Circular RNA: Difference between revisions
CSV import |
CSV import |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
[[Category:RNA]] | [[Category:RNA]] | ||
[[Category:Molecular biology]] | [[Category:Molecular biology]] | ||
==Circular_RNA== | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Circular_RNA_Biogenesis.jpg|Circular RNA Biogenesis | |||
File:Pre-mRNA.svg|Pre-mRNA | |||
File:Hepatitis-d-virion-Pathogens-04-00046-g001-1024.png|Hepatitis D Virion | |||
File:Diagram_human_cell_nucleus.svg|Diagram of Human Cell Nucleus | |||
File:Phylogenetic_tree.svg|Phylogenetic Tree | |||
</gallery> | |||
Latest revision as of 04:38, 18 February 2025
Circular RNA
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a type of single-stranded RNA which, unlike linear RNA, forms a covalently closed continuous loop. This unique structure makes circRNAs more stable than linear RNAs, as they are resistant to exonuclease-mediated degradation. Circular RNAs are found in a wide range of organisms, including humans, and have been implicated in various biological processes and diseases.
Structure and Formation[edit]
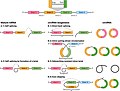
Circular RNAs are formed through a process called back-splicing, where a downstream splice donor site is joined to an upstream splice acceptor site. This process results in the circularization of the RNA molecule. The formation of circRNAs can involve exons, introns, or both, leading to different types of circRNAs such as exonic circRNAs, intronic circRNAs, and exon-intron circRNAs.
Functions[edit]
CircRNAs have been shown to play several roles in cellular processes:
- MicroRNA Sponges: Many circRNAs can act as microRNA sponges, binding to microRNAs and preventing them from interacting with their target mRNAs. This can regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally.
- Protein Scaffolding: CircRNAs can serve as scaffolds for protein complexes, facilitating interactions between proteins and influencing cellular signaling pathways.
- Transcriptional Regulation: Some circRNAs can interact with RNA polymerase II and other transcriptional machinery to regulate the transcription of their parental genes.
- Translation: Although traditionally considered non-coding, some circRNAs have been found to contain open reading frames and can be translated into proteins.
Biological Significance[edit]
CircRNAs are involved in various physiological and pathological processes. They have been implicated in the regulation of neuronal development, immune responses, and cell proliferation. In addition, circRNAs have been associated with diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurological disorders.
Research and Applications[edit]
The study of circRNAs is a rapidly growing field. Advances in high-throughput sequencing technologies have facilitated the identification and characterization of circRNAs. Understanding the functions and mechanisms of circRNAs can lead to novel therapeutic strategies, such as using circRNAs as biomarkers for disease diagnosis or as targets for drug development.
Also see[edit]
| RNA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Molecular biology | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Circular_RNA[edit]
-
Circular RNA Biogenesis
-
Pre-mRNA
-
Hepatitis D Virion
-
Diagram of Human Cell Nucleus
-
Phylogenetic Tree