiokeratomas]]: Small, dark red spots on the skin, often found in the "bathing trunk" area. | ||
* [[Acroparesthesia]]: Episodes of pain and burning sensations in the hands and feet. | * [[Acroparesthesia]]: Episodes of pain and burning sensations in the hands and feet. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 32: | ||
* [[Cardiac involvement]]: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, and heart failure. | * [[Cardiac involvement]]: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, and heart failure. | ||
* [[Cerebrovascular disease]]: Increased risk of [[stroke]] and transient ischemic attacks. | * [[Cerebrovascular disease]]: Increased risk of [[stroke]] and transient ischemic attacks. | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Diagnosis of Fabry disease is typically confirmed through: | Diagnosis of Fabry disease is typically confirmed through: | ||
* [[Enzyme assay]]: Measurement of alpha-galactosidase A activity in blood or skin fibroblasts. | * [[Enzyme assay]]: Measurement of alpha-galactosidase A activity in blood or skin fibroblasts. | ||
* [[Genetic testing]]: Identification of mutations in the ''GLA'' gene. | * [[Genetic testing]]: Identification of mutations in the ''GLA'' gene. | ||
* [[Biopsy]]: Histological examination of affected tissues may show characteristic lipid deposits. | * [[Biopsy]]: Histological examination of affected tissues may show characteristic lipid deposits. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
The management of Fabry disease includes: | The management of Fabry disease includes: | ||
* [[Enzyme replacement therapy]] (ERT): Intravenous administration of recombinant alpha-galactosidase A to reduce globotriaosylceramide accumulation. | * [[Enzyme replacement therapy]] (ERT): Intravenous administration of recombinant alpha-galactosidase A to reduce globotriaosylceramide accumulation. | ||
* [[Chaperone therapy]]: Use of pharmacological chaperones to stabilize the mutant enzyme and enhance its activity. | * [[Chaperone therapy]]: Use of pharmacological chaperones to stabilize the mutant enzyme and enhance its activity. | ||
* [[Symptomatic treatment]]: Pain management, renal protection, and cardiovascular care. | * [[Symptomatic treatment]]: Pain management, renal protection, and cardiovascular care. | ||
* [[Gene therapy]]: An emerging approach aimed at correcting the underlying genetic defect. | * [[Gene therapy]]: An emerging approach aimed at correcting the underlying genetic defect. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
The prognosis of Fabry disease varies depending on the severity of organ involvement and the effectiveness of treatment. Early diagnosis and initiation of therapy can improve outcomes and quality of life. | The prognosis of Fabry disease varies depending on the severity of organ involvement and the effectiveness of treatment. Early diagnosis and initiation of therapy can improve outcomes and quality of life. | ||
==Epidemiology== | ==Epidemiology== | ||
Fabry disease is estimated to affect approximately 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 117,000 live births. It is more common in males due to its X-linked inheritance pattern, but females can also be affected, often with milder symptoms. | Fabry disease is estimated to affect approximately 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 117,000 live births. It is more common in males due to its X-linked inheritance pattern, but females can also be affected, often with milder symptoms. | ||
==Images== | |||
<gallery> | |||
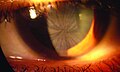
File:Morbus Fabry Cornea verticillata 01.jpg|Fabry disease | |||
File:Angiokreatoma.jpg|Fabry disease | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Lysosomal storage disease]] | * [[Lysosomal storage disease]] | ||
* [[X-linked genetic disorders]] | * [[X-linked genetic disorders]] | ||
* [[Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy]] | * [[Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy]] | ||
{{Lysosomal storage disorders}} | {{Lysosomal storage disorders}} | ||
{{Genetic disorders}} | {{Genetic disorders}} | ||
[[Category:Genetic disorders]] | [[Category:Genetic disorders]] | ||
[[Category:Lysosomal storage diseases]] | [[Category:Lysosomal storage diseases]] | ||
[[Category:Rare diseases]] | [[Category:Rare diseases]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:10, 6 April 2025

Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD's medical weight loss NYC, sleep center NYC
Philadelphia medical weight loss and Philadelphia sleep clinics
| Fabry disease | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Anderson-Fabry disease, alpha-galactosidase A deficiency |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | Pain, angiokeratoma, hypohidrosis, corneal opacity, tinnitus, hearing loss, kidney failure, heart disease |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Childhood to adulthood |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Mutations in the GLA gene |
| Risks | Family history |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing, enzyme assay |
| Differential diagnosis | Rheumatic fever, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Enzyme replacement therapy, pain management, kidney transplantation |
| Medication | Agalsidase alfa, agalsidase beta, migalastat |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on organ involvement and treatment |
| Frequency | 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 117,000 males |
| Deaths | |
Fabry Disease[edit]
Fabry disease is a rare genetic disorder that results from the buildup of a particular type of fat, called globotriaosylceramide, in the body's cells. It is an X-linked recessive disorder caused by mutations in the GLA gene, which leads to a deficiency of the enzyme alpha-galactosidase A.
Pathophysiology[edit]
Fabry disease is characterized by the accumulation of glycosphingolipids in the lysosomes of various cell types. The deficiency of alpha-galactosidase A enzyme activity results in the progressive deposition of globotriaosylceramide in the vascular endothelium, smooth muscle cells, and other tissues, leading to multi-systemic manifestations.
Clinical Manifestations[edit]
The symptoms of Fabry disease can vary widely among affected individuals, but common manifestations include:
- Angiokeratomas: Small, dark red spots on the skin, often found in the "bathing trunk" area.
- Acroparesthesia: Episodes of pain and burning sensations in the hands and feet.
- Corneal verticillata: Whorled patterns on the cornea, detectable by an eye examination.
- Renal impairment: Progressive kidney damage leading to chronic kidney disease.
- Cardiac involvement: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, and heart failure.
- Cerebrovascular disease: Increased risk of stroke and transient ischemic attacks.
Diagnosis[edit]
Diagnosis of Fabry disease is typically confirmed through:
- Enzyme assay: Measurement of alpha-galactosidase A activity in blood or skin fibroblasts.
- Genetic testing: Identification of mutations in the GLA gene.
- Biopsy: Histological examination of affected tissues may show characteristic lipid deposits.
Treatment[edit]
The management of Fabry disease includes:
- Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT): Intravenous administration of recombinant alpha-galactosidase A to reduce globotriaosylceramide accumulation.
- Chaperone therapy: Use of pharmacological chaperones to stabilize the mutant enzyme and enhance its activity.
- Symptomatic treatment: Pain management, renal protection, and cardiovascular care.
- Gene therapy: An emerging approach aimed at correcting the underlying genetic defect.
Prognosis[edit]
The prognosis of Fabry disease varies depending on the severity of organ involvement and the effectiveness of treatment. Early diagnosis and initiation of therapy can improve outcomes and quality of life.
Epidemiology[edit]
Fabry disease is estimated to affect approximately 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 117,000 live births. It is more common in males due to its X-linked inheritance pattern, but females can also be affected, often with milder symptoms.
Images[edit]
-
Fabry disease
-
Fabry disease
See Also[edit]
Template:Lysosomal storage disorders
| Genetic disorders relating to deficiencies of transcription factor or coregulators | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|